
1
MLA817 project code:
V.RMH.0079
Prepared By:
J. Green, K. Bryan
Greenleaf Enterprises
Date Published:
PUBLISHED BY
Meat and Livestock Australia Limited
Locked Bag 991
NORTH SYDNEY NSW 2059
Final Report
Collagen Business Case Report
This is an MLA Donor Company funded project.
Meat & Livestock Australia acknowledges the matching funds provided by the Australian
Government and contributions from the Australian Meat Processor Corporation to support the
research and development detailed in this publication.

2
This publication is published by Meat & Livestock Australia Limited ABN 39 081 678 364 (MLA). Care is taken to ensure the accuracy of the
information contained in this publication. However, MLA cannot accept responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of the information or
opinions contained in the publication. You should make your own enquiries before making decisions concerning your interests. Reproduction
in whole or in part of this publication is prohibited without prior written consent of MLA.

3
1 Executive Summary
Collagen is the most abundant source of protein in the human body. It binds cells and tissue
together, and maintains the body’s integrity, shape and strength. However, collagen levels
naturally decline as humans age, which adversely affects humans’ general health and
wellbeing. There has been growth in interest and demand for collagen-based products that
are obtained through various animal sources, including bovine, ovine, porcine, marine and
poultry.
This project evaluates the current state of the market for collagen, and forecasted future
growth for bovine and ovine collagen producers, together with emerging opportunities for
higher value returns from collagen. The global collagen market size has an estimated
valuation of $3.136 billion USD for 2018. The market is expected to experience compounded
annual growth (CAGR) of 5.09% from 2017-2025, resulting in an estimated market size of
$4.150 billion USD in 2025 (QY Research 2018).
Consumer interest in collagen-based products is growing in various applications, including
food and beverage, nutraceutical supplements, cosmetics and medical products. Consumers
are particularly focusing on health and performance nutrition, with the nutraceutical collagen
market forecasted to account for 40.06% of collagen product sales in 2025.
Collagen’s characteristics as a bioavailable bonding material has resulted in growth in both
cosmetic and medical applications. Its most prevalent use among cosmetic consumers is in
skincare products, with this popularity due to its ‘revitalising’ and ‘renewing’ properties.
Advanced medical applications such as tissue regeneration and bone substitutes are
beginning to use collagen; a potential lucrative new frontier for medical collagen is artificial
organs, with research being undertaken into 3D printable organs using biomaterials like
collagen (Breed 2017).
Challenges for Australian companies looking to compete in the red-meat collagen
market
Marine Collagen: Why it is a barrier:
- Higher projected compounded annual growth (CAGR) at 6.33% through to 2025
(bovine forecasted at 4.61%)
- Doesn’t have same speculation regarding safety of consumption (BSE outbreaks
cause uncertainty among many consumers)
How to overcome this barrier:
- Marine collagen extracted at lower yield from raw material collagen extraction (1.2%
yield; bovine collagen extracted at 8-20% yield)- less efficient process
- Lower yield = higher price; marine collagen costs $44539 USD/ metric tonne,
whereas bovine costs $33457/MT. Cost leadership allows bovine collagen to have
big cost advantage in lower-value products (e.g. food)
- Australia has BSE-free status; big selling point for bovine collagen-based products

4
- Focus on medical and nutraceutical applications; BSE-free bovine collagen
commonly used due to being more genetically compatible with humans than marine
Ovine Collagen can only be produced by Holista Colltech in Australia and NZ (2018):
Why this is a barrier:
- Holista Colltech has a patent on production process for ovine collagen- they have
exclusivity to produce ovine collagen in Australia & New Zealand
- Australian ovine is the only disease and prion-free ovine in the world: Holista
basically have a monopoly on the ovine collagen market
How to overcome this barrier:
1. Explore the possibilities of using a different extraction process- can this be used to
circumvent the patent?
2. Invest in Holista Colltech- opportunity to form partnerships: there is excess demand
for ovine collagen- a partner investment may help raise production to meet demand
3. Focus solely on bovine collagen opportunities- access to lucrative value-adding
opportunities for bovine collagen is open; major medical market players using BSE-
free bovine collagen
Counter-acting growing vegan population: Other challenges for red meat collagen
include a growing vegetarian/vegan population who will not consume animal collagen
products; additionally, 3% of the world is allergic to bovine collagen. These problems cannot
inherently be solved; however, the negative impact of these consumers on the market can
be minimised through sustainable production of bovine/ovine herds and raising public
awareness of the benefits of collagen supplements for consumers.
Recommendations for Australian bovine/ovine collagen companies:
There is opportunity for bovine collagen to increase its annual collagen supply by 40,000
tonnes to meet market demand in 2025. Based on a 10% yielding extraction process, this is
equal to 400,000 tonnes of raw bovine product. Should Australia take 12% of this (in
proportion with 2016 bovine export data), the value for secondary bovine product is
forecasted to have nearly doubled by 2025. Below are some points of focus for Australian
producers.
1. Focus on high-value opportunities- the nutraceutical market segment
Countries such as Brazil and China can undercut Australian collagen producers on price due
to factors such as lower cost of labour. Therefore, it is important for Australian companies to
service high value applications. The nutraceutical segment will experience the highest
growth in demand between 2017 and 2025 and is the second highest value per tonne
market segment as well.

5
2. Marketing of BSE-free status
As discussed, Australia’s BSE-free status is a significant competitive advantage and will be a
key selling point of bovine collagen in coming years.
3. Growing demand for Halal/Kosher certified products
Consumers of Muslim and Jewish faith are religiously forbidden to eat porcine-based
products. Therefore, bovine and ovine collagen have a good opportunity to cater to these
consumers by obtaining Halal/Kosher certification. Marine is also able to cater to these
consumers, so BSE-free countries (i.e. Australia) will need to take initiative to service the
growing demand.

6
2 Contents
Executive Summary 2
1 Introduction 7
1.1 Background 7
2 Objectives 8
3 Methodology 8
3.1 Desktop research 8
3.2 Industry consultation 8
4 Global Collagen Market 9
4.1 Definition of Collagen 9
4.2 Global Market Size 9
4.3 Applications for Collagen 10
4.4 Product Trends 11
4.4.1 Food and Beverage Products 13
4.4.2 Nutraceutical Products 13
4.4.3 Cosmetic Products 14
4.4.4 Medical Products 14
4.5 Sources of Collagen 15
4.6 Australian Industry Players 18
4.7 Key Global Market Players 19
5 Results & Discussion 21
5.1 Size of Opportunity in Collagen Market 21
5.2 Competitive Advantage for Australian red-meat collagen value-adding 23
5.2.1 BSE free status- bovine 23
5.2.2 Growing demand for Halal/Kosher products- bovine & ovine 24
5.2.3 Cost Leadership over marine collagen- bovine 24
5.3 Challenges for Australian red-meat collagen growth 25
5.3.1 Importance of accessing high-value opportunities 25
5.3.2 Growing demand for marine collagen products 25
5.3.3 Vegan/Vegetarian population growing 25
5.3.4 Ovine collagen production restricted 25
5.4 Other Relevant Considerations for red-meat value-adding parties 27
5.4.1 Other uses of bovine/ovine hides 27

7
5.4.2 De-valuation of Australian red meat skins 27
6 Summary of Findings 28
7 Bibliography 29
8 Appendices 32
8.1 In-depth overview of global market players 32
8.1.1 Food & beverage market players 32
8.1.2 Nutraceutical market players 32
8.1.3 Cosmetic market players 33
8.1.4 Medical market players 33
8.2 Figures from QY Research 35
8.3 Examples of collagen products by application and their price/kg (Figure 9) 36

8
3 Introduction
3.1 Background
MLA's "High Value Food Frontiers" strategy has an aspiration goal to significantly change
the current paradigm of commodity red meat offer with innovative products and services that
represent a 3-5 value multiplier in value; and that by 2025, 50% of the value will be derived
from these HVFF streams instead of current commodity offers.
Collagen has traditionally been processed in Australia as a commodity product and
marketed accordingly. However, some overseas companies are developing food, beauty and
sports supplements underpinned by the health benefits of high quality beef derived collagen.
These products are being imported and targeting changing consumer lifestyles and
behaviours to address high value market needs.
This report analyses the consumer trends affecting the market for high value collagen
products and provides recommendations based on these trends and market data. These
recommendations provide insight into potential opportunities for Australian companies
interested in red-meat value-adding opportunities, as well as challenges that will need to be
overcome to become a successful player in the collagen market.

