
Oracle® Application Express
Application Migration Guide
Release 4.2 for Oracle Database 12c
E17962-07
August 2013
Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide, Release 4.2 for Oracle Database 12c
E17962-07
Copyright © 2003, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Primary Author: Terri Jennings
Contributors: Christina Cho, Joel Kallman, Sharon Kennedy, Hilary Farrell, David Peake
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on
use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your
license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license,
transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse
engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is
prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If
you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it
on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software,
any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users
are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and
agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and
adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on
the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to
the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management
applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including
applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous
applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other
measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages
caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of
their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks
are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD,
Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced
Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information on content, products,
and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly
disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services. Oracle
Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your
access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.

iii
Contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................................................ vii
Topic Overview .......................................................................................................................................... vii
Audience..................................................................................................................................................... viii
Documentation Accessibility................................................................................................................... viii
Related Documents ................................................................................................................................... viii
Conventions ................................................................................................................................................. ix
Changes in This Release ......................................................................................................................... xi
Changes in Oracle Application Express Release 4.2 .............................................................................. xi
1 Getting Started with Application Migration Workshop
About Migrating a Microsoft Access Application ............................................................................. 1-1
Preparation Checklist for Migrating Microsoft Access Applications......................................... 1-1
Analyze Your MDB File in Microsoft Access................................................................................. 1-2
About the Microsoft Access Migration to Oracle Application Express Forum ........................ 1-3
About Converting an Oracle Forms Application ............................................................................... 1-3
Preparation Checklist for Converting Oracle Forms Applications............................................. 1-3
About the Oracle Application Express Forum............................................................................... 1-4
2 Overview of the Migration Process
Why Migrate to Oracle Application Express?..................................................................................... 2-1
Before Starting the Conversion Process............................................................................................... 2-2
Evaluating Whether to Convert or Build an Application from Scratch......................................... 2-2
Understanding What an Oracle Application Express Application Conversion is Not .............. 2-2
Key Differences with Oracle Application Express ............................................................................ 2-3
Stateless Web Applications............................................................................................................... 2-3
Evaluating User Interface Design .................................................................................................... 2-3
About Business Logic Replication ................................................................................................... 2-4
Creating an Oracle Application Express Migration Project............................................................. 2-4
3 Migrating a Microsoft Access Application
How to Migrate a Microsoft Access Application ............................................................................... 3-1
Export Microsoft Access Metadata........................................................................................................ 3-2
Migrate the Microsoft Access Database to Oracle ............................................................................. 3-3
iv
Verifying If Generated DDL Executes Against the Appropriate Instance ................................ 3-4
Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users ................................................... 3-4
Creating a Workspace Manually ..................................................................................................... 3-5
Creating Oracle Application Express Users................................................................................... 3-7
Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace...................................................... 3-8
Create a Migration Project ...................................................................................................................... 3-9
About the Application Migrations Page...................................................................................... 3-10
Utilizing Interactive Reports .................................................................................................. 3-11
Review Your Retrieved Objects.......................................................................................................... 3-12
Reviewing Retrieved Tables .......................................................................................................... 3-12
Reviewing Retrieved Queries........................................................................................................ 3-16
Reviewing Retrieved Forms .......................................................................................................... 3-18
Reviewing Retrieved Reports........................................................................................................ 3-20
Reviewing Database, Module, and Pages Information ............................................................. 3-22
Generate the Oracle Application Express Application.................................................................. 3-22
Deleting a Migration Project............................................................................................................... 3-24
4 Converting an Oracle Forms Application
How to Convert Your Application ........................................................................................................ 4-1
Convert Oracle Forms to XML ............................................................................................................... 4-2
Converting FormModules, ObjectLibraries, or MenuModules to XML .................................... 4-2
About the Forms2XML Conversion Tool ................................................................................ 4-3
Using the Forms2XML Conversion Tool From a Command Line....................................... 4-3
Using the Forms2XML Conversion Tool in a Java Program ................................................ 4-4
Converting a PL/SQL Library ......................................................................................................... 4-4
Converting an Oracle Report to XML ............................................................................................. 4-5
Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users ................................................... 4-5
Creating a Workspace Manually ..................................................................................................... 4-5
Creating Oracle Application Express Users................................................................................... 4-7
Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace...................................................... 4-8
Upload Database Objects into the Schema Associated with Your Workspace ............................ 4-9
Create a Conversion Project ................................................................................................................ 4-10
Review and Edit Forms Metadata ...................................................................................................... 4-11
About the Application Migrations Page...................................................................................... 4-11
Understanding the Project Page ............................................................................................ 4-12
Uploading Additional Files.................................................................................................... 4-14
Editing Project Details .................................................................................................................... 4-15
Reviewing Forms Modules............................................................................................................ 4-17
Viewing an Imported FormModule ..................................................................................... 4-17
Viewing Object Metadata and Selecting Specific Objects .................................................. 4-17
Viewing and Selecting Blocks ................................................................................................ 4-18
Viewing and Selecting Items.................................................................................................. 4-19
Reviewing Oracle Reports ............................................................................................................. 4-20
Viewing Reports....................................................................................................................... 4-20
Selecting Reports to Include................................................................................................... 4-21
Reviewing PL/SQL Libraries........................................................................................................ 4-21
About Annotations .................................................................................................................. 4-21
v
About Audit.............................................................................................................................. 4-21
Reviewing Forms Menus ............................................................................................................... 4-22
Viewing Form Menus.............................................................................................................. 4-22
Viewing a Summary of Forms Menus .................................................................................. 4-22
Viewing Form Menu and Program Unit Details................................................................. 4-23
Reviewing Object Libraries............................................................................................................ 4-24
About Annotations .................................................................................................................. 4-24
About Audit.............................................................................................................................. 4-24
Viewing an Uploaded Object Library................................................................................... 4-24
Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process ................................................................ 4-25
Why Use Annotations? ........................................................................................................... 4-25
Generate the Oracle Application Express Application.................................................................. 4-26
Setting Up Application Defaults................................................................................................... 4-26
Creating an Application................................................................................................................. 4-26
Deleting a Migration Project............................................................................................................... 4-28
A Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds
Oracle Forms Modules ........................................................................................................................... A-1
Overview of Oracle Forms Components ....................................................................................... A-1
Alerts............................................................................................................................................ A-1
Blocks........................................................................................................................................... A-2
Canvases...................................................................................................................................... A-2
Coordinates................................................................................................................................. A-2
Editors.......................................................................................................................................... A-2
List of Values .............................................................................................................................. A-2
Program Units ............................................................................................................................ A-2
Property Classes......................................................................................................................... A-2
Record Groups............................................................................................................................ A-3
Triggers........................................................................................................................................ A-3
Visual Attributes ........................................................................................................................ A-3
Windows ..................................................................................................................................... A-3
About Generated Applications ....................................................................................................... A-3
Primary Key Assumptions ....................................................................................................... A-3
Block to Page Region Mappings ..................................................................................................... A-4
Single Record Block ................................................................................................................... A-4
Tabular Form .............................................................................................................................. A-5
Master Detail Blocks.................................................................................................................. A-5
Non-Database Block .................................................................................................................. A-6
List of Values Implementation ........................................................................................................ A-6
Implementing Business Logic ......................................................................................................... A-6
Processes...................................................................................................................................... A-7
Computations ............................................................................................................................. A-7
Validations .................................................................................................................................. A-7
Oracle Reports.......................................................................................................................................... A-8
PL/SQL Libraries ..................................................................................................................................... A-8
Forms Menus............................................................................................................................................ A-8

vii
Preface
Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide describes how to convert
applications from either Microsoft Access or Oracle Forms to Oracle Application
Express.
To learn more about developing Oracle Application Express applications, see Oracle
Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's Guide and "Quick Start" in Oracle
Application Express Application Builder User's Guide.
Topics:
■ Topic Overview
■ Audience
■ Documentation Accessibility
■ Related Documents
■ Conventions
Topic Overview
This document contains the following chapters:
Title Description
Changes in This Release Describes changes in this document for Oracle
Application Express, release 4.2.
Getting Started with Application
Migration Workshop
Provides an overview of the steps needed to migrate a
Microsoft Access application or Oracle Forms application
and generate an Oracle Application Express application.
Overview of the Migration Process Explains how specific types of logic is handled in Oracle
Application Express.
Migrating a Microsoft Access
Application
Explains how to migrate a Microsoft Access and generate
an Oracle Application Express application.
Converting an Oracle Forms
Application
Explains how to convert an Oracle Forms application and
generate an Oracle Application Express application.
Oracle Forms Generation
Capabilities and Workarounds
Describe how objects are generated during the conversion
process, or alternatively how the same functionality can
be implemented post-generation if necessary.
viii
Audience
Oracle Application Express Migration Guide is intended for application developers who
are building database-centric web applications using Oracle Application Express. This
guide describes how to migrate a Microsoft Access application or Oracle Forms
application and generate an Oracle Application Express application.
To use this guide, you must have a general understanding of relational database
concepts and an understanding of the operating system environment under which you
are running Oracle Application Express.
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle
Accessibility Program website at
http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Access to Oracle Support
Oracle customers have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For
information, visit
http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit
http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are
hearing impaired.
Related Documents
For more information, see these Oracle resources:
■ Oracle Application Express Application Builder User's Guide
■ Oracle Application Express Release Notes
■ Oracle Application Express Installation Guide
■ Oracle Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's Guide
■ Oracle Application Express End User's Guide
■ Oracle Application Express Administration Guide
■ Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop Guide
■ Oracle Application Express API Reference
■ Oracle Database Concepts
■ Oracle Database Advanced Application Developer's Guide
■ Oracle Database Administrator's Guide
■ Oracle Database SQL Language Reference
■ SQL*Plus User's Guide and Reference
For additional documentation available on Oracle Technology Network (OTN), visit
the Oracle Application Express website located at:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/apex/overview/index.h
tml
See Also: Oracle Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's
Guide

ix
For additional application examples, go to the Learning Library. Search for free online
training content, including Oracle by Example (OBE), demos, and tutorials. To access
the Oracle Learning Library, go to:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/tutorials/index.html
Printed documentation is available for sale in the Oracle Store at:
http://shop.oracle.com/
If you have a user name and password for OTN, then you can go directly to the
documentation section of the OTN website at:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/indexes/documentation/index.html
Conventions
The following text conventions are used in this document:
Convention Meaning
boldface Boldface type indicates graphical user interface elements associated
with an action, or terms defined in text or the glossary.
italic Italic type indicates book titles, emphasis, or placeholder variables for
which you supply particular values.
monospace Monospace type indicates commands within a paragraph, URLs, code
in examples, text that appears on the screen, or text that you enter.
x

xi
Changes in This Release
This preface contains:
■ Changes in Oracle Application Express Release 4.2
Changes in Oracle Application Express Release 4.2
The following are changes in Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide for
Oracle Application Express release 4.2.
■ All content has been updated to reflect new functionality.
■ Screen captures and graphics have been added and updated to reflect Oracle
Application Express release 4.2 user interface enhancements.
xii

1
Getting Started with Application Migration Workshop 1-1
1Getting Started with Application Migration
Workshop
Oracle Application Express Application Migration Workshop (Application Migrations)
enables you to migrate a Microsoft Access application or convert an Oracle Forms
application to an Oracle Application Express application.
This section provides a general description of the steps needed to migrate applications
from Microsoft Access or Oracle Forms to Oracle Application Express to Oracle
Application Express.
Topics:
■ About Migrating a Microsoft Access Application
■ About Converting an Oracle Forms Application
About Migrating a Microsoft Access Application
You begin the migration process by exporting your Microsoft Access metadata using
the Exporter tool and Oracle SQL Developer. After this initial step, you use
Application Migration to review the retrieved objects and resolve any issues regarding
invalid objects. As the final step, you have the option of generating either an
application based on valid forms and reports or a maintenance application based on
valid tables and views.
Once you have generated the application, you can take advantage of all the
functionality in Oracle Application Express to further develop and enhance the
migrated application.
Topics:
■ Preparation Checklist for Migrating Microsoft Access Applications
■ Analyze Your MDB File in Microsoft Access
■ About the Microsoft Access Migration to Oracle Application Express Forum
Preparation Checklist for Migrating Microsoft Access Applications
Before you begin the migration process, verify that your system meets these
requirements:
■ Oracle Application Express version 3.0 or later
You must install Oracle Application Express 3.0 or later. You use the Application
Migration feature within Oracle Application Express to download the Exporter

About Migrating a Microsoft Access Application
1-2 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
tool and to migrate Microsoft Access forms and reports to Oracle Application
Express.
■ Oracle SQL Developer 2.1 or later (available in English only)
You must install Oracle SQL Developer version 2.1 or later. You use the migration
capabilities extension to migrate the Microsoft Access schema and data to Oracle.
■ Exporter tool version 10.2.0.2.5 or later (available in English only)
You can install the Exporter tool using the Download Exporter link within Oracle
Application Express. For instructions, see "Export Microsoft Access Metadata" on
page 3-2.
If you are using Oracle SQL Developer version 2.1 or later, you can access the
Exporter tool directly from the Migration menu.
■ Microsoft Access
Your local system must have Microsoft Access installed, and it must be installed
where the Exporter tool and .mdb file reside.
■ Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC)
Your local system should have the latest version of Microsoft Data Access
Components (MDAC) installed. You can download the latest version from the
Microsoft website.
■ Printer
Your local system must have a printer installed so that a report can be opened in
design view. This is a requirement for exporting your Reports information from an
.mdb file.
■ Analyze your .mdb file before you export your database. Follow the instructions
in the next section.
Analyze Your MDB File in Microsoft Access
Using Microsoft Access, you should analyze your .mdb file before you export your
database. Performing these steps minimizes errors in the migration.
1. In Microsoft Access, analyze the objects in your .mdb file:
a. From the Microsoft Access menu bar, select To ol s, Analyze, and then
Documenter.
b. Select the All Object Types tab, and then click the Select All button to select
all the objects within the application for analysis.
c. Remove or resolve any erroneous objects reported by the Documenter.
2. Ensure the application contains no missing references:
a. In Microsoft Access, launch the design IDE (press Alt+F11 keys).
b. From the menu bar, select Tools and then References.
c. Remove or resolve any missing references.
3. Ensure the application compiles successfully:
a. From the menu bar in the IDE view, select Debug and then Compile.
b. Resolve any reported errors.
4. Perform a compact and repair on the database:

