
Kansas State University Agricultural Experiment Station and Cooperative Extension Service
Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas:
Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
Overview: Allowed Foods, Label Requirements
Direct-to-consumer sales of food, including at farmers
markets, are growing in popularity across the United States and
across Kansas. ese sales provide a valuable market outlet for
local farmers and allow consumers to purchase healthy local
produce and other foods. To protect this key market outlet, it is
essential that the food sold directly to consumers is produced and
processed safely according to the relevant governmental rules,
regulations, and guidelines. Not only will this produce products
that are as safe as possible, it will also assure your customers that
your business has product quality and safety in mind.
Any food sales (other than fresh, whole fruits, vegetables,
cultivated mushrooms, and herbs) to another business entity
for use, resale, or further distribution requires food safety
licensing (generally a KDA food processing license). For
example, selling to a restaurant, grocery store, variety store, or
convenience store. Consignment sales are also not subject to
the direct-to-consumer exemptions. Contact KDA for more
information about wholesale licenses.
** Retail food sales (including at farmers markets) in Kansas are
regulated for food safety by the Kansas Department of Agriculture
(KDA) Food Safety and Lodging program. erefore, if you
are selling products direct to consumers in Kansas, the state
requirements listed in this document are what you need to follow.
More information on how to obtain the various KDA licenses
mentioned in this document is included after the tables and in
subsequent sections of the document. KDA encourages vendors to
contact them with any questions regarding safety or licensing, as
KDA is happy to answer food safety questions and guide people
through the licensing process.
* Vendors should also check with the market where they are selling, as
their requirements may be more stringent than state governmental
regulations.
* More detailed requirements for most products listed in the tables
below are included in subsequent sections of this document.
Note: ese requirements apply to all direct-to-consumer sales of
food, including festivals, bazaars, craft shows, and similar events
where people making the products sell their own products. e listed
licensing exemptions would also apply to exempt foods sold online
and shipped to the customer’s home or delivered by the producer
directly to the end consumer. Note that for foods sold online to a
person in another state(s), the seller must also follow the rules of the
receiving state(s). Foods sold under the direct-to-consumer licensing
exemption may be sold in bulk and the customer can bring their
own clean container to transport the foods. If a food does NOT
require licensing to be sold directly to consumers, it can be made in
