
Data as reported by 12 February 2020*
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Situation Report – 23
SITUATION IN NUMBERS
total and new cases in last 24
hours
Globally
45 171 confirmed (2068 new)
China
44 730 confirmed (2022 new)
8204 severe (871 new)
1114 deaths (97 new)
Outside of China
441 confirmed (46 new)
24 countries
1 death
WHO RISK ASSESSMENT
China
Very High
Regional Level
High
Global Level
High
*The situation report includes information provided by national authorities as of 10 AM Central European Time
HIGHLIGHTS
• No new countries reported cases of COVID-19 in the past 24 hours.
• WHO has published key considerations for repatriation and quarantine of
travellers in relation to COVID-19. More information can be found here.
• The UN activated a Crisis Management Team (CMT) on the COVID-19
outbreak, to be led by WHO. The WHO Director-General nominated Dr Mike
Ryan, Executive Director of WHO Health Emergencies Programme as the Crisis
Manager. The CMT brings together WHO, OCHA, IMO (International Maritime
Organization), UNICEF, ICAO, WFP, FAO, the World Bank and several
departments of the UN Secretariat. It held its first meeting yesterday via
teleconference. This mechanism will help WHO focus on the health response
while the other agencies will bring their expertise to bear on the wider social,
economic and developmental implications of the outbreak. Additional
members will be included depending on the evolution of the outbreak and its
impact globally.
• WHO has prepared a list of Q&A on infection prevention and control for
health care workers caring for patients with suspected or confirmed 2019-
nCoV
Figure 1. Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed cases of COVID-19, 12 February 2020

TECHNICAL FOCUS: Internationally exported COVID-19 cases
Excluding China, there are 24 countries reporting cases of COVID-19. Among these 24 countries, 23 report cases with
an exposure in China. In addition, 11 of these 23 countries report cases attributed to local transmission inside the
reporting country. Four of the 24 countries report cases where likely exposure occurred outside the reporting
country and outside of China. Among these four reporting countries the most likely countries where exposure
occurred were France, Germany, Japan and Singapore (see map below). All transmissions occurred within known
defined clusters.
SURVEILLANCE
Table 1. Confirmed cases of COVID-19 acute respiratory disease reported by provinces, regions and cities in China,
12 February 2020
Province/Region/City
1
Population (in 10,000s)
Confirmed Cases
Suspect
Cases
2
Total Deaths
Hubei
5917
33366
11295
1068
Guangdong
11346
1219
135
1
Zhejiang
5737
1131
263
0
Henan
9605
1135
538
8
Hunan
6899
946
135
2
Anhui
6324
889
79
4
Jiangxi
4648
844
155
1
Jiangsu
8051
543
62
0
Chongqing
3102
505
428
3
Shandong
10047
497
71
1
Sichuan
8341
436
432
1
Heilongjiang
3773
378
171
8
Beijing
2154
352
218
3
Shanghai
2424
306
177
1
Fujian
3941
272
74
0
Hebei
7556
251
43
2
Shaanxi
3864
225
367
0
Guangxi
4926
222
248
1
Yunnan
4830
154
89
0
Hainan
934
145
206
3
Shanxi
3718
124
65
0
Guizhou
3600
131
53
1
Liaoning
4359
111
287
0
Tianjin
1560
106
328
2
Gansu
2637
86
18
2
Jilin
2704
83
57
1
Inner Mongolia
2534
60
11
0
Xinjiang
2487
59
31
0
Ningxia
688
58
31
0
Hong Kong SAR
745
49
0
1
Qinghai
603
18
0
0
Taipei and environs
2359
18
0
0
Macao SAR
66
10
0
0
Xizang
344
1
0
0
Total
142823
44730
16067
1114
1
China Statistical Yearbook - 2019
National Bureau of Statistics of China, 1 October 2019
2
Number of individuals under investigation for COVID-19 as of 12 Feb 2020. This category is not cumulative.