About Converting an Oracle Forms Application
Getting Started with Application Migration Workshop 1-3
■ From the menu bar in Microsoft Access, select Tools, Database Utilities, and
then Compact and Repair Database.
5. Ensure that all linked tables are valid links:
a. From the menu bar in Microsoft Access, select Tools, Database Utilities, and
then Linked Table Manager.
b. Verify that all links are up-to-date and pointing to an existing .mdb file that is
not read-only.
About the Microsoft Access Migration to Oracle Application Express Forum
In addition to Oracle support, you can post questions on the Database and
Applications Migrations forum:
http://forums.oracle.com/forums/category.jspa?categoryID=27
About Converting an Oracle Forms Application
You begin the process by converting Oracle Forms metadata to Extensible Markup
Language (XML). Then, you create a conversion project within Oracle Application
Express. Once you have reviewed and edited the application metadata within the
project, you generate an Oracle Application Express application. Then, you can
customize your application and change application attributes or add new pages within
Application Builder.
Topics:
■ Preparation Checklist for Converting Oracle Forms Applications
■ About the Oracle Application Express Forum
Preparation Checklist for Converting Oracle Forms Applications
Before you begin the conversion process, you must:
■ Install Oracle Application Express version 3.2 or later
You must install Oracle Application Express 3.2 or later to convert an Oracle
Forms application to Oracle Application Express.
■ Install Oracle9i Oracle Developer Suite or later
You must install Oracle Developer Suite to convert Oracle Forms applications and
Oracle Reports to XML format. Specifically, you need:
– Oracle Forms Builder
You must have Oracle Forms Builder installed to access the Forms2XML
conversion tool and the File Conversion utility for converting Oracle Forms
application files.
– Oracle Reports Builder
You must have Oracle Reports installed, to convert Oracle Reports (including,
binary (.RDF), ASCII (.REX), and .JSP) to XML format.
■ Convert Oracle Forms Metadata
To start the conversion process, you convert:
See Also: "Migrating a Microsoft Access Application" on page 3-1

About Converting an Oracle Forms Application
1-4 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
– Oracle Forms FormModule (.FMB), ObjectLibrary (.OLB), or MenuModule
(.MMB) files to XML format using the Forms to XML conversion tool,
Forms2XML
– Oracle Reports (including, binary (.RDF), ASCII (.REX), and .JSP) to XML
format using the File Conversion option in Reports Builder
– PL/SQL library .PLL files to .PLD text files using the File Conversion option in
Oracle Forms Builder
■ Associate Oracle Forms Schema with Oracle Application Express workspace
You must ensure the schema associated with your Oracle Application Express
workspace contains the database objects for your Oracle Forms application.
Further information on Oracle Application Express workspaces and associating
schemas is provided in subsequent chapters.
About the Oracle Application Express Forum
In addition to Oracle support, you can post questions on the Oracle Application
Express Forum:
http://forums.oracle.com/forums/forum.jspa?forumID=137
See Also: "Converting an Oracle Forms Application" on page 4-1

2
Overview of the Migration Process 2-1
2Overview of the Migration Process
Whether converting from Oracle Forms or migrating from Microsoft Access, Oracle
Application Express Application Migration is an effective tool to start your conversion
project. This section outlines the tool’s capabilities and provides important information
that should be reviewed before starting a conversion project.
Topics:
■ Why Migrate to Oracle Application Express?
■ Before Starting the Conversion Process
■ Evaluating Whether to Convert or Build an Application from Scratch
■ Understanding What an Oracle Application Express Application Conversion is
Not
■ Key Differences with Oracle Application Express
■ Creating an Oracle Application Express Migration Project
Why Migrate to Oracle Application Express?
Oracle Forms modernization projects are often undertaken to convert legacy
applications to the latest Oracle Database version and enable developers to satisfy user
demands for greater user interactivity and Web 2.0 capabilities.
Microsoft Access presents organizations with a myriad of manageability issues. Often
simple applications grow in size and complexity and become mission critical. These
same applications are often scattered throughout the network making maintenance,
backups, security, and access increasingly costly and inconsistent. One key reason for
migrating from Microsoft Access to an Oracle Database is to consolidate the data and
build common applications based on a single data source.
Migrating to Oracle Application Express provides a robust, scalable, secure application
development tool that takes full advantage of the Oracle Database. Oracle Application
Express requires only a web browser and no client software for development,
deployment, or run time. The resulting web pages are rendered as hypertext mark-up
language (HTML). The Oracle Application Express development environment
provides many out-of-the-box features, such as interactive reports and charts, and
enables developers to rapidly deploy web application that greatly enhance user
interactivity.

Before Starting the Conversion Process
2-2 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Before Starting the Conversion Process
Before starting a conversion project, it is important to learn how to build applications
with Oracle Application Express. The first step is to install Oracle Application Express
within an Oracle Database instance. Oracle Application Express requires an Oracle
database that is release 10.2.0.4 or later. To learn more, see Oracle Application Express
Installation Guide. To learn how to build applications based on existing Oracle database
tables, review Oracle Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's Guide.
The Oracle Application Express development environment utilizes wizards within a
declarative environment and enables you to easily extend components using SQL and
PL/SQL. You can further extend the Oracle Application Express framework by
incorporating JavaScript and Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (AJAX). To learn
more, see "Implementing Business Logic" on page A-6.
Evaluating Whether to Convert or Build an Application from Scratch
Thanks to how quickly you can build a new application within Oracle Application
Express, it may seem quicker to build an application from scratch rather than loading
the source application definitions into an Oracle Application Express conversion
project and then generating an initial design.
When compared with developing an application from scratch, converting an existing
application provides many benefits. Once the source files for the original application
are loaded into the Oracle Application Express project, all developers can review the
pertinent information without needing to refer back to Oracle Forms or Microsoft
Access. There is no need for developers to become familiar with the source tool
development environment.
Having the forms, reports, and queries loaded into a conversion project also provides
an easy way to review the functionality and application logic provided in the old
application. Even if these components are not used to generate an Oracle Application
Express application, you can view, copy, and reuse the underlying SQL.
When converting from Oracle Forms another major benefit is the ability to track the
conversion to ensure you fully implement all the business logic within the new
application. By utilizing annotations within the conversion project, you can assign
priorities, resources, and add notes or tags to any component. Completion progress
can also be tracked to provide low-level project management capabilities.
Understanding What an Oracle Application Express Application
Conversion is Not
When you convert an application to Oracle Application Express, you do not simply
load the source files, press a few buttons, and magically generate a completed
application. The conversion capabilities are designed to provide an initial design that
you then must enhance and expand to fully replicate the original application. The
generated applications use the same Create Application wizard that you use to build
applications based on existing Oracle tables or views. However, instead of needing to
specify the generated pages, these are determined from the information loaded into
the conversion project. For more information on how various source components are
generated, see "Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds" on page A-1.
Once you have generated the initial design, you can take full advantage of the rapid
application development capabilities available in Oracle Application Express to
enhance the generated pages. Built-in wizards also enable you to quickly expand your
new application by adding new pages and links as necessary.

Key Differences with Oracle Application Express
Overview of the Migration Process 2-3
Key Differences with Oracle Application Express
Understanding some of the key differences between Oracle Application Express and
Oracle Forms or Microsoft Access will greatly assist you in redeveloping your
applications.
Topics:
■ Stateless Web Applications
■ Evaluating User Interface Design
■ About Business Logic Replication
Stateless Web Applications
Oracle Application Express does not maintain a constant state between the client (that
is, the web browser) and the database, but performs stateless transactions. A database
session is only utilized when requesting or submitting a page. Because Oracle
Application Express is stateless between the start and the end of a logical transaction,
(for example, when updating a record,) it is imperative to use optimistic locking rather
than pessimistic locking.
Oracle Forms and Microsoft Access use pessimistic locking whereby the record is
locked when a user requests a record for update. This lock is maintained until the
record is completed (or committed) or canceled (or rolled back). One of the key reasons
for not using pessimistic locking within a stateless web application is that if a user
closes their web browser or looses their connection in the middle of a transaction, the
record would remain locked.
Once form pages are generated by the Create Application or Create Page wizards,
Automatic Row Fetch and Automatic Row Processing processes are generated which
incorporate the MD5 checksum validation to enforce the optimistic locking. Before the
record is sent to the database to be updated or deleted the MD5 initially created is
compared to the MD5 value of the current database record to ensure they are the same.
If they differ, then the database record has been updated since it was queried and an
error displays to the user.
One consequence of an HTML application is that a rendered page does not perform
actions such as validations or hiding and showing fields as the user interacts with the
page. Validations are performed when the user submits the page for processing.
However, you can change this default behavior by utilizing JavaScript and AJAX. The
time needed to load a page is influenced by the transmission speed and the speed with
which the web browser renders the page. Therefore, it is not advisable to attempt to
completely replicate the client-side interactivity within an HTML application as the
weight (or size) of the page adversely affects page performance. As a best practice,
only implement critical client-side actions.
Evaluating User Interface Design
Oracle Forms and Microsoft Access use different underlying technologies to present
screens to users. In contrast, an Oracle HTTP Server renders HTML through a web
browser. As a consequence, the design of screens and items is markedly different.
When thinking about screen design, some screen layouts commonly used in Oracle
Forms are not readily reproducible in Oracle Application Express. Oracle Application
Express renders a complete HTML page and does not support the concept of windows
and canvases. Oracle Application Express also has a limitation of one tabular form per
page. Therefore, it is important to understand that it may be difficult to exactly

Creating an Oracle Application Express Migration Project
2-4 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
reproduce the screen layouts of the source application. This difference in screen design
presents opportunities to redesign some of the key business processes and potentially
streamline them, or include additional paths to provide greater flexibility.
For example, a common layout in Oracle Forms, such as a master detail form, can be
redeployed using a master form with reports for each of the detail views that link to
separate pages for editing these details. These same detail pages can also be accessed
from elsewhere in the application very easily.
Oracle Forms often uses the same screen for both querying records and then updating
a single record at a time. This is achieved by performing a query directly on the form
used for updating a single record. Oracle Application Express does not support the
notion of Enter Query and Execute Query. Therefore, the conversion project generates
an interactive report where records can be queried with a link to a form for editing a
single record.
Oracle Application Express does not support coordinate positioning of fields on a page
out-of-the-box, but uses a grid layout to set out elements such as labels and items.
Items can be specified with attributes (such as New Line, New Field, Column Span,
and Row Span) to determine how items are located.
About Business Logic Replication
One of the major facets of converting from either Oracle Forms or Microsoft Access is
replicating the business user interface specific logic. It is important to separate
business logic from logic for manipulating the user interface. Given the differences in
user interface implementation, the majority of the associated logic from the original
application will no longer be relevant. Oracle Application Express uses processes,
computations, and validations to implement business logic. Some logic can also be
replicated by utilizing default and source values within the Oracle Application
Express item definition.
The key to ensuring your new application performs correctly is to understand how
and when each of these functions operate. The ability to add conditional logic to any
component within Oracle Application Express (including regions, items, branches,
processes, computations and validations) also provides extensive flexibility when
replicating the original business logic. For more information, see "Implementing
Business Logic" on page A-6.
Creating an Oracle Application Express Migration Project
In an Oracle Forms conversion project, the data structures are defined in an Oracle
Database and do not necessarily need to be migrated. However, with Microsoft Access
the data structures and data must first be migrated across to Oracle using SQL
Developer. For more information on how to migrate data structures "Migrating a
Microsoft Access Application" on page 3-1.
Once the data structures are correctly implemented into a schema accessible to Oracle
Application Express, then the basic process for conducting a conversion is to load the
source application files into a project. The project is designed to show all the applicable
components and provide the ability to generate an initial application design. After
reviewing the project components and selecting the valid screens, reports, and items to
be included, you can generate an Oracle Application Express application. With both a
Forms Conversion project and an Access Migration project, some components loaded
into a project cannot be generated. To learn more about generation capabilities and
workarounds, see "Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds" on
page A-1.

Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-1
3
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application
This section describes the steps to migrate applications from Microsoft Access to
Oracle Application Express.
Topics:
■ How to Migrate a Microsoft Access Application
■ Export Microsoft Access Metadata
■ Migrate the Microsoft Access Database to Oracle
■ Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
■ Create a Migration Project
■ Review Your Retrieved Objects
■ Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
■ Deleting a Migration Project
How to Migrate a Microsoft Access Application
Before You Begin
Read "Preparation Checklist for Migrating Microsoft Access Applications" on page 1-1.
To migrate applications from Microsoft Access to Oracle Application Express, you
must perform the steps described in this section. The following illustration outlines the
entire process:

Export Microsoft Access Metadata
3-2 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
The migration process consists of the following steps:
Export Microsoft Access Metadata
Migrate the Microsoft Access Database to Oracle
Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
Create a Migration Project
Review Your Retrieved Objects
Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
Export Microsoft Access Metadata
To export your metadata from Microsoft Access, download the correct version of the
Exporter tool, as explained in this section. Then, run the Exporter and extract the
metadata from the Microsoft Access .mdb file. The metadata contains the necessary
database and application schema information.
The export process creates two output files:
■ database (.xml file)
■ application (.sql file)
Exporter Tool System Requirements
To use the Exporter tool, the Microsoft Windows operating system where the Exporter
tool runs must include the following libraries:
■ Microsoft DAO 3.6 Object Library
■ Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.5 Library
Important: You must follow the steps in the exact sequence
presented in this section.