the producer’s regular home kitchen, as long as the kitchen provides
a clean and sanitary environment for preparation of that food.
KDA also encourages people producing and selling products direct-
to-consumer that do not require licensing to use suitable shared-
kitchen spaces to make their products.
Revised January 2024
Overview: Allowed Foods, Label Requirements ................. 1
General Food Safety Practices, Selling
Fresh Produce, Samples, and Demos .......................................8
Selling Prepared Foods and Baked Goods ........................ 12
Selling Meat, Eggs, and Dairy Products ............................... 13
Key Contacts ...................................................................................... 15
2 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
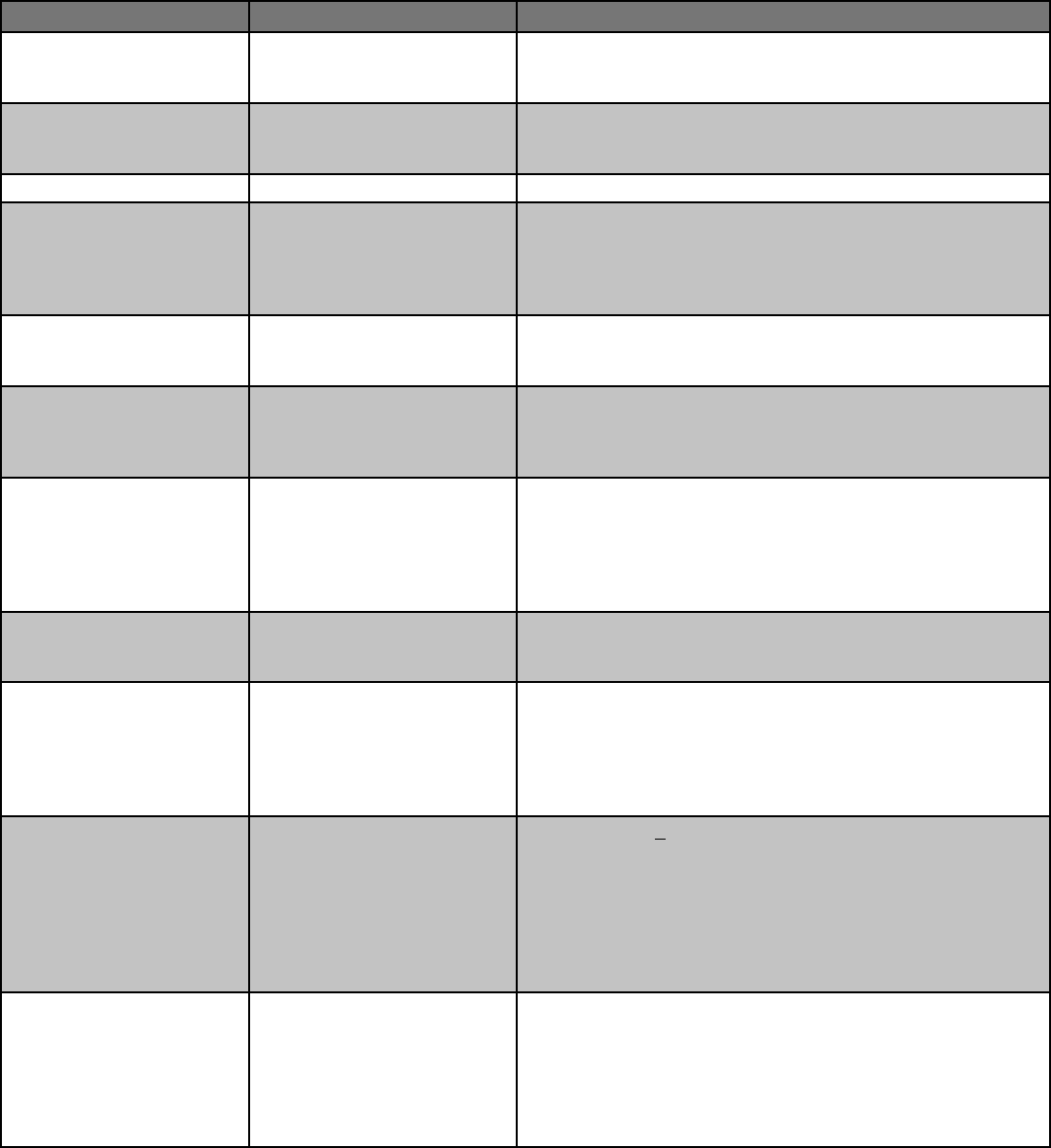
Foods that are ALLOWED to be sold directly to consumers in Kansas WITHOUT licensing, according to state
regulations (Note: If your product is not listed in this section, please refer to the Licensing Required table starting on page 4.)
Food Product Type Examples Regulatory requirements
Baked goods (home kitchen) Cookies, breads, cakes, cinnamon
rolls, fruit pies, fruit cobbler
Follow labeling requirements (on page 8). Note that breads with
cheese and/or vegetables (e.g. jalapenos) baked in/on them require
testing to determine their category (see testing table on page 6).
Icing/frosting, including cream
cheese-based, with >65% sugar
by weight
Icing on cinnamon rolls If the icing is known to contain >65% sugar by weight, testing and
licensing is not needed. Otherwise, testing is required to determine if
licensing is required or not (see page 6).
Dry baking mixes Cookie mix, brownie mix Follow labeling requirements (on page 8).
Fresh (or dried or freeze-dried)
uncut fruits, vegetables (not
cut beyond normal harvesting),
or any herbs
Tomatoes, melons, okra, apples,
basil, garlic scapes
May be home-grown; any pesticide use must comply with label direc-
tions. If products are heat treated before drying, a KDA Food Establish-
ment License is required. If they are not heat treated before drying, a
license is not required. Note that licensing is not required for buying
and re-selling produce direct-to-consumer.
Whole, frozen fruits or veg-
etables NOT heated before
freezing
Whole, uncut tomatoes that have
not been blanched before freezing
If intact and the product is maintained frozen to the customer, no
license is required.
Intact salad greens (not cut
beyond normal harvesting)
Mixed greens with only intact
leaves, includes microgreens and
shoots (not cut beyond normal
harvesting practices)
Follow weights and measures requirements. All sprouts and any leafy
greens cut beyond normal harvesting cuts require a KDA Food Estab-
lishment License.
Certain cut produce and cut
herbs (other than cut tomatoes,
melons, or leafy greens)
Cut berries, cut herbs, cut carrots,
zucchini noodles, etc. Can be
frozen, fresh, dried, or freeze dried.