9
4 Objectives
The objectives of this project involved the following:
● Future scenario business model opportunities for collagen supported by data
collection and analysis using excel charts and reports.
● Recommendations on activities that would improve the value of collagen and
resultant positive contribution to the Australian red meat industry.
● Final delivery of a sanitised case study report which describes key lessons learnt,
framework developed and recommendations for MLA to make available on MLA
website.
5 Methodology
5.1 Desktop research
Desktop research was undertaken through Internet searches. Databases such as Mintel
Innova Market Insights Database and University sources were used to enforce previous
findings with organised information on market trends.
Extracts of a report on the global collagen market authored by QY Research (QY Research
2018) was obtained to validate general findings with consistent data that was obtained
through primary research, secondary research and with industry contacts. Figures from
these are displayed throughout the report and are listed in the appendices.
5.2 Industry consultation
Industry research was undertaken by communicating with a range of companies who are
considered market leaders in various capacities within the collagen market. Communication
with industry parties was established through emails and phone call.
In-depth interviews were conducted with two Australian-based companies in particular;
Gelita and Holista Colltech. Greenleaf gratefully acknowledges the time and information that
they contributed to this project.
Communication also occurred between Greenleaf and Freeze Dry Industries, a company
interested in collagen value-adding opportunities and potential commercial applications for
their business within the collagen market.

10
6 Global Collagen Market
6.1 Definition of Collagen
Collagen is the body’s primary structural protein that maintains shape, integrity and strength
of the body. As humans age, their natural collagen production decreases, which adversely
impacts on their wellbeing. As consumers are becoming increasingly focused on health and
wellbeing, the market for products that provide boosts in the body’s collagen levels has
experienced steady growth in recent years, with a focus upon products containing animal-
based collagen. The market for value-added collagen products is expected to experience
continued growth in the years to come.
In the following sections, reference will be made to different ‘types’ of collagen. These refer
to where the collagen was sourced from the animal. 29 types of collagen have been
identified, with over 90% found in Type I and III, and Type II, IV and V, accounting for most
of the rest. Types I – V are in the following:
● Type I: 80% of dermis (skin), tendons, organs, bone
● Type II: Cartilage
● Type III: 15% of dermis (skin), reticulate fibres (e.g. bone marrow)
● Type IV: Base for cell membranes
● Type V: Dermal junction, placental tissue
6.2 Global Market Size
Global market for collagen peptides forecasted at $4.150 billion USD in 2025
According to data from QY Research, the global collagen market size has an estimated
valuation of $3.136 billion USD for 2018. The global collagen market is expected to
experience compounded annual growth (CAGR) of 5.09% from 2017-2025, resulting in an
estimated market size of $4.150 billion USD in 2025 (QY Research 2018).

11
6.3 Applications for Collagen
Table 1 provides an overview of the current annual sales by volume (measured in metric
tonnes; values as of 2017) and the projected future sales by volume (for 2025) for collagen
peptides. It also shows market share by application and expected compounded annual
growth rates for each application (QY Research 2018).
Application
2013
(MT)
2017
(MT)
2025
(MT)
Market
Share in
2025
CAGR
(%)
2017-
2025
Revenue
(million
USD
2017)
$/MT
2017
Food
17,614
21,694
32,399
27.23%
5.14%
692.38
31,916
Nutraceuticals
25,989
32,125
47,665
40.06%
5.06%
1,262.13
39,288
Cosmetics
6,605
8,239
12,374
10.40%
5.22%
306.81
37,238
Medical
9,117
11,183
16,812
14.13%
5.23%
447.26
39,995
Other
5,243
6,751
9,733
8.18%
4.68%
241.79
35,815
Total
64,568
79,993
118,983
100%
5.09%
2,950.38
36,883
Table 1: Statistics for Collagen Market by Application
The market for collagen peptides in nutraceuticals is the largest and is expected to remain
so over the next eight years, with a forecasted 40.06% market share in 2025. Food
applications are the second largest, with a forecasted 27.23% market share. Comparatively,
medical and cosmetic applications for collagen are smaller, with forecasted 2025 market
shares of 14.13% and 10.40% respectively.
Additionally, the $/MT is not as variable as may be expected. Food does have a significantly
lower $/MT, due to the competitive pricing of commodity food products. However, the pricing
for nutraceuticals, cosmetics and medical collagen peptides are all similar. This implies one
of two possibilities:
1. The high-value applications for medical collagen products (worth $ millions per kg)
are a very small proportion of the overall medical collagen market.
2. There is little difference between the grade of raw collagen peptides supplied for
each application, and most of the value-adding happens after raw material collagen
extraction.
It is more likely that the second of the two possibilities is true, as no medical grade collagen-
based products have been found through research that are worth less than $10,000 USD/kg.
Section 8.3 provides examples of medical products and their price/kg.
6.4 Product Trends
The following table (Table 2) provides an overview of consumer trends that are impacting
each application, and the product opportunities that are arising as a result of these trends.
Application
Consumer Trends
Food &
Beverage
- Millennials & young consumers are becoming more adventurous in
consumption of health food & drinks

12
- 70% of consumers are willing to consume unfamiliar food if it has a
health benefit (Mintel 2017)
- Consumers are focusing on natural sources of food- functional
ingredients popular
- ‘You are what you eat’- consumers are consuming more vitamins &
nutrients to feel and look good (Mintel 2017)
Nutraceutical
- Nutraceutical supplements focused on ease of use and functionality
- Rising middle class- higher disposable income = 88% of consumers
willing to pay more for healthy food (Nielsen 2015)
- Food is now a means for managing health & reducing disease
- Millennials taking supplements to maintain good health- 20% take
probiotics for gut health
- 47% of AUS consumers avoid refined sugar
- Functionality highest claim surrounding health food
- 73% of meal replacement drinks aimed at ‘weight & muscle gain’
(Nielsen 2015)
Biggest focus is on natural, healthy functional foods focusing on either:
1. General wellbeing
2. Performance nutrition (e.g. strength)
Cosmetic
- Asian consumers indulging in ‘luxury’ cosmetic goods
- A rising ageing population causing more demand for skincare products
Survey of ten EU states found following about skincare & cosmetics:
- 71% of consumers see them as important day to day
- 80% identify them as important for self esteem
- 82% believe they improve quality of life
In China & South Korea:
- Over 50% of premium buyers have extensive, high end beauty routines
- 63% are ‘very interested’ in high-end luxury products
Medical
Products currently in common usage:
- Tissue engineering and regeneration now common (Silva, et al. 2014)
for variety of applications, like dental, orthopaedic, surgical etc.
- Collagen-based fillers for cosmetic surgery are growing in popularity
- Bone substitutes/fillers available
A potential future medical application for collagen is organ transplants.
Development into this field has already started:
- In 2006, bladders were grown from a collagen-based scaffold and
were implanted into patient’s bodies. (Jain and Bansal 2015)
- Experimentation was undertaken in the same year on rats; their ear
cavities were successfully reconstructed using a collagen scaffold.
- 2010- approximately 500,000 Americans benefit from a transplant
annually
- 2010- Approximately 108,000 US citizens waiting for suitable
transplants; many will die (U.S. Department of Health & Human
Services 2013)