Migrate the Microsoft Access Database to Oracle
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-3
Downloading the Exporter Tool
To download the Exporter tool for Microsoft Access:
1. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 3-8.
2. Click the Application Builder icon.
3. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
4. Under Tasks, click Download Exporter for Microsoft Access.
5. In the Download column, click the zip file that corresponds to your version of
Microsoft Access. For example, download the omwb2003.zip file if you are using
Microsoft Access 2003.
6. Save the file.
7. Unzip the file. You must replace the following files with the updated versions in the
msaccess_exporter directory where you unzipped the Exporter tool:
■ schema.dtd file
■ Exporter tool file: omwb<version>.mde
■ online help file: omwb.chm
Be sure to invoke the export from this directory.
Exporting Your Metadata
To export your metadata, follow the instructions found in the help file for the Exporter
tool. To find the instructions, do one of the following:
■ Launch the Exporter tool, and click the Help button.
■ Open the help file (omwb.chm) contained in the Exporter zip file.
The instructions appear in the topic called Exporter Overview.
Migrate the Microsoft Access Database to Oracle
To migrate the Microsoft Access database to Oracle:
1. Start Oracle SQL Developer version 2.1 or later. For example:
Note: Follow the instructions in this section if you are downloading
the Exporter tool from Oracle Application Express release 3.0 or later.
Alternately, you skip the following task and access the Exporter
directly from Oracle SQL Developer using the Migration menu.
See Also: "Migrate the Microsoft Access Database to Oracle" on
page 3-3 and "How to Migrate a Microsoft Access Application" on
page 3-1

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
3-4 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
a.
Create an Oracle user named MIGRATIONS with the default tablespace USER
and temporary tablespace TEMP and grant it at least RESOURCE, CREATE
SESSION, and CREATE VIEW privileges.
b. Create a database connection named Migration_Repository that connects
to the MIGRATIONS user.
c. Right-click the connection, select Migration_Repository, and then select
Migration Repository and then Associate Migration Repository to create the
repository.
2. Load the database metadata (.xml file) created in step 1. On the Oracle SQL
Developer toolbar, select Tools, Migration, and then Capture Microsoft Access
Exported XML.
This captures the schema and creates a Captured Model of the Microsoft Access
database.
3. Convert the captured database schema to Oracle. Right-click Captured Model and
select Convert to Oracle Model.
4. Generate the migrated Oracle database schema. Right-click Converted Model and
select Generate.
The generated DDL statements should execute against your Oracle database
instance, to generate the migrated schema objects.
For more information about Oracle SQL Developer migration capabilities, see:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/migration/index.html
Verifying If Generated DDL Executes Against the Appropriate Instance
When using Oracle SQL Developer migration capabilities, you must verify that the
generated DDL statements are executed against the same instance where Oracle
Application Express 3.0 or later is installed. If you select a Least Privilege Schema
Migration, the migrated objects can be created in an existing schema on your database
instance. Otherwise, a schema of the same name as the captured database (for
example, Northwind) is created on your database instance.
The migrated Oracle database schema objects must be in the same instance where
Oracle Application Express 3.0 is installed. If they are not, you will not be able to
complete the next step.
Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
A workspace is a virtual private database allowing multiple users to work within the
same Oracle Application Express installation while keeping their objects, data and
applications private. Each workspace has a unique ID and name.
An Oracle Application Express administrator can create a workspace manually within
Oracle Application Express Administration Services or have users submit requests.
Oracle Application Express Administration Services is a separate application for
managing an entire Oracle Application Express instance. See "Creating Workspaces"
and "Managing Workspace Requests" in Oracle Application Express Administration
Guide.
See Also: "Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express
Users" on page 3-4 and "How to Migrate a Microsoft Access
Application" on page 3-1

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-5
Topics:
■ Creating a Workspace Manually
■ Creating Oracle Application Express Users
■ Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace
Creating a Workspace Manually
To create an Oracle Application Express workspace manually:
1. Log in to Oracle Application Express Administration Services.
Oracle Application Express Administration Services is a separate application for
managing an entire Oracle Application Express instance. You log in using the
ADMIN account and password created or reset during the installation process.
a. In a web browser, navigate to the Oracle Application Express Administration
Services application. By default, Oracle Application Express Administration
Services installs to the following location:
– If your setup uses the Oracle Application Express Listener, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex/apex_admin
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle Application Express
Listener is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle Application Express Listener.
In a default installation, this number is 8080. These defaults are correct at
the time of the writing of this document. To learn more, see Oracle Applica-
tion Listener Installation and Developer Guide
apex is the service name defined when configuring the Oracle Applica-
tion Express Listener.
– If your setup uses the embedded PL/SQL gateway, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex/apex_admin
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle XML DB Protocol
Server is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle XML DB Protocol Server. In a
default installation, this number is 8080.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the configuration
file.
– If your setup uses Apache and mod_plsql, go to:
http://hostname:port/pls/apex/apex_admin
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle HTTP Server is
installed.
See Also: Oracle Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's
Guide if you are new to Oracle Application Express

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
3-6 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
port is the port number assigned to Oracle HTTP Server. In a default
installation, this number is 7777.
pls is the indicator to use the mod_plsql cartridge.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the mod_plsql
configuration file.
b. On the Login page:
– In Username, enter admin.
– In Password, enter the Oracle Application Express administrator account
password you specified when you installed Oracle Application Express.
– Click Login.
Next, create a workspace.
2. Click Manage Workspaces.
3. Under Workspace Actions, click Create Workspace.
The Create Workspace Wizard appears.
4. For Identify Workspace, enter the following:
a. Workspace Name - Enter a unique workspace name.
b. Workspace ID - Leave Workspace ID blank to have the new Workspace ID
automatically generated. A Workspace ID must be a positive integer greater
than 100000.
c. Workspace Description - Enter a workspace description.
d. Click Next.
5. For Identify Schema, specify whether you are re-using an existing schema or
creating a new one.
If you are using an existing schema:
a. For Re-use existing schema, select Yes.
b. Select a schema from the list.
c. Click Next.
If you are creating a new schema:
a. For Re-use existing schema, select No.
b. Enter a schema name and password.
c. Specify a space quota.
d. Click Next.
6. For Identify Administrator, enter the Workspace administrator information and
click Next.
7. Confirm your selections and click Create Workspace.
See Also: See "Logging in to Oracle Application Express
Administration Services" in Oracle Application Express Administration
Guide.

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-7
Creating Oracle Application Express Users
To create an Oracle Application Express user account:
1. Log in to Oracle Application Express Administration Services. See "Logging in to
Oracle Application Express Administration Services" in Oracle Application Express
Administration Guide.
2. Click Manage Workspaces.
3. Under Manage Workspaces, click Manage Developers and Users.
The Manage Developers and Users page appears.
4. Click Create User.
The Create/Edit User page appears.
5. Under User Attributes, enter:
a. Username - Enter the username used to log in to the system. Restrictions
include:
– Maximum length of 100 characters
– No spaces
– Only these special characters are permitted: ampersand (@) and period (.)
b. Email Address - Enter the valid email address for this user.
c. First Name - Enter the first or given name to further identify the user
(optional).
d. Last Name - Enter the last or family name to further identify the user
(optional).
e. Description - Enter comments about this user (optional).
6. Under Account Privileges:
a. Workspace - Select a workspace in which to create the user.
b. Default Schema - Specify the default schema used for data browsing,
application creation, and SQL script execution.
c. User is an administrator - Specify if this user should have workspace
administrator privileges.
Administrators are given access to all components. Additionally, they can
manage user accounts, groups, and development services. Components may
not be available if they are switched off by Instance Administrators.
d. User is a developer - Specify if this user should have developer privileges.
Developers must have access to either Application Builder, SQL Workshop, or
both. Components may not be available if they are switched off by Instance
Administrators.
e. Application Builder Access - Determines whether a developer has access to
the Application Builder.
f. SQL Workshop Access - Determines whether a developer has access to the
SQL Workshop.
g. Team Development Access - Determines whether a developer has access to
the Team Development.

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
3-8 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
h.
Account Availability - Select Locked to prevent the account from being used.
Select Unlocked to allow the account to be used.
7. Under Password:
■ Password - Enter a case-sensitive password.
■ Confirm Password - Enter the password again.
■ Require Change of Password On First Use - Select No to require this user to
change his or her password at first log in. Select Yes to require the user to
change the password immediately after logging in the first time.
8. Click Create.
Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace
Once you create a workspace, you must log in to it using your login credentials (that
is, the workspace name, user name, and password).
To log in to a workspace:
1. In a web browser, navigate to the Oracle Application Express Login page. By
default, Oracle Application Express installs to the following location:
■ If your setup uses the Oracle Application Express Listener, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle Application Express
Listener is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle Application Express Listener. In a
default installation, this number is 8080. These defaults are correct at the time
of the writing of this document. To learn more, see Oracle Application Listener
Installation and Developer Guide
apex is the service name defined when configuring the Oracle Application
Express Listener.
■ If your setup uses the embedded PL/SQL gateway, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle XML DB Protocol Server is
installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle XML DB Protocol Server. In a
default installation, this number is 8080.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the configuration file.
■ If your setup uses Oracle HTTP Server (Apache) and mod_plsql, go to:
http://hostname:port/pls/apex
Where:
See Also: See "Creating Workspaces" and "Managing Workspace
Requests" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide

Create a Migration Project
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-9
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle HTTP Server is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle HTTP Server. In a default
installation, this number is 7777.
pls is the indicator to use the mod_plsql cartridge.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the mod_plsql
configuration file.
The Login page appears.
2. Under Login, enter the following:
■ In the Workspace field, enter the name of your workspace.
■ In the Username field, enter your user name.
■ In the Password field, enter your case-sensitive password.
3. Click Login.
Depending on your setup, you might be required to change your password when
you log in for the first time.
Create a Migration Project
To create a migration project:
1. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 3-8.
2. Click the Application Builder icon.
3. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
4. On the Application Migrations page, click Create Project.
The Create Migration Project wizard appears. The steps included in the wizard
appear in a graphic at the top of the page.
5. Enter the project details:
a. Project Name - Enter a unique name. For example, consider using the same
name as the Microsoft Access .mdb file you used to create the project.
b. Type - Select Access.
c. Description - Enter a meaningful description for this project. For example,
describe the Microsoft Access .mdb file that you used to create the project.
d. Schema - Select the schema.
The default schema is the schema associated with your workspace. If multiple
schemas are associated with your workspace, all associated schemas appear in
the select list, arranged in alphabetical order. When this situation exists, select
the schema associated with the SQL script you want to upload.
e. Migration Export File - Locate the .sql file created by the Exporter tool for
Microsoft Access.

Create a Migration Project
3-10 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
f.
Click Next.
6. Review the project details, and click Finish.
The project page appears.
This page displays as an interactive report. To customize the report, use the Search
bar at the top of the page. See "Customizing Interactive Reports" in Oracle
Application Express Application Builder User's Guide.
About the Application Migrations Page
The Application Migrations page initially shows a high-level overview of the
Microsoft Access objects retrieved from your Microsoft Access database.
This page displays the project name, project type, related application, and number of
objects.
After you generate an application from a migration project, the application name
displays in the Application column. To link to the application, select the application
name.
To view project details, click the project name. The project page appears.
See Also: "About the Application Migrations Page" on page 3-10,
"Review Your Retrieved Objects" on page 3-12, and "How to Migrate a
Microsoft Access Application" on page 3-1

Create a Migration Project
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-11
Note that your project might not include all object types. The project page lists only
object types that exist in your database.
Utilizing Interactive Reports
Many pages in Application Migration Workshop display as interactive reports. You
can customize the appearance of interactive reports using the Search bar at the top of
each page.
Use the Search bar to create custom searches and customize and filter the information
that appears on the page.
Available controls on the Search bar include:
See Also: "Review Your Retrieved Objects" on page 3-12 and "How
to Migrate a Microsoft Access Application" on page 3-1

Review Your Retrieved Objects
3-12 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
■ Select columns to search icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to
narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All
Columns.
■ Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wildcard characters are implied)
and then click Go.
■ Go button - Executes a search.
■ Actions menu - Use the Actions menu to customize an interactive report.
To learn more, see "Customizing Interactive Reports" in Oracle Application Express
Application Builder User's Guide.
Review Your Retrieved Objects
Next, you want to select the objects to include in the migration. The initial list consists
of the Microsoft Access application metadata that is retrieved, both valid and invalid.
To include an object, it must have a status of Valid. By default, all objects with a Valid
status are selected.
From within Application Migration, you can fix objects identified as invalid so that
they can be included. Since the Application Migration also identifies tables without
primary keys and objects without user interface defaults, you can correct those
situations to maximize application design recovery.
Topics:
■ Reviewing Retrieved Tables
■ Reviewing Retrieved Queries
■ Reviewing Retrieved Forms
■ Reviewing Retrieved Reports
■ Reviewing Database, Module, and Pages Information
Reviewing Retrieved Tables
Next, review the Oracle tables retrieved from the Microsoft Access database.
Application Migration identifies invalid tables without primary keys and those
without user interface defaults, which you can add before migrating.
After you update the tables, select the ones you want to include in the migration. If
you do not include a table, all forms and reports based on the table are excluded from
the migration.
To review retrieved tables:
1. From the project page, click the project name.
Tip: Extensive Oracle documentation is available for broadening
your knowledge of database concepts and objects. For example, to
learn more about primary keys and constraints, see Oracle Database
Concepts. You can download Oracle documentation from:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/documentation/index
.html

Review Your Retrieved Objects
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-13
2.
From the project page, click Tables.
The Tables page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
For each Microsoft Access table, the Tables page shows:
■ Oracle Table - Identifies the corresponding Oracle table, which defaults to the
Microsoft Access table name in all capital letters.
Note that the name may differ from the original one because of the collision
management facility in Exporter tool. For information about naming
guidelines and restrictions, click Help in Oracle SQL Developer and go to the
Frequently Asked Questions section.
If the Microsoft Access object was not successfully migrated to Oracle, then
this field will not have a corresponding Oracle table name. Instead, it will
contain a link to a page where you can create a corresponding Oracle table.
■ Primary Key - Indicates if a primary key exists for the table.
A table without a primary key is considered invalid in Application Migration.
You can create a primary key at this point. All tables you want to migrate
should have a primary key.
■ Foreign Key - Indicates if a foreign key exists for the table.
If you know a relationship exists between two tables, you should create a
foreign key. You can do this in Object Browser by creating a Foreign Key
Constraint. For more information, see "Managing Database Objects with
Object Browser" Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop Guide.
■ UI Defaults - Indicates if user interface defaults are set for the table.

Review Your Retrieved Objects
3-14 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
User interface defaults are used by Oracle Application Express to populate
initial values for region and item properties. Using user interface defaults
provides consistency across multiple applications or across multiple pages in
an application.
■ Status - Table status as either Valid or Invalid.
Only valid tables can be included in the migration.
3. To create a table:
a. On the Tables page, click the link in the Oracle Table column for the table you
want to create.
The Object Browser opens.
b. Click the Create button.
c. From the list of object types, select Tab le .
d. Follow the on-screen instructions.
4. To add a primary key:
a. On the Tables page, click the Oracle table name.
b. From the Tasks list, click Create Primary Key.
c. For Constraint Details, fill in the information.
d. Click Next.
e. Confirm the information and click Finish.
5. To add an index:
a. On the Tables page, click the Oracle table name.
b. From the Tasks list, click Create Index.
c. Select the type of index you want to create on this table.
Tip: To review the list of existing columns or constraints, expand the
Existing Columns or Existing Constraints regions.

Review Your Retrieved Objects
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-15
For indexing NUMBER, VARCHAR, and DATE, select Normal. For indexing CLOB
columns, select Text.
d. Click Next.
e. For Index Definition, fill in the information.
The following graphic shows the fields to fill out if you selected Normal as the
type of index.
f. Click Next.
g. Confirm the information and click Create.
6. To set user interface defaults:
a. On the Tables page, click the Oracle table name.
b. From the Tasks list, click UI Defaults.
c. On the UI Defaults page, click Create Defaults.
d. On the Create Table Dictionary Defaults page, click Create Defaults.
Tip: To review the list of existing table indexes or columns, click the
Table Indexes or Table Columns links.