If product is blanched before freezing and has a pH above 4.2, a
KDA Food Establishment License is required for frozen foods. If not
blanched rst, no licensing required. Note that if produce is heated
before selling, a license is required. Herbs are NOT included in the leafy
greens category and do not require a license to be sold even if cut.
Produce purchased from other sources is included in this category.
Nuts and nut butters Walnuts, pecans, peanut butter May be sold shelled or in-shell. Peanut and other nut butters can also
be sold direct to consumer without licensing. Nuts may also be roast-
ed/smoked without a license.
Honey Includes honey and spun honey.
Includes honey infused with items
that do not require temperature
control for safety (such as cinna-
mon sticks).
Can sell direct-to-consumer without licensing. Sales of packaged
honey to grocery stores and other businesses (including consignment
sales) for resale or sales by an individual that did not package the hon-
ey requires a KDA Food Processing License. Infusing honey with items
that require temperature control for safety would require appropriate
licensing.
Eggs (< 250 hens) Chicken, duck, goose, turkey, etc.
Should be sold at <45°F. Cartons should be clean and labeled properly.
(Temperature control and labeling strongly suggested for establish-
ments with fewer than 50 hens; temperature control and labeling
required for farms with 51 to 249 hens.) Eggs must be ungraded. Egg
licensing (and grading) is required with > 249 hens or if selling graded
eggs.) Fertilized eggs (not baluts) are also allowed for sale if they are
raised in Kansas (not coming in from out of state). Baluts require a food
safety license.
Poultry (< 20,000 birds/year) Chicken, duck, goose, turkey, etc. Growers raising fewer than 1,000 birds/year can slaughter at their own
facility and sell direct-to-consumers at their farm without registration
or inspection. Growers selling 1,001 to 20,000 birds/year must obtain
a KDA Meat & Poultry Wholesaler license with a poultry exemption.
The cost of a license is $25 per calendar year. More details available in
https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-source/meat-and-poultry/poul-
try-exemption-5-1-19.pdf?sfvrsn=43488bc1_4
NOTE: It is a regulatory requirement that ALL foods on sale or display (even if no licensing is required) must be eectively protected from contamination and sold in a sanitary manner.
Uninspected food products in Kansas do NOT need to be labeled as “homemade” or other indication that they are not inspected. However, homemade food products can be labeled as
such.
*Products requiring specialized processing include beef jerky, vacuum-packaged temperature control for safety foods, acidifying and/or pickling, curing using nitrites, fermenting, and