13
Technology is rapidly advancing in the field of tissue regeneration, with
scientists now able to 3D print stem cells from cellulose that multiply into a
material very similar to human cartilage tissue (CBS News 2017). They are
now looking to compounds more biologically compatible with the human body
for:
- Development of 3D-printable tissue and organs that can be safely
merged into the body.
This may be an exciting and lucrative new frontier for medical-grade collagen.
Table 2: Consumer Trends for Collagen by Application
The following sections provide examples of value-added collagen products for each
applications and the relevant consumer trends that they service.
6.4.1 Food and Beverage Products
Figure 1: Examples of Collagen-Based Food & Beverage Products
Figure 1 illustrates food and beverage products that are advertised as containing collagen.
Commonly known examples include collagen jelly and gummy products, as well as sausage
and burger casings. However, collagen beverages have begun to become mainstream
products, particularly in Asia. As seen in the far-right image, the collagen-based beverages
are marketed in a similar fashion to health and cosmetic collagen supplements, with key
words including ‘anti-ageing’, ‘radiance’ and ‘vitality’.

14
6.4.2 Nutraceutical Products
Figure 2: Examples of Collagen-Based Nutraceutical Supplements
The products in Figure 2 have a variety of health purposes and benefits. Some, such as
Optimum Nutrition’s Creatine powder, support muscular strength and endurance, or use
slow and fast release proteins to stimulate muscle growth. They also include multivitamins
for diet supplementation.
These products are examples of nutritional supplements that are targeted at providing
consumers with healthy nutritional supplements that have a particular purpose and give a
specific benefit. Some of these benefits include enhanced muscle growth, improved gut
health, natural boosts in energy levels and increased strength.
6.4.3 Cosmetic Products
15
Figure 3: Examples of Collagen-Based Cosmetic Products
The products in Figure 3 are examples of collagen-based products that are commercially
sold for cosmetic use. Skincare products include anti-wrinkle creams, face creams and anti-
ageing formulas. Other cosmetic applications include hair and nail health products, marketed
as products that ‘revitalise’ and ‘replenish’ your skin, with the focus on natural, youthful
radiance.
6.4.4 Medical Products
Figure 4: Examples of Collagen-Based Medical Products
The products in Figure 4 are examples of other collagen-based medical products. Products
such as these fulfil a wide array of applications; the above products provide only a snapshot

16
of the possible medical solutions collagen may be able to service in future. Medical products
sourced from collagen function for different purposes. These purposes include the natural
regeneration of tissue for both dental and surgical purposes, fillers for cosmetic surgery and
bone substitutes for increasing the structural integrity of bones.
Table 3 provides a more detailed overview of medical products/devices that commonly use
collagen as an active ingredient.
Medical Devices
Surgical or Medical Application
Product Types
Aesthetic Surgery
Dermal Fillers
Dental Surgery
Bone substitutes and haemostatic sponges
General Surgery
Haemostatic sponges
Orthopaedic Surgery
Bone substitutes, matrixes for cartilage engineering
Vascular Surgery
Coating solutions for vascular prostheses
Visceral Surgery
Prosthetic coatings and anti-adhesion film
Haemodialysis
Compressive haemostatic sponges
Burns and dermal reconstruction
Bi-layered dermal regeneration matrixes
Table 3: Medical devices that use collagen
Collagen is usually used in these products due to its bio-compatibility with human cells, that
enable faster regeneration of tissue and other bio-structures.
6.5 Sources of Collagen
Table 4 provides an overview of the market for each source of collagen. These figures are
values for the collagen peptides used in value-added products, not the value-added collagen
products themselves (QY Research 2018).
Source
Volume
Sales
(MT)
2017
Volume
Sales
(MT)
2025
CAGR
2017-
2025
Sales
Share
2017
Sales
Share
2025
Revenue
2018
(million $
USD)
Revenue
Share
2018
Bovine
34,053
48,819
4.61%
42.57%
41.03%
1,186.91
37.85%
Porcine
17,230
23,951
4.20%
21.54%
20.13%
568.81
18.14%
Marine
24,502
40,038
6.33%
30.63%
33.65%
1,200.24
38.28%
Others
4,208
6,175
4.91%
5.26%
5.19%
179.62
5.73%
Total
79,993
118,983
5.09%
(Average)
100%
100%
3,135.58
100%
Table 4: Statistics for Collagen Market by Source
All the collagen sources discussed share the following 2 characteristics:
1. Most abundant types are Type I and Type III collagen
2. They are rich in glycine and proline: Glycine promotes lean muscle building, prevents
ulcers & diabetes, and is an anti-inflammatory. Proline simulates collagen synthesis
and prevents cell damage (Patiry, n.d.).

17
The following section provides the benefits and negatives of each collagen source.
Bovine:
● High processing yields
● Most widely used- plenty of raw materials
● Comparatively inexpensive to marine collagen
● Able to be Halal/Kosher certified
● Negative consumer perception due to BSE (see section 5.2.1 for analysis of
Australian status)
● Culturally sensitive to those who identify as Hindu, Sikh or Buddhist (Holista Colltech
Limited 2010)
● Nearly 3% of the global population is allergic to the usage of bovine collagen
Bovine is primarily obtained from the skin and bone of the cow. Use of the collagen is also
impacted by the cow’s development stages; for example, foetal bovine dermis is used for
skin and wound healing and tendon reinforcement (QY Research 2018). Depending on the
quality of bovine hides, the yield from the processing of the hide is 8% to 20%.
Bovine collagen currently has the largest market share by volume sales with 48,819 MT of
sales, which equals a sales share of 42.57%. This is expected to decrease to 41.03% in
2025, due to large sales growth of marine collagen.
Porcine
● Cheapest collagen source
● Doesn’t suffer from same speculation regarding safety as bovine
● Culturally sensitive- forbidden for those of Jewish or Islamic faith
Porcine collagen is mostly known for its skin benefits (Further Food, 2018); however, as
seen in Figure 9, under section 4.7, it is used in a wide range of applications. Market share
(by sales volume) for porcine collagen is expected to decrease from 21.54% to 20.13%
between 2017 and 2025, with an anticipated sales volume of 23,951 MT in 2025.
Marine
● Highly bioavailable
● Considered as safe for all applications
● More expensive than other sources of collagen- low processing yields (1.2%- 12g of
collagen per 1kg of raw materials processed)
● Non-mammalian- not considered as genetically similar, which may adversely affect
usage in medical applications
Marine collagen is expected to experience high growth over the next 7-8 years, with a
forecasted CAGR of 6.33%. This will result in the sales share of marine collagen increasing
from 30.63% in 2017 to 33.65% in 2025. This is likely attributable to a more favourable
consumer perception of the safety of marine collagen over bovine collagen.

18
Ovine
● Not restricted by disease or cultural sensitivity- can be Halal certified
● Highly bioavailable
● Australia = the only disease/prion-free sheep producer in the world
● Holista Colltech (Australian company) has patented rights for production process-
they have the exclusive right to produce ovine collagen in Australia and New
Zealand. However, this also presents opportunities for investment and partnerships
to take advantage of Australia’s status as the world’s sole disease-free sheep
producer (further developed in section 5.3.3)
The production levels of ovine collagen in volume terms have been very small, with Holista
Colltech the only company in the world currently involved in ovine collagen production.
However, due to the benefits Australian ovine collagen provides, demand has outsourced
Holista’s supply. They have rejected orders that they cannot realistically meet and are
providing food-grade collagen to China for a purchase price worth nearly 3x what Chinese
manufacturers can buy locally.
There is also sufficient opportunity for value-adding raw ovine collagen; when fully refined as
medical-grade collagen, 10kg has a retail value of $5.4 million USD.
Poultry
● Generally regarded as safe
● Variable supply- affects the consistency of production (Holista Colltech Limited 2010)
● Possible transmission of avian influenza- may negatively affect consumer perception
Poultry-sourced collagen likely accounts for a significant part of the ‘other’ source of
collagen. It is chiefly processed from chicken feet. However, variable supply and difficulty in
processing/extracting poultry collagen prevents its ability to provide consistent supply to
manufacturers and will probably inhibit the growth/scalability of poultry collagen in future.
This is reflected in an absence of forecasted growth of market share; other sources of
collagen dropped from 5.26% to 5.19% of sales share from 2017 to 2025.