Review Your Retrieved Objects
3-16 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
The Table Dictionary page appears. Note that you are now working within
SQL Workshop. SQL Workshop is a component of Oracle Application Express
with utilities to load and unload data from an Oracle database, generate DDL,
view object reports, and restore dropped database objects.
e. On the Table Dictionary report, click the Oracle table name in the Object Name
column.
The Table and Column Properties page appears, listing column information as
it will appear in forms and reports.
f. To edit the information, click the Column name.
The Column Defaults page appears. You can update the column label, change
the sequence of how the columns appear by default, and so on.
g. Click Apply Changes to save your updates.
7. To include tables in the migration, select them in the left column.
8. Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
Reviewing Retrieved Queries
Next, review the queries retrieved from the Microsoft Access export. Application
Migration identifies invalid queries and those without user interface defaults, which
you can set before migration.
After you update the views, select the ones you want to include in the migration. If
you do not include a query, any forms or reports based on the query are excluded from
the migration.
To review retrieved queries:
1. From the project page, click Queries.
The Queries page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
For each Microsoft Access query, the Queries page shows:
■ Oracle View - Indicates the corresponding Oracle view, which defaults to the
Microsoft Access query name in all capital letters.
See Also: "Reviewing Retrieved Queries" on page 3-16, "Review
Your Retrieved Objects" on page 3-12, and "How to Migrate a
Microsoft Access Application" on page 3-1

Review Your Retrieved Objects
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-17
If the Microsoft Access object was not successfully migrated to Oracle, then
this field will not have a corresponding Oracle view name. Instead, it will
contain a link to a page where you can create a corresponding Oracle view.
■ Status - Query status is either Valid or Invalid.
Only valid queries can be included in the migration.
■ UI Defaults - Indicates if user interface defaults are defined for the query.
User interface defaults are used by Oracle Application Express to populate
initial values for region and item properties. Using user interface defaults
provides consistency across multiple applications or across multiple pages in
an application.
2. To run a bulk process that attempts to compile all invalid queries, click Attempt to
compile invalid queries.
Using this option can validate some queries that show a status of invalid when
initially migrated.
3. To create a view:
a. On the Queries page, click the link in the Oracle View column for the view you
want to create.
The Oracle View appears. The editor is populated with the syntax of the
original Microsoft Access query. You may need to edit the syntax to ensure it is
valid Oracle syntax before compiling.
b. Click the Compile button.
c. From the list of object types, select View.
d. Follow the on-screen instructions.
4. To edit a query:
a. On the Queries page, click the Oracle view you want to edit.
b. Click Compile to find the invalid part of the query.
The Microsoft Access Query syntax appears in the edit window. It may require
some modification to make it valid Oracle syntax.
c. Click Access Query to review the initial query and compare it to the converted
query.
d. Update the query and recompile it.
e. When it is validated, click the Queries breadcrumb.
f. To include this validated query, select it in the left column on the Queries page
and click Apply Changes.
5. To set user interface defaults:
a. On the Queries page, click the Oracle view.
b. In the Tasks list on the right, click UI Defaults.
c. On the UI Defaults page, click Create Defaults.
d. On the Create Defaults page, click Create Defaults.
The Table Dictionary page appears. The Table Dictionary page appears. Note
that you are now working within SQL Workshop. SQL Workshop is a
component of Oracle Application Express with utilities to load and unload

Review Your Retrieved Objects
3-18 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
data from an Oracle database, generate DDL, view object reports, and restore
dropped database objects.
e. To edit the information, click the object name.
The Table and Column Properties page appears.
f. To edit the information, click the Column name.
The Column Defaults page appears. You can update the column label, change
the sequence of how the columns appear by default, and so on.
g. Click Apply Changes to save your updates.
6. To include queries in the migration, select the Include check box in the left column
on the Queries page.
7. Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
Reviewing Retrieved Forms
Next, review the forms retrieved from the Microsoft Access export. Application
Migration identifies invalid forms and lists additional information, such as the form’s
source type and source name.
For valid forms with a source type of table, you can select the type of object you want
the form to become within Oracle Application Express: form (default), report and
form, or tabular form.
Microsoft Access forms based on a query are migrated to Oracle Application Express
forms. Microsoft Access forms based on a SQL query are migrated to Oracle
Application Express reports.
After you update the forms, select the ones you want to include in the migration.
To review retrieved forms:
1. From the project page, click Forms.
The Forms page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
See Also: "Reviewing Retrieved Forms" on page 3-18, "Review Your
Retrieved Objects" on page 3-12, and "How to Migrate a Microsoft
Access Application" on page 3-1

Review Your Retrieved Objects
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-19
For each Microsoft Access form, the Forms page shows the following information,
if available:
■ Source type:
– Table - The Oracle table that was migrated from the Microsoft Access
table.
– Query - The Oracle view that was migrated from the Microsoft Access
query.
– SQL Query - The original Microsoft Access SQL query that the Microsoft
Access form is based on. Note that this query has not been parsed.
Therefore, you must edit it to make it valid Oracle SQL syntax.
– Nothing - The form has no underlying source type.
■ Source name - The Oracle table or view name if the source type is a table or
query.
■ Status - Form status as Valid or Invalid. The source of the form must have a
status of Valid before you can select it for migration.
A form’s status is based on two factors: status of its underlying source object
and inclusion of the source object in the migration. Specifically, a form has a
status of valid if either one of these situations exists:
– Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is valid, and it has been
included in the migration. Its check box is enabled and can be selected.
– Its Source type object has a status of valid, but the source object was not
included in the migration. Its check box is disabled.
A form has a status of invalid if either one of these situations exists:
– No Source Type is listed. Its check box is disabled.
– Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is invalid. Its check box
is disabled.
■ Startup form - Identifies the form that displays when you open your Microsoft
Access database.
■ Parent form - Indicates the form and subform relationship that exists in your
Microsoft Access database. For example, the CallListSub form shows
Contacts as its Parent Form.
■ Migrate to: Form, Tabular Form, or Report and Form - The select list appears if
the source type is a valid table.
2. To run a bulk process that attempts to compile all invalid SQL queries, click
Attempt to compile invalid SQL queries at the bottom of the page.
Using this option can validate some SQL queries that show a status of invalid.
Note that SQL queries from Microsoft Access forms are not loaded into the
Exporter tool, and are therefore not parsed.
3. To edit a SQL query:
a. On the Forms page, click the SQL Query you want to edit.
b. Click Validate to find the invalid part of the SQL query.
c. Update the query and validate it.
d. When it is validated, click the project name breadcrumb.

Review Your Retrieved Objects
3-20 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
e.
To include the validated query, click Forms on the project page to go to the
Forms page. Then select the newly validated query in the left column and click
Apply Changes.
4. To edit a query:
a. On the Forms page, click Query for the form you want to edit.
b. Click Compile to find the invalid part of the query.
c. Click Access Query to review the initial query and compare it to the converted
query.
d. Update the query and recompile it.
e. When it is validated, click the Queries breadcrumb.
f. To include this validated query, select it in the left column on the Queries page
and click Apply Changes.
5. To review details about a form, click the link in the Access Form column.
6. To include forms in the migration, select the Include check box in left column on
the Forms page.
7. Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
Reviewing Retrieved Reports
Next, review the reports retrieved from the Microsoft Access export. Application
Migration identifies invalid reports and lists additional information, such as the
report’s source type and source name.
After you update the reports, select the ones you want to include in the migration. To
include a report, the source of the report must have a status of Valid.
To review retrieved reports:
1. From the project page, click Reports.
The Reports page appears, showing the status of the objects ready for migration.
See Also: "Reviewing Retrieved Reports" on page 3-20, "Review
Your Retrieved Objects" on page 3-12, and "How to Migrate a
Microsoft Access Application" on page 3-1

Review Your Retrieved Objects
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-21
For each Microsoft Access report, the Reports page shows the following
information, if available:
■ Source type:
– Table
– Query - The Oracle view that was migrated from the Microsoft Access
query.
– SQL Query - The original Microsoft Access SQL query that the Microsoft
Access form is based on. Note that this query has not been parsed.
Therefore, you must edit it to make it valid Oracle SQL syntax.
– Nothing - The report has no underlying source type.
■ Source name
■ Status of the report: Valid or Invalid. The source of the report must have a
status of Valid before you can select it for migration.
A report status is based on two factors: status of its underlying source object
and inclusion of the source object in the migration. Specifically, a report has a
status of valid if either one of these situations exists:
– Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is valid, and it has been
included in the migration. Its check box is enabled and can be selected.
– Its Source type object has a status of valid, but the source object was not
included in the migration. Its check box is disabled.
A report has a status of invalid if either one of these situations exists:
– No Source Type is listed. Its check box is disabled.
– Its Source Type object (table, query, or SQL query) is invalid. Its check box
is disabled.
2. To run a bulk process that attempts to compile all invalid SQL queries, click
Attempt to compile invalid SQL queries at the bottom of the page.
Using this option can validate some SQL queries that show a status of invalid.
Note that SQL queries from Microsoft Access forms are not loaded into the
Exporter tool and are therefore not parsed.

Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
3-22 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
3.
To edit a SQL query:
a. On the Reports page, click the SQL Query link you want to edit.
b. Click Validate to find the invalid part of the SQL query.
c. Update the query and validate it.
d. When it is validated, click the project name breadcrumb.
e. To include the validated query, click Reports on the project page to go to the
Reports page. Then select the newly validated SQL query in the left column
and click Apply Changes.
4. To edit a query:
a. On the Reports page, click Query for the report you want to edit.
b. Click Compile to find the invalid part of the query.
c. Click Access Query to review the initial query and compare it to the converted
query.
d. Update the query and recompile it.
e. When it is validated, click the Queries breadcrumb.
f. To include this validated query, select it in the left column on the Queries page
and click Apply Changes.
5. To review details about a report, click the link in the Access Report column.
6. To include reports in the migration, select the Include check box in left column on
the Reports page.
7. Click Apply Changes to save your selections.
Reviewing Database, Module, and Pages Information
From the project page, you can drill down to see information about the database,
modules, and pages for the migration project.
■ Database - Displays summary information about the Microsoft Access database,
including the full path and size of the .mdb file.
■ Modules - Displays the Visual Basic Code, enabling you to extract embedded SQL
statements for you to use or edit in your Oracle Application Express application.
■ Pages - Displays information for reference purposes.
Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
After validating and updating objects, you now must generate the application in
Oracle Application Express. You can create an application based on valid forms and
reports, or a maintenance application based on valid tables and views.
See Also: "Reviewing Database, Module, and Pages Information" on
page 3-22, "Review Your Retrieved Objects" on page 3-12, and "How to
Migrate a Microsoft Access Application" on page 3-1
See Also: "Generate the Oracle Application Express Application" on
page 3-22 and "How to Migrate a Microsoft Access Application" on
page 3-1

Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-23
When creating an application, a home page is defined by default. You have the option
to create additional blank pages so that you can introduce further navigation
possibilities.
You can then choose which user interface theme your application should be based on.
By default, the application uses one level of tabs.
As a shortcut, you can also set some application defaults. These defaults are used
whenever you create new applications.
Setting Up Application Defaults
To set up application defaults (optional):
1. On the right side of the project page, click Set Application Defaults in the Tasks
list.
2. Select the options you want to use as defaults.
For more information, see item Help. Clicking the item label opens a separate
window describing the item and its options.
3. Click Apply Changes.
The project page appears.
Generating Applications
To generate either type of application:
1. On the right side of the project page, click one of the following in the Tasks list:
■ Generate Application - This option generates an application based on the
forms and reports you selected to include.
■ Generate Maintenance Application - This option generates an application
based on the tables and queries you selected to include.
2. In the Selected Application Objects section, you can customize specific pages.
For example:
■ To rename a page, click the page name link and enter the new name on the
New Page Definition page that appears.
■ To select the type of navigation on the application’s home page, click the
Home Page link.
On the New Page Definition page that appears, select Vertical Unordered List
with Bullets, Vertical Images List, or Horizontal Images List.
■ To display an image on a parent page, click the page link.
On the New Page Definition page that appears, go to the Page Icon field and
select the image you want to appear on that page. You can either select an
image from the select list or click the Find icon (flashlight) to open a page of
options.
Repeat this step for each parent page. If you do not explicitly select an image
for a page, the default image appears for that page.
Note that for the image to appear in your application, you must have selected
either Vertical Images List or Horizontal Images List for the Home page
navigation.
3. To add a blank page to the application, scroll down to the Add Page section and
click Add Page.

Deleting a Migration Project
3-24 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
The new page appears at the bottom of the list in the Selected Application Objects
section.
4. Click Next.
5. On User Interface, select a theme for the application.
A theme is a collection of templates that define the layout and style of an
application, including buttons and pages.
Options include:
a. Show - Select the type of themes to display.
b. Select a Theme - Select a theme from the list.
c. Click Next.
6. Confirm your selections and click Create.
7. To preview the application, click Run Application.
8. Log in using your Oracle Application Express workspace credentials.
Your application now appears as a separate application in Oracle Application
Express.
9. To customize your application, scroll down to the Developer toolbar and click Edit
Application.
You might want to do the following customizations immediately after you
generate your application:
■ Rename the application. Each application has a unique ID, but the migration
project name becomes the application name by default. To more easily identify
an application, you might want to change its name to something more
meaningful by editing the application attributes.
■ Change the authentication scheme. By default, the authentication scheme is
Application Express authentication. You can change this by editing the
application attributes.
Deleting a Migration Project
When you delete a migration project, you delete only the metadata associated with the
migration project. Deleting a migration project does not delete or impact applications
you have generated from the project or any objects, such as tables or views, in the
schemas associated with your workspaces.
To delete a migration project:
1. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 3-8.
2. Click the Application Builder icon.
3. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
4. On the Application Migrations page, click the project name.
5. On the Tasks list, click Delete Project.
See Also: Oracle Application Express Application Builder User's Guide
to learn more about editing application attributes, adding pages,
deploying your application, and so on.

Deleting a Migration Project
Migrating a Microsoft Access Application 3-25
6.
Click the Delete Project button and confirm the deletion.

Deleting a Migration Project
3-26 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide

Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-1
4
Converting an Oracle Forms Application
This section describes the steps to convert applications from Oracle Forms to Oracle
Application Express.
Topics:
■ How to Convert Your Application
■ Convert Oracle Forms to XML
■ Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
■ Upload Database Objects into the Schema Associated with Your Workspace
■ Create a Conversion Project
■ Review and Edit Forms Metadata
■ Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
■ Deleting a Migration Project
How to Convert Your Application
Before You Begin
To convert applications from Oracle Forms to Oracle Application Express, you must
perform the steps described in this section. The following graphic outlines the entire
process.