sprouting. All of these products require food safety licensing regardless of the number of days they are sold, as listed in the table on pp. 4-6.
K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices 3
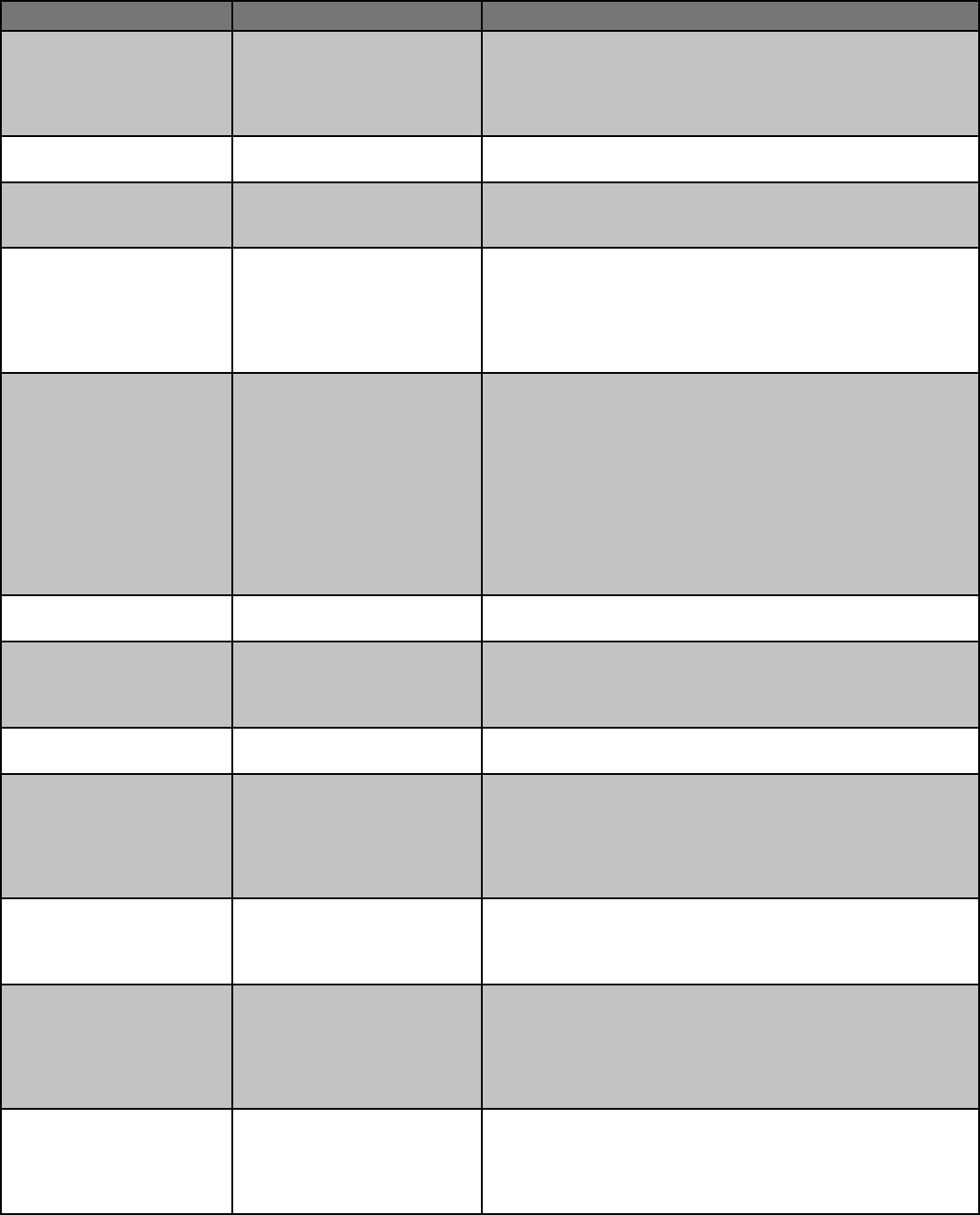
Food Product Type Examples Regulatory requirements
Home-canned fruit jams and
jellies; jams and jellies avored
with pepper-avored vinegar or
small amounts of pepper powder,
apple butter
Fruit jams and jellies (note that
reduced or no-sugar jams or jellies
require a product assessment)
Must follow labeling requirements (see page 8). Products with low-acid
fruits such as mangoes require product evaluation.
Canned soda/pop-based jelly Lemon-lime soda jelly Must follow labeling requirements. May be canned in a home kitchen
without a license for direct-to-consumer sales.
Canned, shelf stable natural-
ly high acid foods, canned
high-acid fruit pie lling
Canned applesauce, canned fruits Must follow labeling requirements. Requirements for other canned
foods listed below. May be canned in a home kitchen without a license
for direct-to-consumer sales.
Juice, cider: high-acid Apple juice, apple cider May be sold under the direct-to-consumer exemption without a
license if sold packaged (served by the glass requires license.) If not
pasteurized, must include a warning statement on the label (see p. 61,
Kansas Food Code, https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-source/fsl--
handouts/2012_kda_food_code_12_14_12.pdf). May be kept cold for
quality and consumer expectation.
Juices: low-acid (NOT heat treat-
ed/lled/sealed, sold refrigerat-
ed less than 6 days a year)
Celery, beet, carrot, leafy greens,
wheat grass juice, etc.
If the low-acid juice is NOT heat treated and sealed in its preparation, it
must be sold refrigerated. If it is made and sold less than 6 days a year,
a license is not required. If it is sold more than 6 days a year, licensing
is required. If it is heat treated and sealed in its preparation, then it is
considered a low acid canned food, which will require licensing. Note:
Tomato juice requires a product evaluation to determine its category.
If not pasteurized, all juices must include a warning statement on the
label (see p. 58, Kansas Food Code, https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/
default-source/fsl--handouts/2012_kda_food_code_12_14_12.pdf). Can
be put into bottles or jugs, but not sealed or hot-lled to be exempt. A
Food Establishment License is required if sold by the drink/cup/glass.
Candy and fudge (made by the
producer)
Cinnamon hard candy; caramels,
toee, fudge
Homemade chocolates (other than fudge) must be tested to determine
if a Food Establishment License is needed (see testing table on page 6).
Products not requiring refrig-
eration for safety dipped in or
decorated with commercially
prepared melting chocolate
Chocolate-covered pretzels, straw-
berries, nuts, etc.