19
6.6 Australian Industry Players
Current gelatine or collagen production in Australia, from beef or sheep, is undertaken by
Gelita (Beaudesert, Qld), Devro (Bathurst, NSW), Sonac (Maryborough, Victoria) and Holista
Colltech (Perth, WA), amongst others.
Gelita: a world leader in gelatine and collagen production. At their Queensland facility they
process hairy cattle hides to make edible gelatine, with 60% to the confectionary industry
and the remainder to jelly crystal and dairy applications. Their production goal for 2019 is to
produce 4000 tonnes of gelatin.
Devro: involved in the manufacture, import and sale of collagen, fibrous and other food
casings. Their administration is situated in Kelso, NSW. Their products include edible
casings and films, which are used in the packaging of processed meats (sausages), and
non-edible casings and plastics, which are used as protective packaging for processed
meats (IBISWorld 2017)
Holista Colltech: as of 2017, they were the only company in the world producing sheep-
based (ovine) collagen. Their patent grants them exclusivity to extract collagen from sheep
skin in Australia and New Zealand. Additionally, should companies outside Australia seek to
copy their patented process, they would not have the same disease-free and prion-free
benefits that Holista have. They produce an estimated 48 tonne/annum of food-grade
collagen and 24 tonne/annum of cosmetic-grade collagen, from lamb and sheep hides. They
are (as of 2017) the only company in the world producing ovine (sheep collagen) and have
patented rights to their collagen extraction process.
Based on communication with major market players, the general belief is that while there is
currently enough bovine raw material supply to sustain production as it stands in 2018,
significant growth in demand for increased output may result in shortages in the necessary
bovine raw material from Australian suppliers.