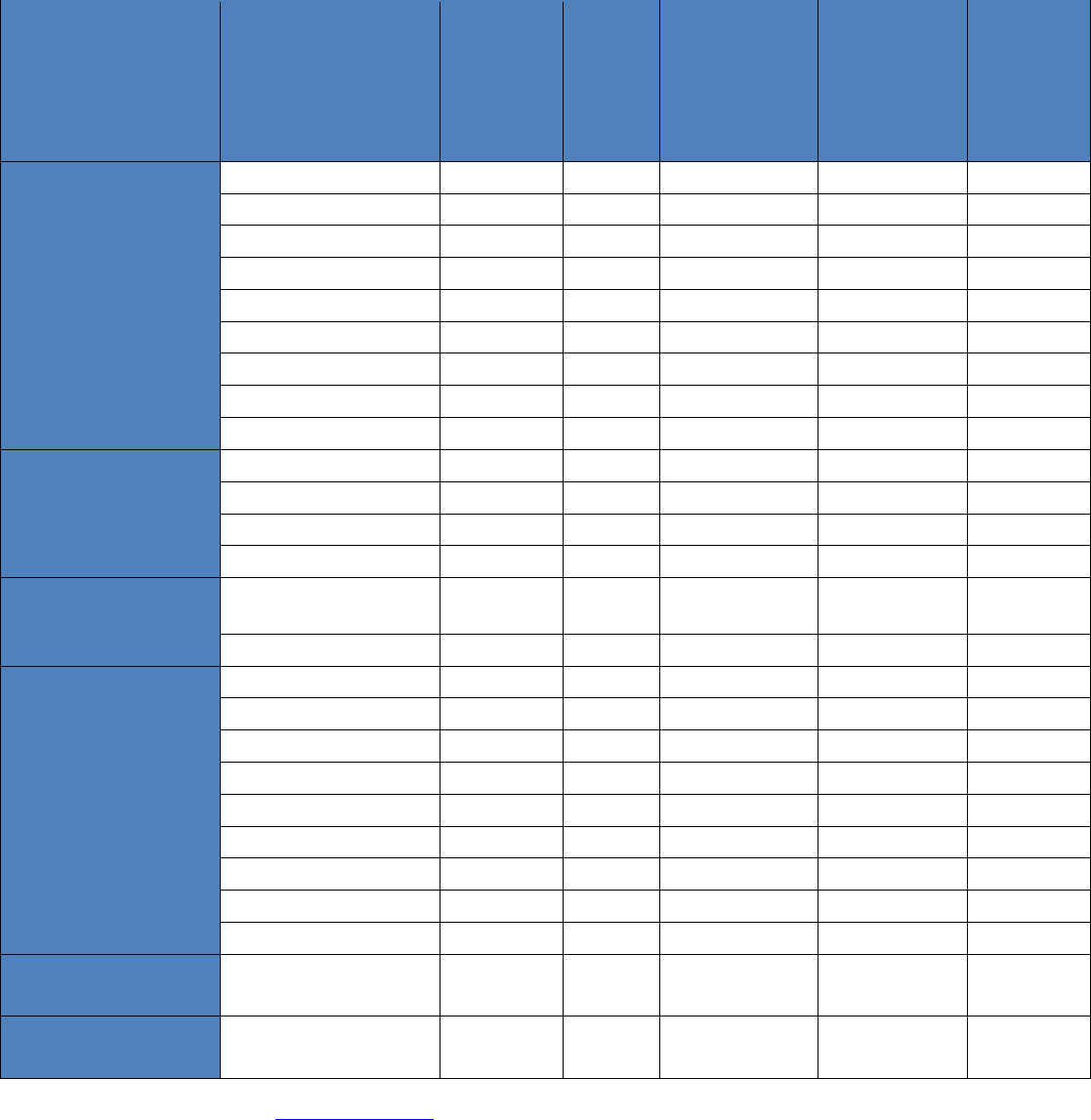
Table 2. Countries, territories or areas with reported confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths. Data as of 12
February 2020
WHO Region
Country/Territory/Area
Confirmed
*
cases (new)
Total
cases with
travel
history to
China
(new)
Total cases with
possible or
confirmed
transmission
outside of China
†
(new)
Total cases with
site of
transmission
under
investigation
(new)
Total deaths
(new)
Western Pacific Region
China
‡
44 730 (2022)
1114 (97)
Singapore
47 (2)
22 (0)
25 (2)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Japan
28 (2)
24 (2)
4 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Republic of Korea
28 (0)
13 (0)
12
§§
(0)
3 (0)
0 (0)
Malaysia
18 (0)
15 (0)
3
‡‡
(0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Australia
15 (0)
15 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Viet Nam
15 (0)
8 (0)
7 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Philippines
3 (0)
2 (0)
0 (0)
1 (0)
1 (0)
Cambodia
1 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
South-East Asia Region
Thailand
33 (0)
23 (0)
6
†††
(0)
4 (0)
0 (0)
India
3 (0)
3 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Nepal
1 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Sri Lanka
1 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Region of the Americas
United States of
America
13 (0)
11 (0)
2 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Canada
7 (0)
6 (0)
0 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
European Region
Germany
16 (2)
2 (0)
14 (2)
0 (0)
0 (0)
France
11 (0)
5 (0)
6 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
The United Kingdom
8 (0)
1 (0)
7
***
(0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Italy
3 (0)
3 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Russian Federation
2 (0)
2 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Spain
2 (0)
0 (0)
2
§
(0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Belgium
1 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Finland
1 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Sweden
1 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Eastern Mediterranean
Region
United Arab Emirates
8 (0)
6 (0)
1 (0)
1 (0)
0 (0)
Other
International
conveyance (Japan)
175
**
(40)
0 (0)
1 (1)
174 (39)
0 (0)
*
Case classifications are based on WHO case definitions for COVID-19.