Homemade chocolate mixtures must be tested to determine their
category, but melting commercially prepared chocolates for
decorating or dipping does not require testing or a license.
Freeze dried shelf-stable
candies
Freeze dried purchased or home-
made shelf-stable candies
If the candy requires refrigeration for safety before it is freeze-dried, it
will require a Food Establishment License to freeze dry it to sell.
Cultivated mushrooms (culinary
and medicinal)
Fresh or dried If not processed beyond cleaning and not heat-treated, cultivated
mushrooms may be sold without a license. Mushrooms must be grown
in protected environments and kept free from contaminants. Following
Mushroom Good Agricultural Practices as indicated on page 10 is rec-
ommended. Blanching or heat treating requires a Food Establishment
license.
Fish and seafood — sold whole
on ice (does NOT include catsh
and other Siluriformes)
Whole tilapia, shrimp No HACCP plan or food processing license required. Wild-caught sh
sales are illegal without a commercial shing permit from the Kansas
Department of Wildlife, Parks and Tourism. See K.S.A. 115-17-10 and
115-17-13 for more information.
Foods and beverages prepared
o site, sold ready for immedi-
ate consumption — six or fewer
times per calendar year.
Sandwiches, pizza, potato salad,
refrigerated cold-brew coee,
etc. prepared and sold by any
entity intended to be eaten at the
market — six or fewer times per
calendar year.
No licensing required; however, must follow Kansas Administrative
Regulations (KAR) 4-28-33 “Sanitation and hygiene requirements for
exempt food establishments”. More details also in KAR 4-28-34 (Ex-
emption from licensure; denitions). This includes cooking classes and
competitions, such as BBQ competitions.
Foods and beverages sold
ready for immediate consump-
tion by community groups for
fundraising purposes
Sandwiches, pizza, etc. prepared
and sold by 4-H groups, church
groups, schools, etc. (with no sta
paid by the proceeds of the food
sales).
No licensing required; however, must follow “Sanitation and hygiene
requirements for exempt food establishments”. (KAR 4-28-33)
Fundraising for community or humanitarian purposes and educational
or youth activities is exempt from licensing with no restriction on num-
ber of times done per year.
Foods ALLOWED WITHOUT licensing, cont.

4 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
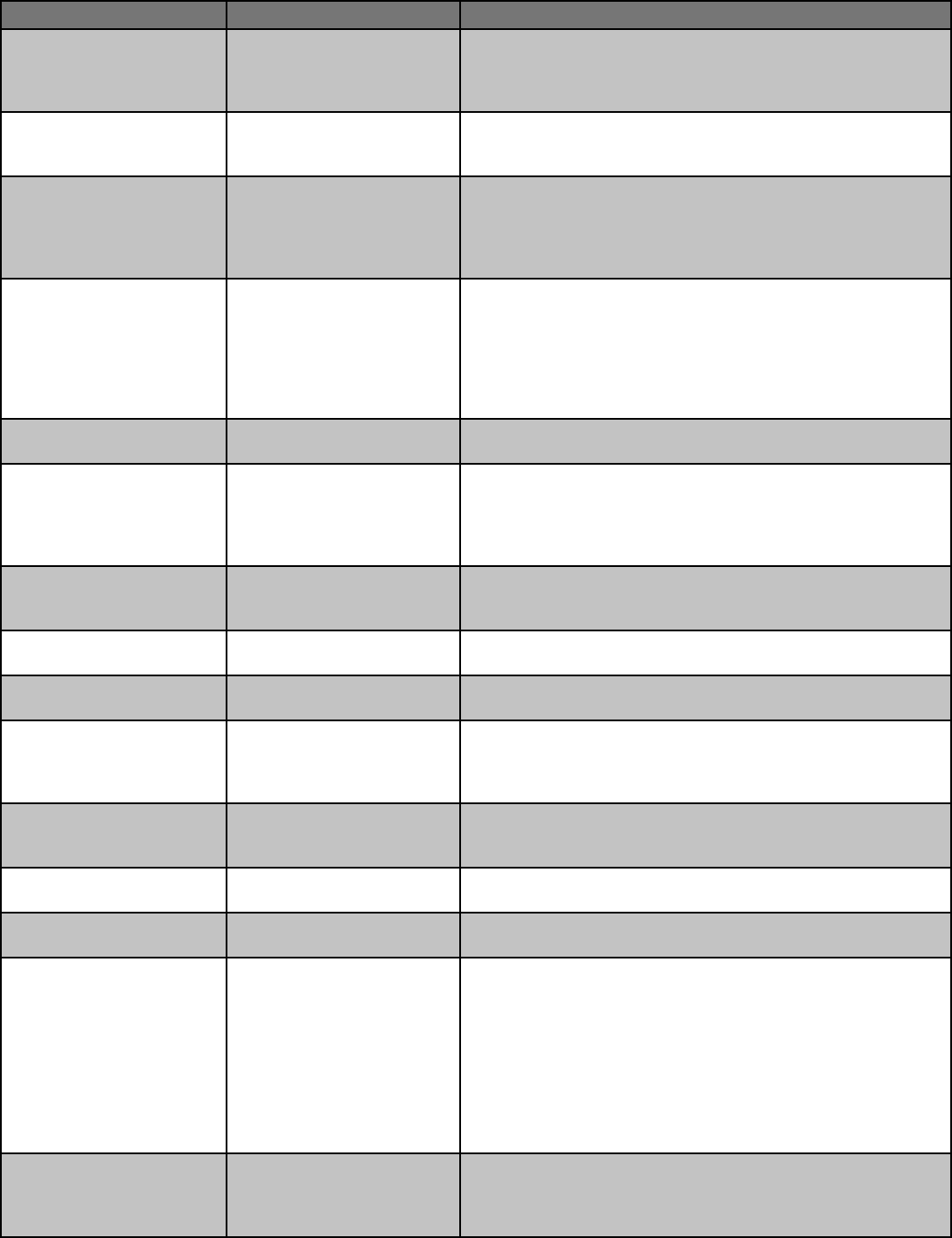
Food Product Type Examples Regulatory requirements
Non-specialized processed food
that is made and sold six or
fewer days in a year. (Intended
for people to purchase and
consume at home.)
Frozen bierocks, frozen protein
popsicles, pork rinds, refrigerated
noodles, pesto, refrigerator pick-
les, refrigerated salsa, refrigerated
elderberry syrup, refrigerated
cold-brew coee, etc. Other items
that are included in this category
are also indicated with a ** in the
table below.