20
6.7 Key Global Market Players
The companies listed in Table 5 are global leaders in their relevant collagen applications.
Certain Australian market leaders have been excluded from the table, as they are evaluated
in section 4.6 (i.e. Gelita). An in-depth overview of these companies and their scope of
operations is provided in the Appendices (section 7.1).
Company
Base Country of
Operation
Relevant Application
Source of
Collagen
Key Products
JBS- NovaProm
Brazil
Food & Beverage, Cosmetic,
Nutraceuticals, Other
Bovine
Collagen peptides for use in food, cosmetics and
health products
Rousselot B.V.
EU, South & North
America, Asia
Food & Beverage, Medical
Bovine,
Porcine
Gelatin & Collagen peptides
PB Leiner/ PB
Gelatins
Whole World
(Large EU)
Food & Beverage,
Nutraceutical
Bovine,
Porcine
Collagen peptides
Ewald Gelatine
GMBH
Germany
Food & Beverage
Bovine
Leaf, powder & Halal gelatine
Certified
Nutraceuticals Inc.
USA
Nutraceutical
Marine
Collagen general health supplements
Vital Proteins LLC
USA
Nutraceutical
Bovine,
Marine
Collagen peptide nutrition supplements & beauty
shakes
Company
Base Country of
Operation
Relevant Application
Source of
Collagen
Key Products
Nitta Gelatin
Asia, North
America
Food & Beverage,
Nutraceutical, Health, Other
Bovine, porcine,
marine
Gelatin and collagen peptides
Nippi Inc.
Japan
Nutraceutical, Food, Medical,
Cosmetic
Bovine, porcine,
marine, poultry
Gelatin, collagen peptides, casings, cosmetics and
PVC foams
ProPlenish
Australia
Cosmetic
Marine
Edible collagen cosmetic powders
Gold Collagen
United Kingdom
Cosmetic
Marine
Collagen beauty supplements
Collagen
Solutions PLC
United Kingdom
Medical
Bovine
Medical collagen biomaterials & devices
Collagen
Matrix
USA
Medical
Porcine, Bovine
Collagen medical devices- spinal, dental etc.
Geistlich
Pharma
Switzerland/
Australia
Medical
Bovine
Natural bone substitutes & tissue regeneration
Medtronic
PLC
Ireland/USA
Medical
Porcine
Collagen repair patch
Advanced
Biomatrix
USA
Medical
Bovine
Collagen powders & solutions
Table 5: Overview of Key Collagen Market Players
21
7 Results & Discussion
7.1 Size of Opportunity in Collagen Market
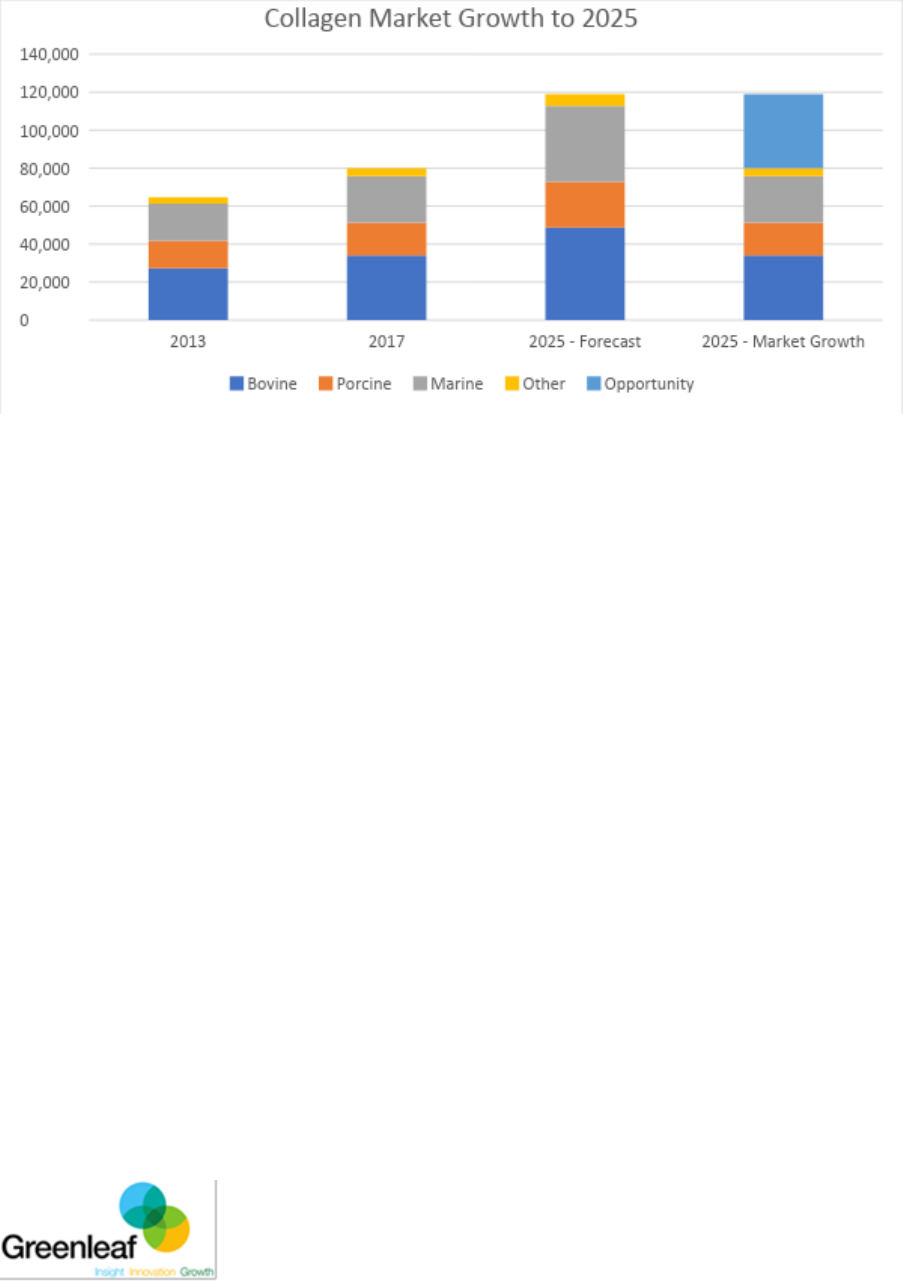
Figure 5: Collagen market growth by volume (MT) to 2025
Figure 5 compares the total volume (MT) of collagen the market needs to meet demand in
2017 and 2025. The light blue section in 2025- Market Growth represents the opportunity for
bovine collagen to increase the volume of supply to the collagen market. This represents
approximately 40,000 tonnes of collagen. Based on the collagen extraction process for
bovine collagen having a yield efficiency of 10%, this means there is opportunity for bovine
collagen equal to 400,000 tonnes of raw bovine product (e.g. hides) in 2025.
The value opportunity for Australian bovine collagen to cater to market demand is explained
in the analysis of Figure 6.
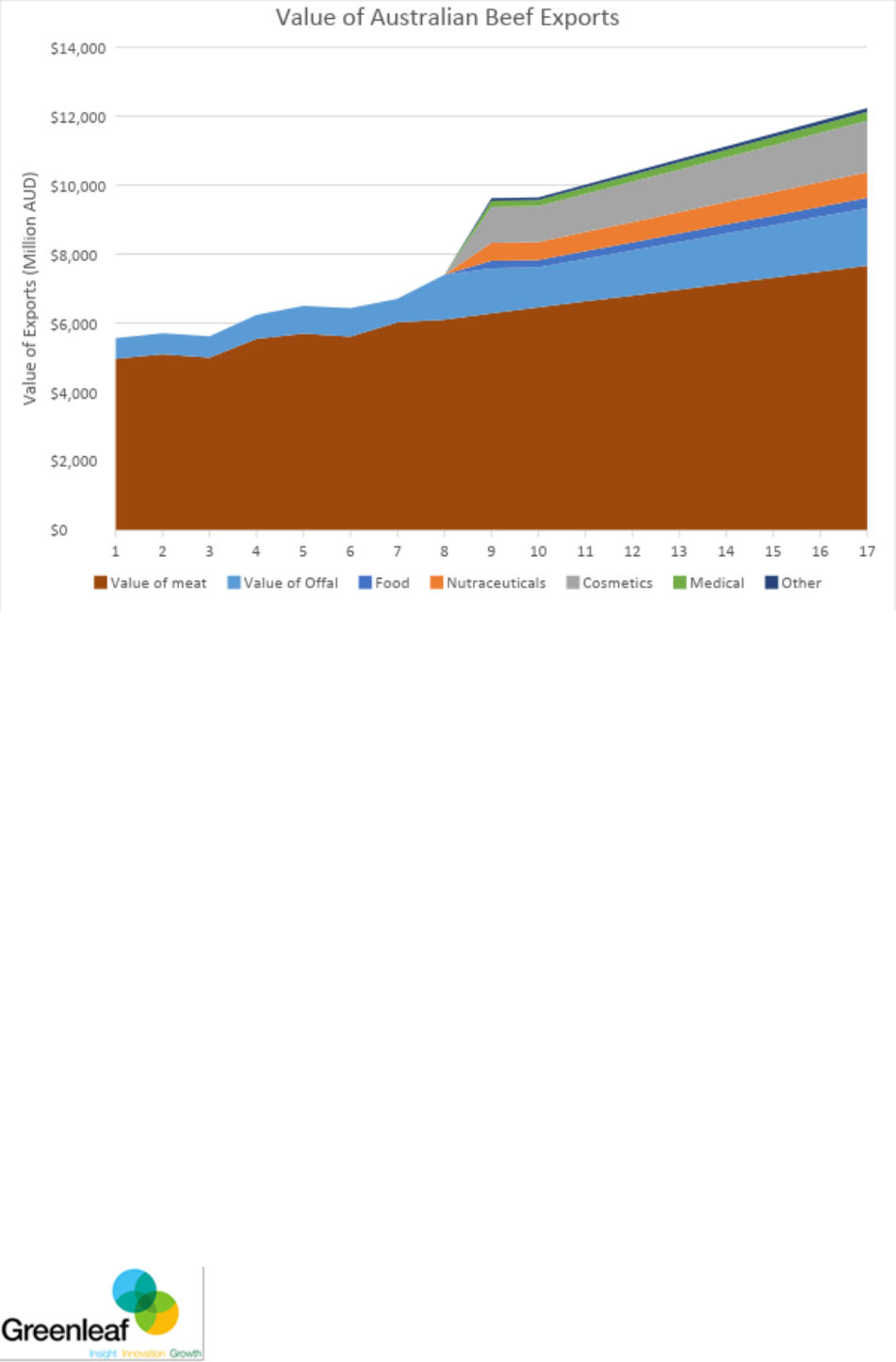
22
Figure 6: Value Increase for Australian Beef Exports due to bovine collagen production
Figure 6 represents the growth in value Australia will derive from meeting the growing
market demand for the relevant collagen products. This is assuming Australia accounts for
12% of bovine collagen products (in proportion with 2016 bovine export figures)- the volume
of collagen is distributed evenly across collagen market segments.
Figure 6 shows that the value for secondary products (offal, bones, hides) has nearly
doubled between 2017 and 2025. It should also be noted that should Australia leverage the
access we have to marketing and technology in a way that emphasises the benefits of using
Australian bovine collagen (as discussed in the following sections), the realised value
multiplier could be much higher (as Australia will account for a higher proportion of collagen
supply than 12%).

23
Figure 7: Collagen market segment growth by volume (MT) and value (USD/MT) to 2025
The trend lines in Figure 7 represent the value (USD) per tonne for collagen by segment.
Value increase for collagen to 2025 is minimal. The primary increase in market value for
collagen is the increase in volume. This increase is largely due to an increase in demand for
food and nutraceutical collagen sales. Nutraceutical collagen yields a substantially higher
sale price per tonne than food collagen; as the market segment with the highest demand and
the second highest $/MT, this should be an area of focus for collagen producers.
7.2 Competitive Advantage for Australian red-meat collagen value-adding
7.2.1 BSE free status- bovine
The recent outbreak of BSE cases among cattle has resulted in consumer uncertainty
regarding the safety of consuming bovine-sourced collagen. This has led to a decrease in its
usage in various collagen applications, substituted chiefly by marine collagen. Therefore, it is
logical to assume that this provides BSE-free countries (such as Australia) with a competitive
advantage for supplying bovine collagen, as their no-risk-of-BSE classification enables them
to assure consumers that their products are 100% disease free.