Convert Oracle Forms to XML
4-2 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
The conversion process consists of the following steps:
Convert Oracle Forms to XML
Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
Upload Database Objects into the Schema Associated with Your Workspace
Create a Conversion Project
Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
Convert Oracle Forms to XML
In order to convert Oracle Forms to Oracle Application Express, you must convert the
Forms modules to formats the Create Migration Project wizard can consume.
Topics:
■ Converting FormModules, ObjectLibraries, or MenuModules to XML
■ Converting a PL/SQL Library
■ Converting an Oracle Report to XML
Converting FormModules, ObjectLibraries, or MenuModules to XML
You can convert Oracle Forms FormModule, MenuModule, and ObjectLibrary files to
Extensible Markup Language (XML) using the Oracle Forms to XML conversion tool,
Forms2XML.
Topics:
■ About the Forms2XML Conversion Tool
Important: You must follow the steps in the exact sequence
presented in this section.

Convert Oracle Forms to XML
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-3
■ Using the Forms2XML Conversion Tool From a Command Line
■ Using the Forms2XML Conversion Tool in a Java Program
About the Forms2XML Conversion Tool
The Oracle Forms to XML conversion tool, Forms2XML was introduced in Oracle9i
Oracle Developer Suite and is also available in Oracle Developer Suite 10g. This tool
should also work on files from earlier releases of Oracle Forms. If the Oracle Forms to
XML Conversion tool does not work for a specific file from an earlier version of Oracle
Forms, then you must upgrade the file to Oracle Developer Suite 9i or 10g and then
convert to XML
Forms2XML produces an XML file that has the same base name as the Forms file with
an .xml extension. The extension _fmb, _mmb, or _olb is added to the base file name
to indicate whether the original file was a Forms Modules, a MenuModule, or an
Object Library. The following table displays a few examples of the changes the tool
makes to the name of the file being converted:
Using the Forms2XML Conversion Tool From a Command Line
The Forms2XML command takes one or more Forms Module files as an argument. The
files can be FormsModule (.fmb), ObjectLibrary (.olb), or MenuModule (.mmb) files.
The output is placed in the current folder. The command has the following syntax:
frmf2xml [options] file1 [file2...]
java oracle.forms.util.xmltools.Forms2XML [options] file1 [file2...]
Available options are described in the following table.
Note: The Forms2XML utility must generate an XML file in English
only. If the generated XML tags are not in English, then the file will
fail to load. The conversion of synonym-based data blocks is not
supported. Only data blocks based on tables or views is supported by
the conversion process. Please ensure that the application you wish to
convert is based only on tables and views.
File name before conversion File name after conversion
myForm.fmb myForm_fmb.xml
myMenu.mmb myMenu_mmb.xml
myLibrary.olb myLibrary_olb.xml
Options Description
USE_PROPERTY_IDS=YES/NO Setting USE_PROPERTY_IDS to YES causes the
Forms to XML conversion tool to write the
internal ID for Real or Character into the XML
file.
The default value (NO) generates property
value names as before.
Note: The Forms2XML utility must be run
with USE_PROPERTY_IDS=NO.

Convert Oracle Forms to XML
4-4 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Using the Forms2XML Conversion Tool in a Java Program
You can pass the Forms2XML tool a JdapiModule Java object (class
oracle.forms.jdapi.JdapiModule) and dump its objects and properties to an
XMLDocument (class oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLDocument). For example:
...
// get the modules in the session
JdapiIterator mods = Jdapi.getModules();
// ... and iterate round them
while(mods.hasNext())
{
JdapiModule mod = (JdapiModule)mods.next();
Forms2XML converter = new Forms2XML(
XMLDocument doc = converter.dumpModule(false);
...
}
The Boolean argument taken by the dumpModule() method instructs the converter to
dump all properties to the XMLDocument doc, not just those which are overridden.
Once you have the module as a XMLDocument object, you could then use the XDK
classes to manipulate it programmatically. For example, you could traverse it, remove
or add objects, change properties, copy objects into other modules that are also saved
as XMLDocument objects, and so on.
To learn more about Oracle Forms, see:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/forms/overview/index.
html
Converting a PL/SQL Library
To convert a PL/SQL library, use the File > Convert option in Oracle Forms
Builder to convert PL/SQL library .PLL files to .PLD text files.
To learn more about Oracle Forms, see:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/forms/overview/index.
html
OVERWRITE=YES/NO Valid values are YES or NO.
If OVERWRITE=YES, the tool overwrites any
XML files with the same name that exist in the
output directory.
If OVERWRITE=NO, (default) the tool does not
overwrite any XML files with the same name
that exist in the output directory. The tool will
stop processing and return the message:
If the file file exists, use argument
OVERWRITE=YES to replace.
DUMP=ALL/OVERRIDEN If DUMP=ALL, the tool dumps all properties.
If DUMP=OVERRIDEN, the tool dumps only
those properties that are overridden.
Options Description

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-5
Converting an Oracle Report to XML
To convert an Oracle Report, use the File Conversion option in Reports Builder to
convert binary (.RDF), ASCII (.REX), and .JSP reports to XML format.
To learn more about Oracle Reports, see:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/reports/overview/index.htm
l
Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
A workspace is a virtual private database allowing multiple users to work within the
same Oracle Application Express installation while keeping their objects, data and
applications private. Each workspace has a unique ID and name.
An Oracle Application Express administrator can create a workspace manually within
Oracle Application Express Administration Services or have users submit requests.
Oracle Application Express Administration Services is a separate application for
managing an entire Oracle Application Express instance. See "Creating Workspaces"
and "Managing Workspace Requests" in Oracle Application Express Administration
Guide.
Topics:
■ Creating a Workspace Manually
■ Creating Oracle Application Express Users
■ Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace
Creating a Workspace Manually
To create an Oracle Application Express workspace manually:
1. Log in to Oracle Application Express Administration Services.
Oracle Application Express Administration Services is a separate application for
managing an entire Oracle Application Express instance. You log in using the
ADMIN account and password created or reset during the installation process.
a. In a web browser, navigate to the Oracle Application Express Administration
Services application. By default, Oracle Application Express Administration
Services installs to the following location:
– If your setup uses the Oracle Application Express Listener, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex/apex_admin
Where:
See Also: Oracle Database 2 Day + Application Express Developer's
Guide if you are new to Oracle Application Express.
Extensive Oracle documentation is available for broadening your
knowledge of database concepts and objects. To learn more, see Oracle
Database Concepts. To view a specific documentation library go to:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/documentation/index
.html

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
4-6 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle Application Express
Listener is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle Application Express Listener.
In a default installation, this number is 8080. These defaults are correct at
the time of the writing of this document. To learn more, see Oracle Applica-
tion Listener Installation and Developer Guide.
apex is the service name defined when configuring the Oracle Applica-
tion Express Listener.
– If your setup uses the embedded PL/SQL gateway, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex/apex_admin
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle XML DB Protocol
Server is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle XML DB Protocol Server. In a
default installation, this number is 8080.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the configuration
file.
– If your setup uses Apache and mod_plsql, go to:
http://hostname:port/pls/apex/apex_admin
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle HTTP Server is
installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle HTTP Server. In a default
installation, this number is 7777.
pls is the indicator to use the mod_plsql cartridge.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the mod_plsql
configuration file.
b. On the Login page:
– In Username, enter admin.
– In Password, enter the Oracle Application Express administrator account
password you specified when you installed Oracle Application Express.
– Click Login.
Next, create a workspace.
2. Click Manage Workspaces.
3. Under Workspace Actions, click Create Workspace.
The Create Workspace Wizard appears.
4. For Identify Workspace, enter the following:
a. Workspace Name - Enter a unique workspace name.
See Also: See "Logging in to Oracle Application Express
Administration Services" in Oracle Application Express Administration
Guide

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-7
b.
Workspace ID - Leave Workspace ID blank to have the new Workspace ID
automatically generated. A Workspace ID must be a positive integer greater
than 100000.
c. Workspace Description - Enter a workspace description.
d. Click Next.
5. For Identify Schema, specify whether you are re-using an existing schema or
creating a new one.
If you are using an existing schema:
a. For Re-use existing schema, select Yes.
b. Select a schema from the list.
c. Click Next.
If you are creating a new schema:
a. For Re-use existing schema, select No.
b. Enter a schema name and password.
c. Specify a space quota.
d. Click Next.
6. For Identify Administrator, enter the Workspace administrator information and
click Next.
7. Confirm your selections and click Create Workspace.
Creating Oracle Application Express Users
To create an Oracle Application Express user account:
1. Log in to Oracle Application Express Administration Services. See "Logging in to
Oracle Application Express Administration Services" in Oracle Application Express
Administration Guide.
2. Click Manage Workspaces.
3. Under Manage Workspaces, click Manage Developers and Users.
The Manage Developers and Users page appears.
4. Click Create User.
The Create/Edit User page appears.
5. Under User Attributes, enter:
a. Username - Enter the username used to log in to the system. Restrictions
include:
– Maximum length of 100 characters
– No spaces
– Only these special characters are permitted: ampersand (@) and period (.)
b. Email Address - Enter the valid email address for this user.
c. First Name - Enter the first or given name to further identify the user
(optional).

Create a Workspace and Add Oracle Application Express Users
4-8 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
d.
Last Name - Enter the last or family name to further identify the user
(optional).
e. Description - Enter comments about this user (optional).
6. Under Account Privileges:
a. Workspace - Select a workspace in which to create the user.
b. Default Schema - Specify the default schema used for data browsing,
application creation, and SQL script execution.
c. User is an administrator - Specify if this user should have workspace
administrator privileges.
Administrators are given access to all components. Additionally, they can
manage user accounts, groups, and development services. Components may
not be available if they are switched off by Instance Administrators.
d. User is a developer - Specify if this user should have developer privileges.
Developers must have access to either Application Builder, SQL Workshop, or
both. Components may not be available if they are switched off by Instance
Administrators.
e. Application Builder Access - Determines whether a developer has access to
the Application Builder.
f. SQL Workshop Access - Determines whether a developer has access to the
SQL Workshop.
g. Team Development Access - Determines whether a developer has access to
the Team Development.
h. Account Availability - Select Locked to prevent the account from being used.
Select Unlocked to allow the account to be used.
7. Under Password:
■ Password - Enter a case-sensitive password.
■ Confirm Password - Enter the password again.
■ Require Change of Password On First Use - Select No to require this user to
change his or her password at first log in. Select Yes to require the user to
change the password immediately after logging in the first time.
8. Click Create.
Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace
Once you create a workspace, you must log in to it using your login credentials (that
is, the workspace name, user name, and password).
To log in to a workspace:
1. In a web browser, navigate to the Oracle Application Express Login page. By
default, Oracle Application Express installs to the following location:
■ If your setup uses the Oracle Application Express Listener, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex
See Also: See "Creating Workspaces" and "Managing Workspace
Requests" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide

Upload Database Objects into the Schema Associated with Your Workspace
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-9
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle Application Express
Listener is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle Application Express Listener. In a
default installation, this number is 8080. These defaults are correct at the time
of the writing of this document. To learn more, see Oracle Application Listener
Installation and Developer Guide
apex is the service name defined when configuring the Oracle Application
Express Listener.
■ If your setup uses the embedded PL/SQL gateway, go to:
http://hostname:port/apex
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle XML DB Protocol Server is
installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle XML DB Protocol Server. In a
default installation, this number is 8080.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the configuration file.
■ If your setup uses Oracle HTTP Server (Apache) and mod_plsql, go to:
http://hostname:port/pls/apex
Where:
hostname is the name of the system where Oracle HTTP Server is installed.
port is the port number assigned to Oracle HTTP Server. In a default
installation, this number is 7777.
pls is the indicator to use the mod_plsql cartridge.
apex is the database access descriptor (DAD) defined in the mod_plsql
configuration file.
The Login page appears.
2. Under Login, enter the following:
■ In the Workspace field, enter the name of your workspace.
■ In the Username field, enter your user name.
■ In the Password field, enter your case-sensitive password.
3. Click Login.
Depending on your setup, you might be required to change your password when
you log in for the first time.
Upload Database Objects into the Schema Associated with Your
Workspace
In order to start the conversion process, the database objects associated with your
Oracle Forms application must reside in the same database as Oracle Application
Express.

Create a Conversion Project
4-10 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
If the database objects associated with your Oracle Forms application do not reside in
the same database as Oracle Application Express, you must upload them.
To upload database objects associated with your workspace:
1. Create a DDL script.
2. Upload it to the SQL Script Repository and run it. See "Executing a SQL Script" in
Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop Guide.
Create a Conversion Project
Next, create a conversion project by running Create Migration Project Wizard and
loading the application metadata extracted in "Convert Oracle Forms to XML" on
page 4-2.
To create a conversion project:
1. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
2. Click the Application Builder icon.
3. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
4. On the Application Migrations page, click Create Project.
The Create Migration Project wizard appears. The steps included in the wizard
appear in a flowchart on the left of the page.
5. Enter the project details:
a. Project Name - Enter a unique name. The project name must be unique to your
current workspace and should not contain any white spaces.
b. Type - Select Forms.
c. Description - Enter a meaningful description for this project.
d. Schema - Select the schema that contains the database schema objects
associated with the Oracle Forms application you want to convert.
The default schema is the schema associated with your workspace. If multiple
schemas are associated with your workspace, all associated schemas appear in
the select list, arranged in alphabetical order. When this situation exists, select
the schema associated with the Oracle Forms you want to upload.
e. Forms Module XML File - Locate the XML file which contains the information
of your converted Oracle FormModule (for example, myForm_fmb.xml).
Note that you must upload the converted Oracle FormModule file first.
f. Click Next.
The Confirm page appears.
g. To add more files, click Upload Another File.
6. To upload a file, specify the following:

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-11
a.
File Type - Select the appropriate file type. Options include:
– Forms Module - Upload a FormModule in XML format (myForm_
fmb.xml). Use the Forms2XML conversion tool to convert Oracle
FormModule .FMB files to .XML format.
– Oracle Report - Upload an Oracle Report in XML format
(myReport.XML). Use the File Conversion option in Oracle Reports
Builder to convert binary(.RDF), ASCII (.REX), and .JSP Reports to XML
format.
– PL/SQL Library - Upload a PL/SQL Library associated with your Oracle
Forms application (myLibrary.PLD). The library must be in text format.
Use the File > Convert option in Oracle Forms Builder to convert
PL/SQL library .PLLs to .PLD text files.
– Forms Menu - Upload an Oracle Form Menu in XML format (myMenu_
mmb.XML). Use the Forms2XML conversion tool to convert MenuModule
.MMB files to .XML format.
– Object Library - Upload an Object Library in XML format (myObjects_
olb.XML). Use the Forms2XML conversion tool to convert Object Library
.OLB files to .XML format.
b. File - Locate the file you want to upload.
c. Click Upload.
The Confirm page appears.
7. To add more files, click Upload Another File and repeat the previous steps until
all files appear on the Confirm page.
8. Review the project details, and click Create.
The Project page appears.
Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Next, use the Project pages to review and edit form attributes and track the manual
conversion process.
Topics:
■ About the Application Migrations Page
■ Editing Project Details
■ Reviewing Forms Modules
■ Reviewing Oracle Reports
■ Reviewing PL/SQL Libraries
■ Reviewing Forms Menus
■ Reviewing Object Libraries
■ Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process
About the Application Migrations Page
The Project page shows a high-level overview of your Oracle Forms conversion
project.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
4-12 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Topics:
■ Understanding the Project Page
■ Editing Project Details
■ Uploading Additional Files
Understanding the Project Page
To view project details, click the project name. The Project page appears.
With the exception of the File Name column, most of the information on the Project
page only applies to FormModule XML files (for example, Blocks, Triggers, and
Program Units columns). If a column does not apply to the uploaded file, a 0 displays.
The Project page lists the following information about uploaded files:
■ Type - Identifies the type uploaded by displaying the appropriate file extension
(for example, RPT for Report and FMB for FormModule files).
■ File Name - Displays the file name and extension (XML or TXT) uploaded into the
project.
■ Blocks - Displays a count of blocks in FormModule XML file. A single block can
be mapped to a region in Oracle Application Express. A region is an area on a
page that serves as a container for content. Each page can have any number of
regions. You control the appearance of a region through a specific region template.
■ DB Blocks - Displays the database data blocks in the uploaded FormModule XML
file. These blocks can be based on any of the following block data source types:
table; procedure; transactional trigger; or subquery. Blocks included in the DB
Blocks count are not control blocks. Note that the associated Database Block
property is set to Yes.
■ Tr ig g er s - Displays a count of all form-level, block-level and item-level triggers
associated with the uploaded FormModule XML file.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-13
■ Record Groups - Displays a count of Record Groups in the uploaded
FormModule XML file.
■ Lists of Values - Displays a count of lists of values (LOVs) in the uploaded
FormModule XML file.
■ Alerts - Displays a count of alerts in the uploaded FormModule XML file.
■ Program Units - Displays the number of schema objects that enable you to access
and manipulate database information.
You can review Forms attributes and track manual conversion by clicking the links on
this page.
Utilizing Interactive Reports Many pages in Application Migration Workshop display as
interactive reports. You can customize the appearance of these pages using the Search
bar at the top of each page.
Use the Search bar to create custom searches and customize and filter the information
that appears on the page.
Available controls on the Search bar include:
■ Select columns to search icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to
narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All
Columns.
■ Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wildcard characters are implied)
and then click Go.
■ Go button - Executes a search.
■ Actions menu - Use the Actions menu to customize an interactive report.
To learn more, see "Customizing Interactive Reports" in Oracle Application Express
Application Builder User's Guide.
About the Upload File, Create Application, and Run Application Buttons Three buttons display
to the above of the Search Bar:
■ Upload File - Add files to your conversion project. See "Uploading Additional
Files" on page 4-14.
■ Create Application - Create an Oracle Application Express application based on
the components included in your conversion project. See "Generate the Oracle
Application Express Application" on page 4-26.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
4-14 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
■ Run Application - Submit the pages within your Oracle Application Express
application to the Application Express engine and render viewable HTML. Note
this button only appears after you generate an application.
About Associated Application The Associated Application only displays after you create
an application. This region displays application name, number of application pages,
last update date, and the user who performed the updates. Click the application name
to link to the Application home page within Application Builder.
About the Tasks List The Tasks list displays on the right side of the page.
The Tasks list contains the following links:
■ Delete Project deletes the current project.
■ Edit Project Details and Applicability links to the Project Details page. See
"Editing Project Details" on page 4-15.
■ About Forms Conversion links to a page that explains how to convert Oracle
Forms applications.
■ Set Application Defaults links to the Set Application Defaults page. See "Setting
Up Application Defaults" on page 4-26.
About the Completion Status Region A Completion Status box displays on the right side of
the page.
The Completion Status region lists the following information:
■ Components - Lists the number of components that have been uploaded to the
project.
■ Completed - Displays a count of components within the conversion process that
have been reviewed and have been marked as Complete.
■ Percent Complete - Lists percent of components which have been marked as
Complete.
Uploading Additional Files
To add files to your conversion project:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-15
b.
Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. On the Project page, click Upload File.
3. For File Type, select one of the following:
– Forms Module - Upload a FormModule in XML format (myForm_fmb.xml).
Use the Forms2XML conversion tool to convert Oracle FormModule .FMB files
to .XML format.
– PL/SQL Library - Upload a PL/SQL Library associated with your Oracle
Forms application (myLibrary.PLD). The library must be in text format. Use
the File > Convert option in Oracle Forms Builder to convert PL/SQL
library .PLLs to .PLD text files.
–Oracle Report - Upload an Oracle Report in XML format (myReport.XML).
Use the File Conversion option in Oracle Reports Builder to convert
binary(.RDF), ASCII (.REX), and .JSP Reports to XML format.
– Object Library - Upload an Object Library in XML format (myObjects_
olb.XML). Use the Forms2XML conversion tool to convert Object Library
.OLB files to .XML format.
– Forms Menu - Upload an Oracle Form Menu in XML format (myMenu_
mmb.XML). Use the Forms2XML conversion tool to convert FormsMenu .MMB
file to .XML format.
4. File - Locate the file you want to upload.
5. Click Upload.
The Confirm page appears.
6. To add more files, click Upload and Upload Another and repeat the previous
steps until all files appear on the Confirm page.
7. Review the file details, and click Finish.
The Project page appears.
Editing Project Details
To edit project details.
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. On the Project page, click the Edit icon to access the Project Details page. The Edit
icon resembles a small yellow pencil.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
4-16 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
The Project Details page appears.
3. Under Project Details, edit the project name, database schema, specify an
associated application, or enter an optional description.
4. Under Component Applicability, specify whether to include specific components
in your conversation project. Select Yes or No adjacent to each component type.
5. Click Apply Changes.
See Also: "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process" on
page 4-25

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-17
Reviewing Forms Modules
From the Project page you can browse the objects included in your uploaded Oracle
FormModule XML file (for example, myForm_fmb.xml).
Topics:
■ Viewing an Imported FormModule
■ Viewing Object Metadata and Selecting Specific Objects
■ Viewing and Selecting Blocks
■ Viewing and Selecting Items
Viewing an Imported FormModule
To view an imported FormModule:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the Edit icon to the left of the XML file name (for example, myForm_
fmb.xml).
The Form Details page appears.
3. To delete an imported FormModule, click Delete.
4. To download the files associated with this project, click Download.
About Annotations Use Annotations to track the overall status of form components
within the conversion process. To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the
Conversion Process" on page 4-25.
Viewing Object Metadata and Selecting Specific Objects
To review object metadata:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the number under the column for the appropriate object type. Alternately,
click the File Name to view a report describing the component.
See Also: "Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds"
on page A-1

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
4-18 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Clicking a number displays a listing of the object type.
3. To include blocks, items, and LOVs select the Include check box adjacent to the
object name and click Apply Changes.
4. To view details about a specific object, click the object name or Edit icon.
Viewing and Selecting Blocks
To review blocks:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the link under the Blocks column.
A listing of blocks appears.
3. To edit a block name, enter a new name in the Title field and click Apply Changes.
4. To include a specific object in your conversion select the Include check box
adjacent to the object name and click Apply Changes.
5. To view details about a specific object, click the Name link.
The Block Details page appears. The sections that follow describe each section of
the Block Details page.
About Block Details Lists the details about the block.
About Annotations Tracks the overall status of the object within the conversion process.
To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process" on page 4-25.
About Application Express Page Query Oracle Forms can be based on database blocks
which correspond to database tables or views. The enhanced query builds a query
based on the database block and database item meta data, and extends it with block
level post-query trigger source to show derived columns
Enhanced Query is the original query with the POST-QUERY logic included. Original
Query is generated from the data source item (table) underlying the block and the
columns that are referenced on that block
To specify the type of query to use:
1. Select one of the following from the User Query list:
■ Custom Query
■ Enhanced Query
Tip: To displays columns not displayed by default, click the Actions
menu and select Select Columns. To learn more, see "Customizing
Interactive Reports" in Oracle Application Express Application Builder
User's Guide.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-19
■ Original Query
2. If you select Custom Query, enter the appropriate syntax in the Custom Query
field.
3. Click Apply Changes.
Relation Details Only displays if a relationship was identified for the block in the XML
file. This section displays the information on that relationship.
Block Items Displays the items in the block. Click the Edit icon associated with the
item to view item details.
Block Triggers Lists the block-level and item-level triggers associated with the block.
Click Edit icon to view additional trigger details.
About Audit Display or hide the Audit section at the bottom of the page to view details
about the object creation and last update dates.
Viewing and Selecting Items
To review items:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the link under the Items column.
A listing of items appears. Click the Actions icon on the Search bar to view
additional information which is not visible in the default report.
3. To edit an item label, enter a new name in the Item Prompt field and click Apply
Changes.
4. To include a specific object in your conversion select the Include check box
adjacent to the object name and click Apply Changes.
5. To view details about a specific item, click the Item Name link.
The Item Details page appears. The sections that follow describe each section of
the Item Details page.
About Item Details Lists the details about the item.
About Annotations Tracks the overall status of the object within the conversion process.
To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process" on page 4-25.
About Audit Display or hide the Audit section at the bottom of the page to view details
about the object creation and last update dates.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
4-20 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Reviewing Oracle Reports
From the Project page you can browse uploaded Oracle Report XML files (for example,
myReport.XML).
Topics:
■ Viewing Reports
■ Selecting Reports to Include
Viewing Reports
Use the Report Details page to view details about the imported report.
To view the Report Details page:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the Oracle Reports XML file name (for example, myReport.XML).
The Report Details page appears.
3. To delete the report, click Delete.
4. To download the report, click the Download link.
The sections that follow describe the Report Details page.
Report Details Lists details about the current report.
About Annotations Use Annotations to track the overall status of the object within the
conversion process. To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion
Process" on page 4-25.
About SQL Query Displays the SQL query associated with the Oracle Report. This SQL
statement is used to generate an Oracle Application Express interactive report.
About Data Items Lists each item in the report. Click the Edit icon adjacent to a specific
item to display the Data Item Details page.
About Summary Items Lists the summary columns associated with the report. These
columns perform a computation on another column's data (for example, sum, average,
count, minimum, maximum, and percent total).
To learn more about Oracle Reports, see the following hosted Help file:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/reports/overview/index.htm
l
About Audit Display or hide the Audit section at the bottom of the page to view details
about the creation and last update dates.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-21
Selecting Reports to Include
Use the Reports page to select reports for inclusion in the conversion process.
To view the Report page:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the Edit icon to the right of the Oracle Reports XML file name (for example,
myReport.XML).
The Reports page appears.
3. To include a report, select the check box and click Apply Changes.
Reviewing PL/SQL Libraries
From the Project page you can browse uploaded PL/SQL libraries associated with
your Oracle Forms application (for example, myLibrary.PLD) and update
annotations. Note that PL/SQL libraries are not generated within Oracle Application
Express. However, the files are imported to enable you to review and track them.
To view the PL/SQL Library Details page:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the PL/SQL library XML file name (for example, myLibrary.PLD).
The PL/SQL Library Details page appears.
3. To delete the library, click Delete.
4. To download the library, click the Download link.
About Annotations
Use Annotations to track the overall status of the object within the conversion process.
To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process" on page 4-25.
About Audit
Display or hide the Audit section at the bottom of the page to view details about the
object creation and last update dates.

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
4-22 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Reviewing Forms Menus
From the Project page you can browse the objects included in your uploaded
MenuModule XML file (for example, myMenu_mmb.XML) and update annotations. Note
that Forms Menus are not generated within Oracle Application Express. However, the
files are imported to enable you to review and track them.
Topics:
■ Viewing Form Menus
■ Viewing a Summary of Forms Menus
■ Viewing Form Menu and Program Unit Details
Viewing Form Menus
To track an imported MenuModule:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the Edit icon to the left of MenuModule XML file name (for example,
myMenu_mmb.XML).
The Edit Imported Form Menu page appears.
3. To delete the MenuModule, click Delete.
4. To download the MenuModule, click the Download link.
About Annotations Use Annotations to track the overall status of form within the
conversion process. To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion
Process" on page 4-25.
Viewing a Summary of Forms Menus
Use the Forms Menus page to view details about specific modules.
To view the Forms Menus page:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the MenuModule XML file name (for example, myMenu_mmb.XML).
The Forms Menus page appears and displays the following information:

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-23
–Edit icon - Depending on the Module Type, clicking this icon displays a
details page describing the selected menu or program unit.
– Name - Display the name of the menu module.
– Module Type - Lists the type of module (that is, either Menu or Program
Unit).
– File Size - Displays the XML file size in kilobytes (KB).
– Module Name - Displays the name of the module.
–Main Menu - Specifies the name of the individual menu in the Forms Menu
that functioned as the main or starting menu at runtime.
– Assignee - Displays the person responsible for an object as specified within
the Annotations for the object.
– Tags - Lists tags created to describe the object as specified within the
Annotations for the object.
– Notes Snippet - Displays a snippet of the Notes specified within the
Annotations for the object.
– File Name - Displays the MenuModule XML file name.
3. To view module details, click the Edit icon adjacent to the menu name.
A details page appears. See the next section, "Viewing Form Menu and Program
Unit Details" on page 4-23.
Viewing Form Menu and Program Unit Details
Clicking the Edit icon on the Forms Menus page displays a details page. The format of
the page that displays depends upon the Module Type (either Menu or Program Unit).
About Form Menu Details The top of the page lists details about the menu, including
■ Name
■ Parent Module
■ Parent Name
■ Parent Type
■ Tear Off Menu
■ Comment
Under Menu Items, click the Edit icon to view details or track the status of a specific
menu item.
About Annotations Use Annotations to track the overall status of an object within the
conversion process. To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion
Process" on page 4-25.
About Program Unit Details The top of the page displays the program unit name, type,
and the actual program unit text (if applicable).
See Also: To learn more about Oracle Forms, see:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/forms/o
verview/index.html