The food product can be made on day one and each day they are sold
adds to the total of up to 6 days without a license. Must follow “Sanita-
tion and hygiene requirements for exempt food establishments” (KAR
4-28-33). Products such as pesto need to be cooled quickly and held
at < 41°F for no more than 6 days after preparing. Any products that
require specialized processing* require a food safety license even
if it is for 6 or fewer days. If the food is sold more than 6 days a year, a
Food Establishment license would be required.
Homemade dried pasta Dried egg noodles No licensing required if dried in a protected environment in a short
time. Directions on package to thoroughly boil the noodles is recom-
mended.
Vanilla extract No licensing needed if the product meets the standard of identity in 21
CFR 169.175 to ensure it is vanilla extract and not a avored alcohol.
Spices and herbs — bulk or
small quantities
Cinnamon, cloves, etc. Product must be labeled properly, unadulterated, and sold in a sanitary
manner.
Loose leaf tea Product must be labeled properly, unadulterated, and sold in a sanitary
manner.
Lard No licensing required if sold direct-to-consumer.
Pepper vinegars RAW peppers or commercially pickled peppers must be used in making
pepper vinegar to sell direct-to-consumer without a license
Herb-avored/infused vinegars Vinegar poured over fresh tarra-
gon, fresh garlic, fresh basil, re
cider
A license and product evaluation are NOT required unless using
low-acid vinegar (pH>4.2) or more than 10% low-acid ingredients, like
herbs, which would raise the equilibrium pH above 4.2
Grain products Home-ground our, cornmeal,
popcorn, intact grain, dehydrated
sourdough starter
Standard hygiene and sanitation requirements, as with all food sold
Dry snacks seasoned with oil
and spices
Dry pretzels mixed with oil and
spices
Standard hygiene and sanitation requirements, as with all food sold.
Fruit leathers Apricot leather, other fruits Standard hygiene and sanitation requirements, as with all food sold
Sampling of food products Fruit, vegetable, prepared food
samples
Samples must be prepared and served in a sanitary manner. More
details available in the KSRE/KDA publication MF3311, “Sampling Safely
at Kansas Farmers Markets. (https://bookstore.ksre.k-state.edu/pubs/
MF3311.pdf)
Foods THAT REQUIRE proper licensing (temperature control for safety or specialized process foods and
beverages)
Note: More information on costs and requirements for a KDA Food Establishment License, Food Processors License, and other various licenses is available from:
https://agriculture.ks.gov/foodlicense or by contacting the KDA Food Safety and Lodging program(KD[email protected] or 785-564-6767). A KDA Food Processing
license allows for distribution to other business entities, often called wholesale sales, such as to grocery stores, restaurants, through a co-op, consignment sales etc.