24
However, while advertising products as BSE-free may be somewhat useful as a marketing
tool to influence consumers, it does not actually have any tangible advantage. The OIE
Terrestrial Animal Health Code (which is the global standard for animal health and product
trading) states that there is no need for veterinary authorities to utilise any BSE related
conditions for ‘gelatine and collagen prepared exclusively from hides and skins’. This is
because there is a negligible risk of disease transmission through products sourced from
hides or skins. As hides and skin are classified as Type I and III collagen, the most abundant
collagen sources used, the BSE-status of countries manufacturing most bovine collagen
products is actually of little relevance.
Despite this, companies involved heavily in production of collagen sourced from bovines
believed that BSE-free was a big selling point, particularly to Asian countries. This was due
to consumers finding greater security in their knowledge that the collagen contained in their
product was sourced from a disease-free country. Thus, Australian- based companies
should seek to market their BSE-free status when selling bovine collagen or BSE-free
collagen products.
7.2.2 Growing demand for Halal/Kosher products- bovine & ovine
Porcine products are forbidden for consumption by people of Islamic and Jewish religion. As
a result, demand is expected to rise heavily for bovine/ovine products that are kosher and
halal-certified.
Marine collagen will also threaten to steal this growth- however, bovine and ovine producers
can use to their advantage the more cost-effective and higher yielding extraction processes
they have access to. This will enable them to compete effectively in the halal/kosher market
through cost leadership.
7.2.3 Cost Leadership over marine collagen- bovine
Table 6 in section 8.2 shows the $/MT based on the collagen source. The 2018 $/MT for
bovine collagen is $33,457 USD, whereas marine is $45,539 USD. This is likely due to
bovine collagen having a higher-yielding extraction process than marine (8-20% compared
to 1.2%); greater efficiency allows bovine collagen processors to charge a more competitive
price. While this is not likely to be an influencing factor for high-value multiplier products in
medical applications, for low-value commodity products in food applications this is a serious
competitive advantage for bovine collagen producers.

25
7.3 Challenges for Australian red-meat collagen growth
7.3.1 Importance of accessing high-value opportunities
For commodity items such as gelatin, there is heavy competition from countries such as
China and South American countries such as Brazil, who can undercut Australia on price.
This is due to factors such as lower costs in labour and raw materials. Therefore, it is
critical for Australian companies to look beyond low-value commodity goods and to
higher-value opportunities that are emerging within the global collagen market.
7.3.2 Growing demand for marine collagen products
Market statistics for marine collagen are provided in Figure 7. It can be seen that marine
collagen has the highest expected CAGR to 2025, at 6.33%. This will provide the marine
collagen market with an approximate 3% gain in volume sales share at the expense of
bovine and porcine collagen. Additionally, as it is more expensive than bovine collagen, it will
have a higher share of revenue, obtaining 38.28% of revenue share in 2018 compared to
37.85% for bovine collagen.
Thus, marine collagen is a serious competitor for bovine collagen, largely due to its higher
bioavailability and perceived higher sustainability. It also does not have the same consumer
misgivings regarding its safety for human consumption and is thus considered a safer
collagen source than bovine collagen.
As mentioned in section 5.2.3, one of the key points of difference for bovine collagen is the
cheaper price per metric tonne, and the more effective extraction processes. Additionally, for
medical purposes, key market players such as Collagen Solutions PLC and Advanced
Biomatrix use BSE-free collagen. This is likely due to bovine collagen having closer genetic
similarity to humans than marine collagen.
7.3.3 Vegan/Vegetarian population growing
Another industry growth inhibitor is the increasingly popular vegetarian/vegan trend. As
collagen can be naturally produced, consuming collagen growth stimulants such as silica,
vitamins and soy are collagen alternatives that vegetarians and vegans may take so they
don’t have to consume bovine collagen sources (Lam-Feist 2017).
The negative impact of these consumers on the red-meat collagen market can be minimised
through sustainable production of bovine/ovine herds and raising public awareness of the
benefits of collagen supplements for consumers.
7.3.4 Ovine collagen production restricted
As mentioned previously, Holista Colltech has a patent on the production process for ovine
collagen, that grants them exclusivity to produce this in Australia and New Zealand.
Additionally, countries that wish to produce ovine collagen outside Australia/New Zealand

26
will not have access to the same disease-free and prion-free benefits that Holista do. With
these factors in play, three viable options with regards to ovine collagen are:
1. Focus solely on bovine collagen opportunities
The market for bovine collagen is large and developed, with bovine collagen being widely
used across most applications for collagen. Access to lucrative value-adding opportunities
for bovine collagen is open, with much of the medical segment opting to use BSE-free
bovine collagen over other sources (see Table 5 for examples of major market players who
are using bovine collagen). As Australian bovine has BSE-free status, it presents a
competitive advantage over countries that do not have this status (as discussed in section
5.2.1). Therefore, Australian bovine collagen is likely to continue as a competitive collagen
source in coming years.
2. Explore the possibilities of using a different extraction process
There is some ambiguity regarding Holista Colltech’s patent (based on Greenleaf’s
research). In contact with Holista Colltech, their patent was described as providing them with
a process that was not allowed to be copied. It may be possible that if a process sufficiently
different to theirs is developed, ovine collagen can be extracted from Australian sheep by
other companies. Should this option be of interest, further research into the coverage of the
patent and other methods of extraction would be necessary.
3. Invest in Holista Colltech- opportunities to form partnerships
Holista Colltech currently uses a mid-scale production plant to cater for orders from collagen
value-adding companies. They are not currently producing at their 72 tonne/annum
production target. There is much higher demand than they are able to cater for- an order of
280 tonnes per annum (from China) was rejected due to their factory not being able to meet
this level of production sustainably (Williamson 2017).
Holista have registered interest in investment and partnership opportunities. As there is
unmet demand for ovine collagen, and Australian ovine collagen has exclusive disease-free
benefits, this may be a valuable opportunity for companies looking to value-add collagen to
source or create high-value ovine collagen-based products.

27
7.4 Other Relevant Considerations for red-meat value-adding parties
7.4.1 Other uses of bovine/ovine hides
Most of the bovine/ovine collagen used in value-added products is obtained from the hide of
the animals. Therefore, for collagen extraction to be worthwhile for red meat processors, the
price obtained for the hide must exceed the value they can obtain from using them for
alternative applications such as leather.
7.4.2 De-valuation of Australian red meat skins
Recent de-valuation in the price paid for bovine/ovine skins means that value-adding
processes like collagen extraction are becoming more important for the consideration of red
meat processors. If greater value can be obtained from skins through collagen extraction
than through selling the hides, then red meat processors should explore the equipment they
need to facilitate the extraction process and determine how worthwhile/profitable an
investment this would be. When extracting collagen, raw materials (hides) account for
approximately 82.26% of the cost of extraction (QY Research 2018), as seen in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Cost of Manufacture for Collagen Peptides

28
8 Summary of Findings
For Australian companies, it is important to use the BSE-free status of Australian bovine as a
selling point for bovine collagen and value added bovine collagen products. This status will
be particularly useful in the medical space and will provide a competitive advantage across
all applications. Additionally, Halal/Kosher certification will be of benefit for bovine collagen
producers and value-added products, as this will allow them to cater to the growing demand
for such products from Muslim and Jewish consumers.
The growth in popularity of marine collagen is a source of competition for bovine collagen,
particularly in nutraceutical and cosmetic applications. However, BSE-free bovine collagen
will find competitive advantage in its more efficient, higher-yielding extraction processes,
which enable it to be sold at a cheaper price per tonne than marine collagen. Countries like
Brazil have lower costs than Australia, so Australian producers should be aware that cost
leadership may not be a particularly sustainable strategy and should rather focus on high
quality BSE-free collagen opportunities in high value applications (i.e. nutraceutical,
medical). As nutraceutical collagen also has both the highest market demand and forecasted
growth to 2025, it is recommended that Australian collagen producers focus on the
nutraceutical collagen segment in the coming years.
Opportunities for ovine collagen production and value-added opportunities is limited by
Holista Colltech’s patent, which is currently preventing supply from meeting demand.
However, this presents a business proposition for interested companies to seek partnerships
and investment opportunities with Holista to scale up production and access new high value
opportunities for Australian ovine collagen.
Overall, there are a range of value-adding opportunities for red meat collagen producers that
will multiply the value obtained from the raw material sources of collagen. It is recommended
that companies involved in the Australian red meat industry explore ways to seize the
opportunities discussed in this report, through involvement in the value-adding of collagen to
service current and future demand for collagen-based products.