†
Location of transmission is classified based on WHO analysis of available official data and may be subject to reclassification as additional data
become available.
‡
Confirmed cases in China include cases confirmed in Hong Kong SAR (49 confirmed cases, 1 death), Macao SAR (10 confirmed cases) and Taipei
and environs (18 confirmed cases).
**
Cases identified on a cruise ship currently in Japanese territorial waters.
§
The exposure for 2 cases occurred outside of Spain.
***
The exposure for 6 cases occurred outside of the United Kingdom.
§§
The exposure for 3 cases occurred outside of Republic of Korea.
‡‡
The exposure for 1 case occurred outside of Malaysia.
ERRATUM – Due to a typographical error, the total confirmed cases and death in China were incorrect. It has been corrected here.
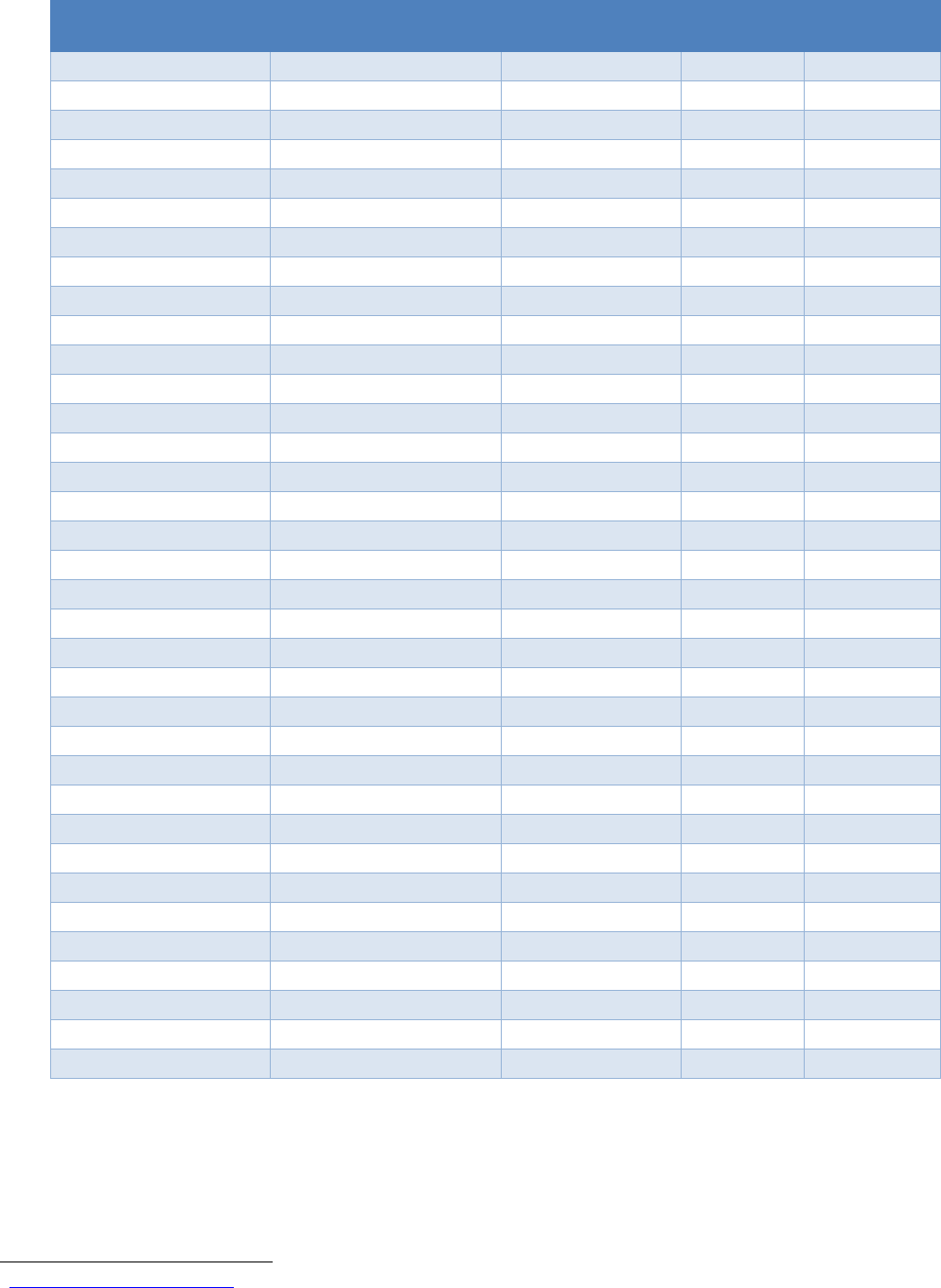
Figure 2: Epidemic curve of COVID-19 cases (n=155) identified outside of China, by date of onset of symptoms and
travel history, 12 February 2020
Note for figure 2: Of the 441 cases reported outside China, 16 were detected while apparently asymptomatic. For
the remaining 425 cases, information on date of onset is available only for the 155 cases presented in the
epidemiologic curve.