A KDA Food Establishment license only allows for direct-to-consumer sales.
The products below indicated with a ** are allowed to be sold without a license if sold 6 or fewer days a year. If they are sold more than 6 days a year, they
require licensing. All other foods listed below require a license regardless of the number of times per year these items are sold. Products that require licensing can
NOT be made in a regular home kitchen unless otherwise noted below. Freeze drying any foods in the list below would still require the indicated license. For
foods requiring licensing, the producer must provide the food container (the customer cannot provide their own container.)
Food Product Type Examples Regulatory requirements
**Baked products with
potentially hazardous dairy and
egg
products
Cheesecake, cream lled cup-
cakes or donuts, cream cheese-
based frostings or llings (unless
>65% sugar content), cream or
meringue pies, custards, pump-
kin pie, quiche
KDA Food Establishment license required at production facility and
point of sale. NO license required if sold 6 days or less in a year. KDA
Food Establishment License required if sold more than 6 days in a year.
**Dough Refrigerated or frozen cookie
dough, pizza dough
Product requires temperature control for safety, so a KDA Food Estab-
lishment license is required. NO license required if sold 6 days or less in a
year. Licensing required if sold more than 6 days in a year.
**Cut leafy greens (fresh or
dried)
Cut or torn lettuce (cut beyond
normal harvesting)
KDA Food establishment License required at production facility and
point of sale. Must be sold at or below 41°F. This does NOT include
cut herbs. NO license required if sold 6 days or less in a year. Licensing
required if sold more than 6 days in a year.
Foods ALLOWED WITHOUT licensing, cont.
K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices 5
Food Product Type Examples Regulatory requirements
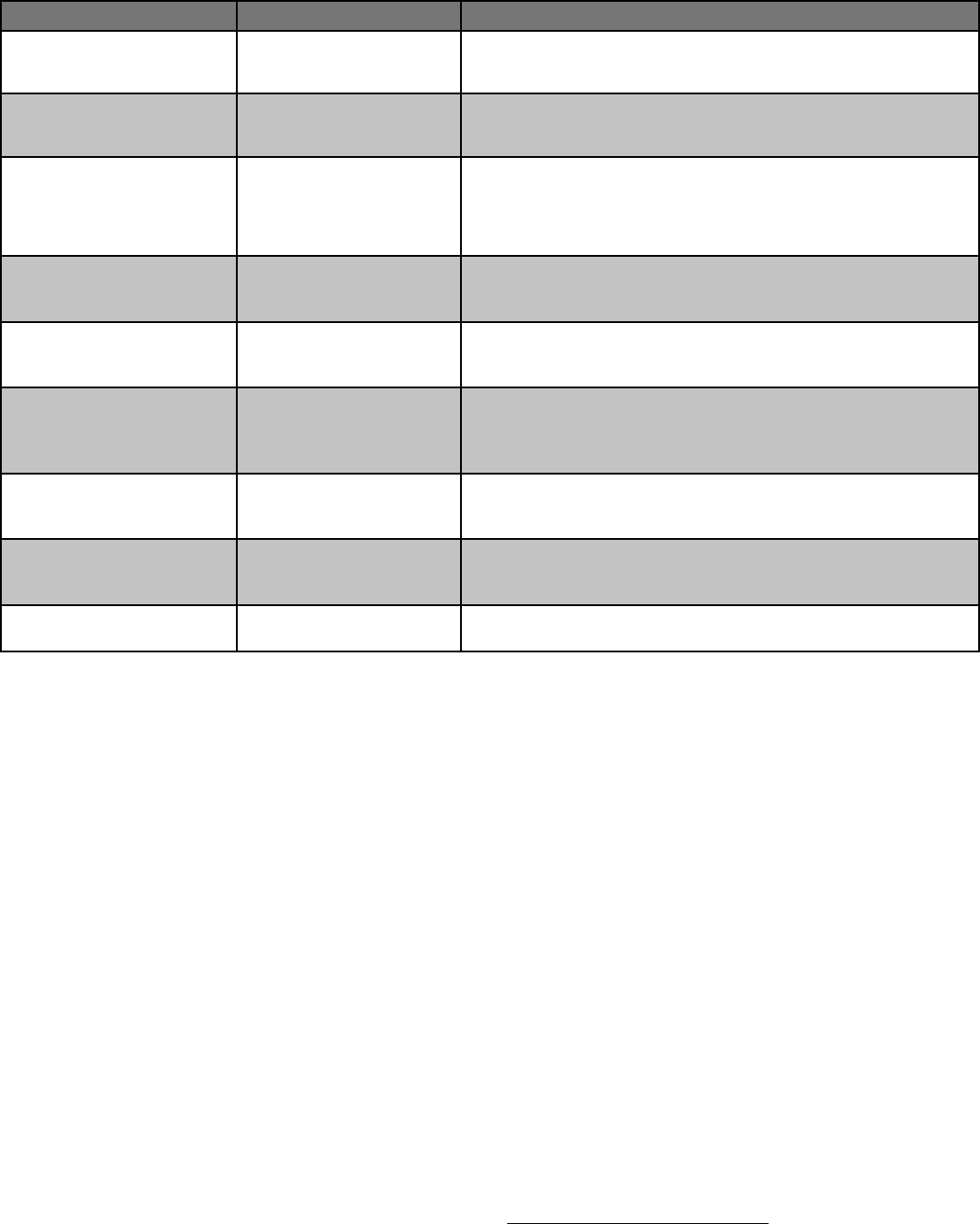
**Cut melons, cut tomatoes
(fresh or dried)
Cut melons, cut tomatoes KDA Food establishment License required at production facility and
point of sale. Must be sold at or below 41°F. NO license required if sold
6 days or less in a year. Licensing required if sold more than 6 days in a
year.
**Dried produce that is heat
treated before drying
Vegetables that are blanched
before drying
KDA Food Establishment license required at production facility. NO
license required if sold 6 days or less in a year. Licensing required if sold
more than 6 days in a year.
**Roasted vegetables Roasted garlic, black garlic,
roasted corn