29
9 Bibliography
Advanced BioMatrix. n.d. https://www.advancedbiomatrix.com/collagen-type-i/purecol-type-i-
bovine-collagen-lyophilized-15mg/ (accessed May 28, 2018).
Bloomberg L.P. Company Overview of Nippi, Incorporated. 2018.
https://www.bloomberg.com/research/stocks/private/snapshot.asp?privcapId=881153
(accessed May 23, 2018).
CBS News. Scientists hit milestone in 3D printing of cartilage. 5 May 2017.
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/scientists-hit-milestone-in-successful-3d-printing-of-
cartilage/ (accessed June 12, 2018).
Certified Nutraceuticals. Healthy Living through Innovative Technology. 2018.
http://certifiednutra.com/products-telos95.php (accessed May 28, 2018).
Covidien. Covidien Collagen Repair Patch. 2009.
http://www.medtronic.com/content/dam/covidien/library/us/en/product/sports-
surgery/collagen-repair-patch-faqs.pdf (accessed May 31, 2018).
delicious. Why vegan is the fastest growing food movement in the world. 28 May 2017.
https://www.delicious.com.au/food-files/article/why-vegan-fastest-growing-food-
movement-world/pGyK8ZIL (accessed June 21, 2018).
Ewald Gelatine. Quality, Safety and Innovation. 2018. https://www.ewaldgelatine.de/english/
(accessed May 29, 2018).
Further Food. What are the types of collagen? 2018. https://www.furtherfood.com/what-are-
the-types-of-collagen/ (accessed June 6, 2018).
Gold Collagen. Products. 2018. http://www.gold-collagen.com/uk/products (accessed June
3, 2018).
Hardman & Co. Collagen Solutions plc (COS.L) Initiation. 2014.
http://ir.collagensolutions.com/pdf/research/Hardman_Research_24Sept2014.pdf
(accessed May 23, 2018).
Holista Colltech. Different Sources of Collagen. 4 June 2018.
http://www.holistaco.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=392
(accessed June 11, 2018).
Holista Colltech Limited. OviColl. 2010. http://ovicoll.com/about.php (accessed June 7,
2018).
IBISWorld. Devro Pty Limited- Profile Company Report Australia. 31 December 2017.
https://www.ibisworld.com.au/australian-company-research-
reports/manufacturing/devro-pty-limited-company.html (accessed June 20, 2018).

30
iHerb. Neocell, Super Collagen, Type 1 & 3, 7 oz (198 g). 2018.
https://au.iherb.com/pr/Neocell-Super-Collagen-Type-1-3-7-oz-198-g/6074 (accessed
June 20, 2018).
Jain, Aditya, and Ramta Bansal. Applications of regenerative medicine in organ
transplantation. September 2015.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4517320/ (accessed June 11, 2018).
Lam-Feist, Monica. “A Vegetarian's Guide to COllagen and Healthy Bones.” AlgaeCal. 20
July 2017. https://www.algaecal.com/expert-insights/vegetarians-guide-protein-
collagen-healthy-bones/ (accessed May 25, 2018).
MarketsandMarkets Research Private Ltd. Collagen & Gelatin Market for Regenerative
Medicine (by Source (Bovine, Porcine, Marine), Application (Wound Care,
Orthopedic, Cardiovascular)), Value and Volume Analysis - Global Forecast to 2022.
2017. https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/collagen-gelatin-
regenerative-medicine-market-
95663122.html?gclid=Cj0KCQjwuMrXBRC_ARIsALWZrIhlwIML9Ir4RifcXMyBqm_3M
1G895wB8YDirTW-m2OiHh6xVb-pw9MaAhOXEALw_wcB (accessed May 10,
2018).
Mintel. Collagen finds mainstream appeal in smoothie offerings. 21 August 2017.
http://reports.mintel.com/display/850695/?highlight (accessed June 6, 2018).
Nielsen. “We are What we Eat.” Nielsen Global Health and Wellness Survey. January 2015.
https://www.nielsen.com/content/dam/nielsenglobal/eu/nielseninsights/pdfs/Nielsen%
20Global%20Health%20and%20Wellness%20Report%20-%20January%202015.pdf
(accessed May 28, 2018).
Nitta Gelatin. Unlocking the Potential of Gelatin & Collagen for Over a Century. 9 March
2018. http://nitta-gelatin.com/ (accessed May 25, 2018).
NovaProm. Collagen & Food Ingredients. 2018. http://www.novaprom.com.br/en/ (accessed
May 25, 2018).
Patiry, Megan. Bovine Collagen VS Marine Collagen. n.d.
https://blog.paleohacks.com/bovine-collagen-vs-marine-collagen/# (accessed June 6,
2018).
ProPlenish. ProPlenish Shop. 2018. https://www.proplenish.com.au/product/anti-ageing-
facemask/ (accessed May 31, 2018).
QY Research. Global Collagen Peptide Market Research Report. Commercial , QY
Research, 2018.
Rousselot. Reaching Further Together. 2018. https://www.rousselot.com/ (accessed May 28,
2018).

31
Roy Morgan. The slow but steady rise of vegetarianism in Australia. 15 August 2016.
http://www.roymorgan.com/findings/vegetarianisms-slow-but-steady-rise-in-australia-
201608151105 (accessed June 21, 2018).
Silva, Tiago, Joana Moreira-Silva, Ana Marques, Alberta Domingues, Yves Bayon, and Rui
Reis. Marine Origin Collagens and Its Potential Applications. 5 December 2014.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4278207/ (accessed May 11, 2018).
Tessenderlo Group. Solugel. 2017. http://www.gelatin.com/en/Pages/SOLUGEL.aspx
(accessed June 21, 2018).
U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Regenerative Medicine. 29 March 2013.
https://report.nih.gov/nihfactsheets/ViewFactSheet.aspx?csid=62 (accessed May 15,
2018).
Vital Proteins. Our Story. 2018. https://www.vitalproteins.com/pages/our-story (accessed
June 21, 2018).
Williamson, Rachel. “An ASX-listed company wants to do what with my collagen?”
Stockhead. 21 August 2017. https://stockhead.com.au/health/an-asx-listed-company-
wants-to-do-what-with-my-collagen/ (accessed May 25, 2018).
10 Appendices
10.1 In-depth overview of global market players
10.1.1 Food & beverage market players
Company: JBS NovaProm
Primary Country: Brazil
Key Applications: Food & Beverage, Cosmetic, Medical, Other
Source: Bovine
Description: NovaProm is a business division of the JBS Group
Company: Rousselot B.V.
Primary Country: EU, South & North America, Asia
Key Applications: Food & Beverage, Medical
Source: Bovine, Porcine
Description: They are a leading producer of gelatin and collagen peptides. (Rousselot
2018).
Company: PB Leiner/PB Gelatins
Primary Country: Whole World (Large EU)
Key Applications: Food & Beverage, Nutraceutical
Source: Bovine, Porcine
Description: They provide easily digestible, quick absorption collagen peptides.
(Tessenderlo Group 2017).