Review and Edit Forms Metadata
4-24 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
About Audit Display or hide the Audit section at the bottom of the page to view details
about the object creation and last update dates.
Reviewing Object Libraries
From the Project page you can browse uploaded Object Libraries associated with your
Oracle Forms application (for example, myObjects_olb.XML) and update the
annotations. Note that Object Libraries are not generated within Oracle Application
Express. However the files are imported to enable you to review and track them.
To view the Forms Object Library details:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the Edit icon to the left of the Object Library XML file name (for example,
myObjects_olb.XML).
The Object Library Details page appears.
About Annotations
Use Annotations to track the overall status of the object within the conversion process.
To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process" on page 4-25.
About Audit
Display or hide the Audit section at the bottom of the page to view details about the
creation and last update dates.
Viewing an Uploaded Object Library
To view the Forms Object Library page:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. On the Workspace home page, click the Applications Migrations link on the
right side of the page.
b. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. Click the Object Library XML file name (for example, myObjects_olb.XML).
The Forms Object Library page appears.
3. To view details about a specific attribute, click the Edit icon. A Details page
appears.
About Annotations Use Annotations to track the overall status of the object within the
conversion process. To learn more, see "Using Annotations to Track the Conversion
Process" on page 4-25.
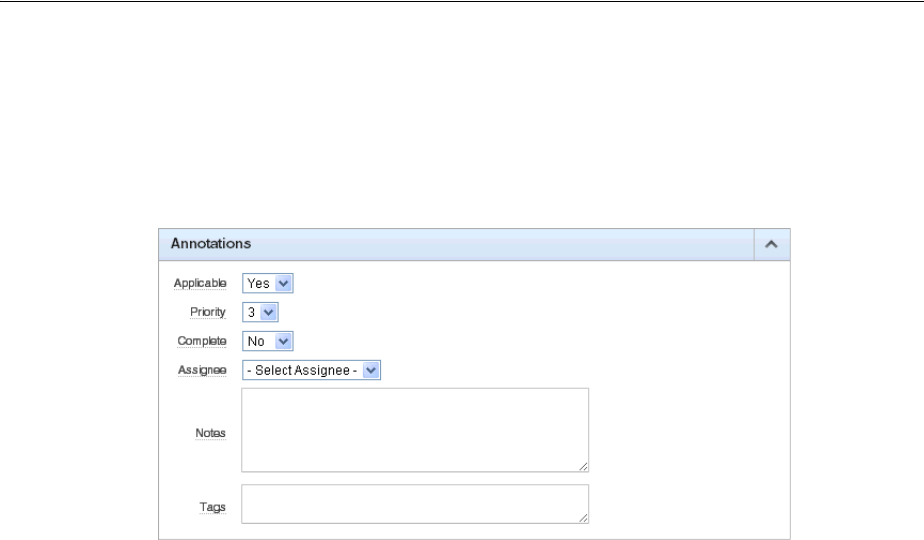
Review and Edit Forms Metadata
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-25
About Audit Display or hide the Audit section to view details about the creation and
last update dates.
Using Annotations to Track the Conversion Process
Use Annotations to track the overall status of an object within the conversion process.
Most detail pages that describe a specific object include an Annotations section.
Use these fields to determine whether an object should be included in the conversion,
assign a priority, track status, assign the object to specific individual, or create notes
and tags.
Options include:
■ Applicable - Tracks whether the object is applicable within the context of the
generated Oracle Application Express application. Select Yes or No.
The initial value is determined by the applicability default settings for that
component or trigger defined on the Project Details page.
■ Priority - Assign a numeric priority to the object.
■ Complete - Track if the conversion is complete. Select Yes or No.
■ Assignee - Assign the object to a specific user.
■ Notes - Enter notes regarding the object.
■ Tags - Assign tags to the object.
The values defined in Applicable and Complete are used in determining the
percentage complete. All the Applicable and Complete values can be changed for a
block at one time from the Bulk Changes page.
Why Use Annotations?
Because Oracle Forms have many separate components, it is important to evaluate
whether functionality in the original application is either not required or has been
replicated in the Oracle Application Express application. Given that the initial design
only incorporates a percentage of the required functionality, you can use these fields as
a reminder of what must be implemented post-generation.

Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
4-26 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
After you have reviewed and updated the Oracle Forms metadata within your
conversion project, you need to generate the application in Oracle Application
Express.
When creating an application, a home page is defined by default. You have the option
to create additional blank pages so that you can include blank pages or reports and
forms on other tables as part of your application.
You can then choose which user interface theme your application should be based on.
By default, the application uses one level of tabs.
As a shortcut, you can also set some application defaults. These defaults are used
whenever you create new applications.
Topics:
■ Setting Up Application Defaults
■ Creating an Application
Setting Up Application Defaults
To set up application defaults (optional):
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.
2. On the right side of the Project page, click Set Application Defaults in the Tasks
list.
3. Select the options you want to use as defaults.
For information, click Help or click the item label. Clicking the item label opens a
separate window describing the item and its options.
4. Click Apply Changes.
The Project page appears.
Creating an Application
To create an application:
1. Go to the Project page:
a. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
b. Click the Application Builder icon.
c. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
d. Click a project name.
The Project page appears.

Generate the Oracle Application Express Application
Converting an Oracle Forms Application 4-27
2.
On the Project page, click Create Application.
3. In Name, specify the following:
a. Name - Enter a name for this application. The default name is based on the
project name.
b. Create Application - Choose a creation method. Select Based on Migration
Project.
c. User Interface - Select a user interface. For applications primarily designed for
desktop use, select Desktop.
d. Click Next.
4. In the Selected Application Objects section, you can customize specific pages.
For example:
■ To rename a page, click the page name link and enter the new name on the
New Page Definition page that appears.
■ To select the type of navigation on the application’s home page, click the
Home Page link.
On the New Page Definition page that appears, select Vertical Unordered List
with Bullets, Vertical Images List, or Horizontal Images List.
■ To display an image on a parent page, click the page link.
On the New Page Definition page that appears, go to the Page Icon field and
select the image you want to appear on that page. You can either select an
image from the select list or click the Find icon (flashlight) to open a page of
options.
Repeat this step for each parent page. If you do not explicitly select an image
for a page, the default image appears for that page.
Note that for the image to appear in your application, you must have selected
either Vertical Images List or Horizontal Images List for the Home page
navigation.
5. To add additional pages to the application, scroll down to the Add page section.
Select a page type and click Add Page. To learn more about each page type, click
item Help.
The new page appears at the bottom of the list in the Selected Application Objects
section.
6. Click Next.
7. On User Interface, select a theme for the application.
A theme is a collection of templates that define the layout and style of an
application, including buttons and pages.
Options include:
a. Show - Select the type of themes to display.
b. Select a Theme - Select a theme from the list.
Tip: Selecting Based on existing application design model enables
you to reuse a model from a previously generated Oracle Application
Express application.

Deleting a Migration Project
4-28 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
c.
Click Next.
8. Confirm your selections and click Create.
9. Log in using your Oracle Application Express workspace credentials.
Your application now appears as a separate application in Oracle Application
Express.
10. To customize your application, scroll down to the Developer toolbar and click Edit
Application.
You might want to do the following customizations immediately after you
generate your application:
■ Rename the application. Each application has a unique ID, but the conversion
project name becomes the application name by default. To more easily identify
an application, you might want to change its name to something more
meaningful by editing the application attributes.
■ Change the authentication scheme. By default, the authentication scheme is
Application Express authentication. You can change this by editing the
application attributes.
Deleting a Migration Project
When you delete a migration project, you delete only the metadata associated with the
migration project. Deleting a migration project does not delete or impact applications
you have generated from the project or any objects, such as tables or views, in the
schemas associated with your workspaces.
To delete a migration project:
1. Log in the workspace you created for your conversion project as described in
"Logging In To Your Oracle Application Express Workspace" on page 4-8.
2. Click the Application Builder icon.
3. Click Migrations on the right side of the page.
4. On the Application Migrations page, click the project you want to delete.
5. On the Project page, click Delete Project from the Tasks list.
6. Click the Delete Project button and confirm the deletion.
See Also: For further details on why the model shows the given
pages based on your Forms, see "Block to Page Region Mappings" on
page A-4. For information on editing application attributes, adding
pages, deploying your application see the Oracle Application Express
Application Builder User's Guide.

A
Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds A-1
AOracle Forms Generation Capabilities and
Workarounds
This appendix lists how objects are generated during the conversion process, or
alternatively how the same functionality can be implemented post-generation if
necessary.
Topics:
■ Oracle Forms Modules
■ Oracle Reports
■ PL/SQL Libraries
■ Forms Menus
■ Object Libraries
Oracle Forms Modules
This section describes various Oracle Forms components, offers a brief overview of
how they are mapped to similar objects within an Oracle Application Express
application, or explains how they can be implemented manually post generation.
Topics:
■ Overview of Oracle Forms Components
■ About Generated Applications
■ Block to Page Region Mappings
■ List of Values Implementation
■ Implementing Business Logic
Overview of Oracle Forms Components
This section provides an overview of Oracle Forms components and the corresponding
Oracle Application Express generation capabilities or workarounds.
Alerts
Alert messages are not generated. However, you can store an alert message as a text
message in Shared Components in an Oracle Application Express application. You can
use text messages to build translatable text strings with substitution variables that can

Oracle Forms Modules
A-2 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
be called from PL/SQL packages, procedures, and functions. See "Working with
Shared Components" in Oracle Application Express Application Builder User's Guide.
Blocks
A single block can be mapped to a region in Oracle Application Express. Based upon
the block type and data source type (that is, table or view) identified in the Forms XML
file, some default mappings are defined. For example, a report block based on an
Oracle view, is mapped to an interactive report in Oracle Application Express. A form
block based upon a table is mapped to an interactive report and form in Oracle
Application Express. For more information see "Block to Page Region Mappings" on
page A-4.
Canvases
In Oracle Forms, the canvas is the object on which the graphical user interface (GUI) is
drawn, or the background of the form. In Oracle Application Express, the Application
Express engine constructs the appearance of each page in an application using
templates. Templates define how pages, page controls, and page components display.
Canvases are ignored when generating pages for an Oracle Application Express
application.
Coordinates
Depending on the coordinate system used in an Oracle Forms application, coordinates
can be expressed in real units such as inches, centimeters, and pixels. The coordinate
values cannot be automatically applied to the generated application. One unit in an
Oracle Application Express item width might not be equal to one physical pixel in an
Oracle Forms application. While Oracle Forms enables specific placement of
individual fields by specifying coordinates, Oracle Application Express uses standard
HTML tables and all items are positioned relative to other elements and columns
within the HTML table.
Editors
In Oracle Forms, editors provide standard editing features, including search and
replace and cut, copy, and paste for text items. For a selected text item, an editor is
mapped to an HTML editor in Oracle Application Express.
List of Values
A list of values (LOV) can be mapped to an equivalent list of values in Oracle
Application Express. When LOVs are selected for inclusion in the conversion to Oracle
Application Express their associated record group is included in the conversion. For
more information, see the "List of Values Implementation" on page A-6.
Program Units
In the post-generation phase of the Forms Conversion process, program units can be
incorporated into your Oracle Application Express application as a PL/SQL package,
page process, computation or validation. For more information, see "Implementing
Business Logic" on page A-6.
Property Classes
In Oracle Forms, a property class is a named object that contains a list of properties
and their settings. An object based on a property class can inherit the settings of any
property in that class. Similarly, in Oracle Application Express, a theme is a named

Oracle Forms Modules
Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds A-3
collection of templates used to define the user interface of an application. Oracle
Application Express has a repository of 20 themes, and you can also create your own
custom themes. Property classes are not used within the generation of Oracle
Application Express applications.
Record Groups
In Oracle Forms, LOV values are derived from a record group. When a record group is
defined, it is associated with a SQL query. When a LOV is generated in Oracle
Application Express, the associated record group is used to determine the SQL Query
for that LOV. For more information, see "List of Values Implementation" on page A-6.
Triggers
An Oracle Forms trigger is an event-handler written in PL/SQL to augment the
default processing behavior. The trigger logic can be incorporated into an Oracle
Application Express application as a computation, validation, or PL/SQL process in
the post-generation phase. Where feasible, POST-QUERY block trigger logic is
automatically incorporated in the generated Oracle Application Express application, as
part of the Enhanced Query generation. For more information refer to "Implementing
Business Logic" on page A-6.
Visual Attributes
Visual attributes are the font, color, and pattern properties that you can set for form
and menu objects that appear in an Oracle Forms application's interface. Using the
default cascading style sheets (CSS) installed with Oracle Application Express, or by
uploading your own CSS files, style can be applied to your Oracle Application Express
application. See "Using Custom Cascading Style Sheets" in Oracle Application Express
Application Builder User's Guide.
Windows
A window is the container for all visual objects that comprise an Oracle Forms
application, including canvases. In Oracle Application Express, a page holds all of the
visual objects for an application. Due to the block mapping resulting in multiple pages,
the windows are not used in the conversion process.
About Generated Applications
Oracle Application Express applications generated from a project conform to standard
out-of-the-box application capabilities. These generated applications do not contain
nonstandard functionality such as JavaScript or Advanced JavaScript and XML
(AJAX). However, you can readily extend the Oracle Application Express framework
to include functionality such as JavaScript and AJAX to enhance the user interaction.
However, such enhancements must be implemented manually post-generation.
Generated forms for inserting, updating, or deleting records include automatic row
fetch processes to load existing records and automatic row processes to commit
changes to the Oracle Database table. Forms also include generated validations for
mandatory columns, and column types of number or date.
Primary Key Assumptions
The generation process assumes that the primary key for an Oracle table is
non-updatable, maintained using a database trigger, and has a maximum of two parts.
If the primary key is updatable, then the generated application must be modified
post-generation. You must modify the item attributes for the primary key. By default,

Oracle Forms Modules
A-4 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
these attributes are generated but displayed as hidden and protected. If there is no
database trigger defined to automatically fetch the primary key when inserting a
record, then the application fails when attempting to insert a record. To avoid this
error either define a database trigger, or modify the generated application
post-generation to populate the primary key value before processing the record. To
populate the primary key value within the application you can use the item default,
create a computation, or create a process. If creating a computation or process, it is
important to include a condition so that execution only occurs when inserting a record
(for example, when the primary key item is NULL).
Oracle Application Express does not support cascading multiple part keys where the
key for a child is defined as the primary key of the parent with a counter for each child
within that parent key. In such cases, you must define a distinct primary key for the
child table with an appropriate means of populating the primary key.
Block to Page Region Mappings
When an Oracle Form is loaded into an Oracle Application Express project, the various
blocks are analyzed to determine how they will be generated. The conversion process
uses information such as block relations, the number of records displayed, and
whether insert or update are allowed. There are inherent differences between Oracle
Forms and Oracle Application Express that have a direct bearing on the resulting
pages that are generated.
Except for specific master detail relationships, each block is generated onto a separate
Oracle Application Express page. Furthermore, the canvases specified in Oracle Forms
are ignored as multiple blocks are not generated as separate regions on the same page
within Oracle Application Express. The sections that follow explain different Oracle
Forms block types and how they are mapped into an Oracle Application Express
application.
Single Record Block
In Oracle Forms a single record block can be used for both querying data and updating
the records returned. Within Oracle Application Express, standard updatable regions
cannot also be used as query regions. When an Oracle Forms block is defined as being
insertable, updatable, and has a primary key, then the generation mapping defines an
interactive report with a form. The interactive report enables you to query the records
and the generated Edit link provides navigation to an individual record for update or
deletion. A Create Record button enables you to insert records.
If not all the conditions are satisfied, then only an interactive report is generated for a
single record block. Therefore, only an interactive report is generated and not the
corresponding form if one of the following conditions exist:
■ The number of records displayed is greater than one
■ INSERT allowed is set to false
■ UPDATE allowed is set to false
■ There is no primary key defined for the underlying table
■ The block is based on a view
The interactive report uses the original query, enhanced query, or custom query
defined within the project for the block. However, the form is based only on the
underlying table. Items characteristics such as radio groups, check boxes, date pickers,
editors and list of values will be generated where possible.