Figure 3: Epidemic curve of COVID-19 cases (n=441) identified outside of China, by date of reporting and travel
history, 12 February 2020

PREPAREDNESS AND RESPONSE
• To view all technical guidance documents regarding 2019-nCoV, please go to this webpage.
• WHO is working closely with International Air Transport Association (IATA) and have jointly developed a
guidance document to provide advice to cabin crew and airport workers, based on country queries. The
guidance can be found on the IATA webpage.
• WHO has developed a protocol for the investigation of early cases (the “First Few X (FFX) Cases and contact
investigation protocol for 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infection”). The protocol is designed to gain an
early understanding of the key clinical, epidemiological and virological characteristics of the first cases of 2019-
nCoV infection detected in any individual country, to inform the development and updating of public health
guidance to manage cases and reduce potential spread and impact of infection.
• WHO has been in regular and direct contact with Member States where cases have been reported. WHO is also
informing other countries about the situation and providing support as requested.
• WHO has developed interim guidance for laboratory diagnosis, advice on the use of masks during home care and
in health care settings in the context of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak, clinical management,
infection prevention and control in health care settings, home care for patients with suspected novel
coronavirus, risk communication and community engagement and Global Surveillance for human infection with
novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV).
• WHO has prepared disease commodity package that includes an essential list of biomedical equipment,
medicines and supplies necessary to care for patients with 2019-nCoV.
• WHO has provided recommendations to reduce risk of transmission from animals to humans.
• WHO has published an updated advice for international traffic in relation to the outbreak of the novel
coronavirus 2019-nCoV.
• WHO has activated of R&D blueprint to accelerate diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics.
• WHO has developed an online course to provide general introduction to emerging respiratory viruses, including
novel coronaviruses.
• WHO is providing guidance on early investigations, which are critical to carry out early in an outbreak of a new
virus. The data collected from the protocols can be used to refine recommendations for surveillance and case
definitions, to characterize the key epidemiological transmission features of 2019-nCoV, help understand spread,
severity, spectrum of disease, impact on the community and to inform operational models for implementation of
STRATEGIC OBJECTIVES
WHO’s strategic objectives for this response are to:
• Limit human-to-human transmission including reducing secondary infections among close contacts and
health care workers, preventing transmission amplification events, and preventing further international
spread from China*;
• Identify, isolate and care for patients early, including providing optimized care for infected patients;
• Identify and reduce transmission from the animal source;
• Address crucial unknowns regarding clinical severity, extent of transmission and infection, treatment
options, and accelerate the development of diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines;
• Communicate critical risk and event information to all communities and counter misinformation;
• Minimize social and economic impact through multisectoral partnerships.
*This can be achieved through a combination of public health measures, such as rapid identification, diagnosis
and management of the cases, identification and follow up of the contacts, infection prevention and control in
health care settings, implementation of health measures for travelers, awareness-raising in the population and
risk communication.

countermeasures such as case isolation, contact tracing and isolation. Several protocols are available here:
https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technical-guidance/early-investigations
• WHO is working with its networks of researchers and other experts to coordinate global work on surveillance,
epidemiology, modelling, diagnostics, clinical care and treatment, and other ways to identify, manage the
disease and limit onward transmission. WHO has issued interim guidance for countries, which are updated
regularly.
• WHO is working with global expert networks and partnerships for laboratory, infection prevention and control,
clinical management and mathematical modelling.
RECOMMENDATIONS AND ADVICE FOR THE PUBLIC
During previous outbreaks due to other coronavirus (Middle-East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe
Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), human-to-human transmission occurred through droplets, contact and
fomites, suggesting that the transmission mode of the 2019-nCoV can be similar. The basic principles to reduce
the general risk of transmission of acute respiratory infections include the following:
• Avoiding close contact with people suffering from acute respiratory infections.
• Frequent hand-washing, especially after direct contact with ill people or their environment.
• Avoiding unprotected contact with farm or wild animals.
• People with symptoms of acute respiratory infection should practice cough etiquette (maintain distance, cover
coughs and sneezes with disposable tissues or clothing, and wash hands).
• Within health care facilities, enhance standard infection prevention and control practices in hospitals, especially
in emergency departments.
WHO does not recommend any specific health measures for travellers. In case of symptoms suggestive of respiratory
illness either during or after travel, travellers are encouraged to seek medical attention and share their travel history
with their health care provider.