32
Company: Ewald Gelatine GMBH
Primary Country: Germany
Key Applications: Food & Beverage
Source: Bovine
Description: They provide a range of qualities of leaf gelatine, powder gelatine, Halal
gelatine and organic gelatine. Users of their products include hotels, restaurants, patisseries,
bakeries and households (Ewald Gelatine 2018).
10.1.2 Nutraceutical market players
Company: Certified Nutraceuticals Inc.
Primary Country: USA
Key Applications: Nutraceutical
Source: Marine
Description: They specialise in quality collagen nutritional ingredients for cardiovascular,
joint, skin, eye health and anti-aging support (Certified Nutraceuticals 2018).
Company: Vital Proteins LLC
Primary Country: USA
Key Applications: Nutraceutical
Source: Bovine (Australia, New Zealand), Marine (Hawaii)
Description: They promote health, fitness and natural beauty through sustainably-sourced
nutrition products. They sell collagen peptide dietary supplements, beauty shakes and
protein powders (Vital Proteins 2018).
Company: Nitta Gelatin
Primary Country: Asia, North America
Key Applications: Nutraceutical, Food and Beverage, Health, Other
Source: Bovine, Porcine, Marine
Description: Nitta Gelatin supply high quality gelatin and collagen peptides. (Nitta Gelatin
2018).
Company: Nippi Inc.
Primary Country: Japan
Key Applications: Nutraceutical, Food, Medical, Cosmetic
Source: Bovine, Porcine, Marine, Poultry
Description: They manufacture gelatin, collagen peptides, casings, cosmetics and PVC
foams. (Bloomberg L.P. 2018).\
10.1.3 Cosmetic market players
Company: Gold Collagen
Primary Country: United Kingdom
Key Applications: Cosmetic
Source: Marine
Description: Gold Collagen provide clinically tested beauty supplements, mainly for
skincare purposes, as well as the promotion of healthy hair and nails (Gold Collagen 2018).

33
Company: ProPlenish
Primary Country: Australia
Key Applications: Cosmetic
Source: Marine
Description: ProPlenish is an Australian brand that was the first to provide edible marine
collagen products to the Australian market. Many of their products are provided in a powder
form that are dissolvable, and are marketed as ‘reinvigorating your skin, hair and nails’. They
also provide other cosmetic products like anti-ageing facemasks, which are to be used in
conjunction with their collagen oral supplements. (ProPlenish, 2018)
10.1.4 Medical market players
Company: Collagen Solutions PLC
Primary Country: United Kingdom
Key Applications: Medical
Source: Bovine (Australia, New Zealand)
Description: Collagen Solutions create biodegradable/bio resorbable devices, and supply
medical collagen biomaterials for research purposes, medical devices and regenerative
medicine. Their goal (as of 2014) was to move from acting a supplier of purified, functional
collagen that was valued at $500-$1,000 per gram to developing and supplying medical
devices that contained the same collagen, but were valued at prices upwards of $1,000 per
gram (Hardman & Co, 2014).
Company: Collagen Matrix
Primary Country: USA
Key Applications: Medical
Source: Porcine, Bovine
Description: Collagen Matrix offers collagen and mineral based medical devices that
support the body’s natural regenerative ability. They provide clinical application solutions for
dental, spinal, orthopaedic, dural repair and nerve repair.
Company: Geistlich Pharma
Primary Country: Switzerland/Australia
Key Applications: Medical
Source: Bovine
Description: Geistlich are market leaders in natural bone substitutes for regenerative
dentistry. Some of the products they sell include Bone Substitutes, Membranes for tissue
regeneration and matrices for soft-tissue regeneration and tissue grafts.
Company: Medtronic PLC
Primary Country: Ireland/USA
Key Applications: Medical
Source: Porcine
Description: Their collagen repair patch is a trusted, reliable soft tissue reinforcement
material. Over 250,000 of these patches have been implanted in medical procedures since

34
1998. It is derived from pig dermis and is used for tissue repair across many surgical
disciplines (Covidien, 2009).
Company: Advanced Biomatrix
Primary Country: USA
Key Applications: Medical
Source: Bovine
Description: Advanced Biomatrix is an industry leader in 3D applications for tissue culture,
cell assay, and cell proliferation. They sell a wide range of medical solutions and powders
(not all collagen-based). They are an industry leader in the science of 3D applications for
tissue culture and cell proliferation.
10.2 Figures from QY Research
Source
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018 (E)
Bovine
32,502
32,617
32,636
33,107
33,365
33,457
Porcine
30,215
30,613
30,243
30,910
31,252
31,564
Marine
44,265
44,531
44,081
44,918
45,261
45,539
Others
38,695
38,909
38,672
39,349
39,625
39,796
Average
35,883
36,224
35,906
36,572
36,883
37,166
Table 6: Global Collagen Peptide Price (USD/MT) by source
Application
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018 (E)
Food
17,614
18,615
19,251
20,604
21,694
23,049
Nutraceuticals
25,989
27,792
29,213
30,925
32,125
34,034
Cosmetics
6,605
7,118
7,502
7,967
8,239
8,563
Medical
9,117
9,645
10,360
10,766
11,183
11,811
Others
5,243
5,673
6,019
6,418
6,751
6,910
Total
64,568
68,842
72,345
76,681
79,993
84,367
Table 7: Global Collagen Peptide Sales (MT) by Application (2013-18)
Revenue
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018 (E)
Bovine
890.88
951.46
974.58
1077.66
1136.19
1186.91
Porcine
434.51
470.81
483.09
513.86
538.49
568.81
Marine
864.58
933.78
995.30
1052.94
1108.98
1200.24
Others
126.92
137.68
144.64
159.92
166.73
179.62
Total
2316.89
2493.73
2597.62
2804.38
2950.38
3135.58
Table 8: Global Collagen Peptide Revenue (million USD) by Source

35
10.3 Examples of collagen products by application and their price/kg (Figure
9)
Company
Product
Application
Collagen-related
ingredients
How it is obtained
Advanced
Biomatrix
PureCol
Lyophilized
Medical- prepares thin layers
for culturing cells
Bovine collagen
(Type I)
Isolated from bovine
hide- >99.9% purity
PureCol EZ Gel
(5mg/mL = 0.5%)
Medical- Improve gel
consistency for cell cultures
Bovine Collagen
Bovine Collagen
Solution
Medical- provides structure for
connective tissue
Bovine Collagen
(Type V)
Isolated from
placenta- final purity
of >95%
Bovine Collagen
Lyophilized Fibrous
Powder
Medical- prepared into tissue
scaffolds, foams, putties etc.
Bovine Collagen
(Type I)
Extracted from
bovine flexor
tendon- >96% purity
Beauty &
Go
Skin Detox
Bioactive Beauty
Drink
Beverage/Health- Skin purifying
drink with antioxidants
Collagen Peptides
Bioactive Collagen
Shot
Beverage/Cosmetic- Firms skin
and smooths wrinkles
Collagen
Ewald
Gelatine
Gelatine Powder
Food- prepared into jellies and
mousse
Porcine Collagen
Extracted from pig
hide
Leaf Gelatine
Sheets
Food- prepared into jellies and
soups
Porcine Collagen
Extracted form pig
hide
Gelatin
Health
Joint Care
Health- Joint Mobility &
Cartilage Formation
Bovine Collagen
Soft Skin
Cosmetic- Wrinkle reduction &
smoother skin
Bovine Collagen
Pet Care Collagen
Health- General mobility and
wellbeing
Collagen peptides
Gold
Collagen
Gold Collagen
Hairlift
Cosmetic- Healthy hair growth
Marine Collagen
Pure Gold
Collagen
Cosmetic- Hair, skin & nail
health
Marine Collagen
Nature’s
Way
Beauty Collagen
Powder
Cosmetic- Healthy, smooth skin
Collagen (Type I &
III)
Collagen Bone
Broth
Health- Joint & Gut Health
Bone Broth &
Hydrolysed Collagen
The Beauty
Chef
Collagen Inner
Beauty Boost
Health- Probiotic Elixir
(VEGAN Alternative)
Does not actually
contain collagen