Oracle Forms Modules
Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds A-5
Tabular Form
A tabular form defined in Oracle Forms is generated as a tabular form in Oracle
Application Expresss providing the number of records displayed is greater than one.
You must implement item characteristics, such as select lists, manually
post-generation. Non-database items specified in Oracle Forms are not generated into
the tabular form generated by Oracle Application Express, even if they have been
included. You must manually implement non-database items in a tabular
post-generation.
Currently adding non-database items on a tabular form is non-declarative and is
covered in the Oracle Application Express Advanced Workshop course. An alternative
is to manually create a report and form to replace the tabular form post-generation
where it is much easier to add validations and add items without a source of database.
Master Detail Blocks
Within Oracle Forms, master detail forms are defined using block relations. There are
several additional criteria that must be examined in order to determine what will be
generated for an Oracle Forms master detail relationship. The master block is
generated as one of the following:
■ An interactive report and a master detail form
■ An interactive report and a form only
■ Only an interactive report
The detail blocks are generated independently as either a single record block or a
tabular form based on the mappings provided.
An interactive report and master detail form is only generated if all the following
criteria are satisfied:
■ The master and detail blocks are both based on tables, but not the same table, and
both have primary keys.
■ There is only one detail block.
■ There is a valid foreign key relationship between the master and detail blocks.
■ The block relations are correctly defined with the Oracle Forms file.
When a master detail form is generated, the detail page is also created within Oracle
Application Express. You can manually remove the detail page when reviewing the
pages to be generated prior to creating the Oracle Application Express application, or
you can delete it manually post-generation.
Alternatively, if both the master and the single detail block are based on the same table
and that table has a primary key, then two interactive reports and forms are generated
for each block. It is recommended that you manually modify one of the resulting forms
post-generation to combine the functionality into a single form and delete the second
interactive report and form. However, if the table does not have a primary key or is
based on a view then only reports are generated.
Oracle Application Express cannot include more than one tabular form on a page.
Therefore, when a file with a master and multiple detail blocks is loaded, the relations
are ignored and the master block and each detail block are treated independently as
either a single record block or a tabular form based on each blocks properties.
If there is no valid foreign key relationship and the table has a primary key, then the
master block is generated as an interactive report and form. Otherwise, it is generated
as an interactive report.

Oracle Forms Modules
A-6 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Non-Database Block
If a block is not associated with a database table or view, then the block is not included
for generation. These blocks typically hold menus, navigation bars, and buttons.
Because these components are handled and defined very differently within Oracle
Application Express, it is not appropriate to generate separate pages. However, such
blocks can be included if required and will be generated as blank pages.
List of Values Implementation
Oracle Application Express dynamic list of values (LOVs) enable one display value
and one return value to be defined within a SQL query. You can specify LOVs
individually for an item or define as a named shared component which can be used
with any item throughout the application.
Oracle Forms record groups define the query for each list of values. These record
groups are analyzed to determine whether the corresponding LOV can be generated.
A named shared component LOV is created utilizing the query from the record group
and then specified on the corresponding Oracle Application Express item. The
implementation style used in Oracle Forms determines whether the item is
implemented as a select list or pop-up list of values.
Where there are multiple display columns in the record group only one is used in the
resulting Oracle Application Express LOV query. If the record group uses bind
variables as parameters, Oracle Application Express application items are defined and
referenced within the resulting LOV query.
Implementing Business Logic
Within Oracle Forms applications, business logic is often interspersed with Oracle
Forms user interface functionality. The Oracle Forms user interface functionality used
to manipulate the screen (for example, go_block, go_item, set_item_property
and so on) are often not appropriate within Oracle Application Express due to the
inherent differences in the user interface.
Business logic can be found in Oracle Forms triggers and program units, or in PL/SQL
libraries. The business logic can be written directly into the objects as SQL or PL/SQL.
This code may in turn call database packages, procedures, or functions. The
underlying tables may also have database triggers defined which implement business
logic.
Because database triggers operate on the underlying tables regardless of the user
interface, they do not need to be altered when converting an application to Oracle
Application Express. You can call database packages, procedures, or functions from
Oracle Application Express because it also uses SQL and PL/SQL. These database
objects do not need to be altered when used within the Oracle Application Express
development environment.
In order to re-implement the business logic defined within Oracle Forms you must
analyze the triggers, program units, and PL/SQL libraries and manually write
corresponding logic within Oracle Application Express. Note that Oracle Forms
triggers, program units, and PL/SQL library code are not automatically generated
except for POST-QUERY triggers. POST-QUERY triggers can be incorporated into
Enhanced Queries as part of the block definition and subsequently included in the
Oracle Application Express application.
Oracle Application Express uses processes, computations, and validations to
implement such business logic. Before undertaking the post-generation task of
re-implementing business logic, it is important to understand how and when to invoke

Oracle Forms Modules
Oracle Forms Generation Capabilities and Workarounds A-7
the various types of processes, computations, and validations. It is also important to
understand how conditional processing can be applied to these types of components
to customize the circumstances under which they execute. For more information, see
Oracle Application Express Application Builder User's Guide.
Processes
Processes are logic controls used to execute data manipulation language (DML) or
PL/SQL. A process performs an action at a specified point during the rendering or
submission of the page. For example, you can create a process to execute logic or to
make a call to the Application Express engine. A process is a unit of logic that runs
when a specific event occurs, such as loading or submitting a page. For more
information, see "Understanding Page Processes" in Oracle Application Express
Application Builder User's Guide.
Processes can be defined as either an application-level process or a page-level process.
From a functional perspective, there is no difference between page-level and
application-level processes. You can call application-level processes form any page
within the application. Calling them On Demand is especially useful when you have
PL/SQL logic that you would like to run from different execution points across
multiple pages. Page-level processes can only be called from the page on which they
are defined.
Computations
Computations are units of logic used to assign a value to an identified item when a
page is submitted or displayed.
Computations can be defined as either an application-level computation or a
page-level computation. Most application-level computations are performed for every
page in an application. In contrast, computations created at the page-level only execute
when that page is rendered or processed. For more information, see "Understanding
Page Computations" and "Understanding Application Computations" in Oracle
Application Express Application Builder User's Guide.
Validations
Validations enable you to create logic controls to verify whether user input is valid. For
example, a validation can check whether a value has been entered into a mandatory
field. When a validation fails then an error message displays and subsequent page
processes and computations do not occur. For more information, see "Understanding
Validations" in Oracle Application Express Application Builder User's Guide.
There are two distinct types of validations:
■ Item-level validations which are specific to a single item.
■ Page-level validations which do not apply to any single item, but apply to an
entire page.
There are several validation methods:
■ SQL - Compares item values to data in the database.
■ PL/SQL - Enables you to enter complex logic to validate entered data.
■ Item Level Null - Checks if an item's value in session state is NULL.
■ Item String Comparison - Compares the value of an item to a specific string.
■ Regular Expression - Provides a method to describe text patterns.

Oracle Reports
A-8 Oracle Application Express Application Migration Guide
Oracle Reports
The underlying SQL query used to define an Oracle Report is used within Oracle
Application Express when generating an interactive report. When one or more Oracle
Report files are loaded, an additional Reports page is generated with links to each of
the generated interactive report pages. You must manually implement additional logic
defined within the Oracle Report post-generation. Oracle Application Express
supports the creation of printable reports utilizing Oracle Business Intelligence (BI)
Publisher, Apache FOP, or another standard XSL-FO report processing engine. To learn
more, see:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/apex/application-expr
ess/configure-printing-093060.html
PL/SQL Libraries
PL/SQL libraries contain logic which can be called from any of the Forms Modules to
which it is linked. Such libraries are primarily used to define commonly used business
logic that must be manually re-implemented post-generation. See "Implementing
Business Logic" on page A-6. Generally such logic should be implemented as
application-level processes so that they can be called from any generated page.
Forms Menus
Oracle Forms menus are not automatically generated within Oracle Application
Express. Oracle Application Express uses lists displayed in a region to replicate a
menu structure. The default generation process creates a Home page with a list of
horizontal images as the basis for a menu within your Oracle Application Express
application. This list can be manually updated post-generation to incorporate
conditional logic to implement the business logic defined within the Forms Menu. For
information, see "Creating Lists" in Oracle Application Express Application Builder User's
Guide.
Object Libraries
Object Libraries contain common visual elements used to define Oracle Form layouts
for specified components. These visual elements are not used within the Oracle
Application Express generation process. You must manually create these visual
attributes contained within these libraries post-generation. Depending on the visual
attribute there are different ways of implementing such features including customizing
templates, shared list of values, item types, item attributes and so on.

Index-1
Index
A
Access migration project, 3-1
annotations, using, 4-25
application
creating, 4-26
setting up defaults, 4-26
application conversion forum, 1-4
Application Express Administration Services, 3-5,
4-5
application migration
forum, 1-3
overview, 2-1
Application Migrations page, 4-11
about, 3-10
B
business logic, implementing, A-6
C
converting, Oracle Forms, 1-3
D
deleting
Microsoft Access migration project, 3-24
Oracle Forms project, 4-28
F
FormModules
converting to XML, 4-2
viewing, 4-17
Forms Menu
reviewing, 4-22
viewing details, 4-23
viewing summary, 4-22
Forms Menus, about conversion, A-8
Forms2XML conversion tool
about, 4-3
using from command line, 4-3
using in Java program, 4-4
forum
application conversion, 1-4
application migration, 1-3
G
generated applications
about, A-3
about primary keys, A-3
L
list of values, implementing, A-6
M
MDB file, analyzing, 1-2
MenuModules
converting to XML, 4-2
viewing, 4-22
Microsoft Access application
about migrating, 1-1
analyzing MDB file, 1-2
checklist, 1-1
preparing for migration, 1-1
Microsoft Access migration
about, 3-1
about Application Migrations page, 3-10
adding Oracle Application Express users, 3-4
creating a migration project, 3-9
creating a workspace, 3-4
exporting metadata, 3-2
generate applications, 3-22
migrating Microsoft Access database, 3-3
overview, 3-1
reviewing database, 3-22
reviewing forms, 3-18
reviewing module, 3-22
reviewing page information, 3-22
reviewing queries, 3-16
reviewing reports, 3-20
reviewing retrieved objects, 3-12
reviewing tables, 3-12
Microsoft Access migration project
creating, 3-9
deleting, 3-24
Microsoft Access, migrating to Oracle Application
Express, 3-1

Index-2
O
object libraries
about conversion, A-8
converting to XML, 4-2
reviewing, 4-24
viewing, 4-24
Oracle Application Express
about processes, A-7
about validations, A-7
computations, A-7
creating users, 3-7, 4-7
creating workspace manually, 3-5, 4-5
logging in to a workspace, 3-8, 4-8
programming concepts, 2-1
Oracle Forms
about converting, 1-3
creating conversion checklist, 1-3
migrating to Oracle Application Express, 4-1
Oracle Forms components
mappings, A-1
overview, A-1
Oracle Forms conversion
about, 4-1
about Associated Application box, 4-14
about Completion Status box, 4-14
about Tasks box, 4-14
adding Oracle Application Express users, 4-5
Application Migrations page, 4-11
converting Oracle Report, 4-5
converting PL/SQL library, 4-4
converting to XML, 4-2
Create Application button, 4-13
creating a conversion project, 4-10
creating a workspace, 4-5
creating an application, 4-26
deleting, 4-28
editing component applicability, 4-15
editing Forms metadata, 4-11
editing project details, 4-15
Forms2XML, 4-3
generating an Oracle Application Express
application, 4-26
reviewing blocks, 4-18
reviewing Forms menu, 4-22
reviewing Forms objects, 4-17
reviewing items, 4-19
reviewing object libraries, 4-24
reviewing Oracle Report, 4-20
reviewing PL/SQL libraries, 4-21
Run Application button, 4-13
selecting items, 4-19
selecting specific objects, 4-17
setting up application defaults, 4-26
step overview, 4-1
tracking MenuModules, 4-22
Upload File button, 4-13
uploading additional files, 4-14
uploading objects into schema, 4-9
using annotations, 4-25
viewing an imported report, 4-20
viewing an uploaded object library, 4-24
viewing blocks, 4-18
viewing Form Menu details, 4-23
viewing FormModules, 4-17
viewing Forms Menus, 4-22
viewing items, 4-19
viewing object metadata, 4-17
viewing Program Unit details, 4-23
Oracle Forms mappings
alerts, A-1
block to page region, A-4
blocks, A-2
canvases, A-2
coordinates, A-2
editors, A-2
list of values, A-2
master detail blocks, A-5
non-database blocks, A-6
program units, A-2
property classes, A-2
record groups, A-3
single record block, A-4
tabular forms, A-5
triggers, A-3
visual attributes, A-3
windows, A-3
Oracle Report
about conversion, A-8
converting to XML, 4-5
reviewing, 4-20
selecting, 4-21
P
PL/SQL libraries
about conversion, A-8
converting to TXT file, 4-4
reviewing, 4-21
U
user accounts
creating, 3-7, 4-7
W
workspace
creating, 4-5
logging in to, 3-8, 4-8