Temperature control is required for safety; therefore, KDA Food Estab-
lishment license is required. If you are selling raw produce and providing
roasting services on-site, a license is required. Wash produce before
roasting. NO license required if sold 6 days or less in a year. Licensing
required if sold more than 6 days in a year.
Meat, poultry (>20,000 birds/
year), and catsh — raw
Note: products containing 2%
or more cooked meat or poultry
or more than 3% raw meat by
weight are considered meat
products.
Steaks, ground beef, fresh sau-
sages, turkey, chicken, catsh
Product must be processed at a fully an inspected facility, pre-packaged,
and properly labeled. A KDA Meat & Poultry Wholesale license must be
obtained before any product is sold, regardless if the target buyer is the
end consumer or a wholesale account. Product may be sold refrigerated
or frozen.
Meat, poultry, and catsh
ready-to-eat
Jerky, summer sausage and simi-
lar products, freeze-dried meat
Product must be inspected by KDA or USDA and sold at the appropriate
temperature. Meat products cured with nitrites require proper licensing.
Fish and seafood — cleaned
(other than catsh — see more
information on that above)
Degutted tilapia KDA Food Establishment or Food Processing license at preparation
facility, and Food Establishment license at the point of sale. A Seafood
HACCP plan is also needed if any hazards are identied. Wild-caught sh
sales are illegal without a commercial shing permit from the Kansas
Department of Wildlife, Parks and Tourism.
Vacuum-packaged foods
requiring temperature control
for safety
Vacuum-packaged cheese or
vacuum-packaged meats requir-
ing refrigeration for safety
Must follow the requirements listed above for cheese or meat products
or whatever category the food is in.
Sprouted grains (fresh or dried/
dehydrated)
Sprouted buckwheat KDA Food Establishment license required for production facility and for
the point of sale.
Sprouts Alfalfa sprouts, bean sprouts KDA Food Establishment license required at production facility and
point of sale.
Low-acid vegetable juices that
have been heat treated and
sealed
Juice from kale or other leafy
greens, carrot, celery, beet juice
that has been heat treated and
sealed
KDA Food Establishment license required at production facility and
point of sale. A license is also required if juice is sold by the cup/glass.
Wild mushrooms Morel mushrooms Mushrooms picked in the wild must be individually inspected for safety
by a KDA-registered mushroom identier. More information available in
the Selling Fresh Produce section (page 10).
Naturally fermented canned
foods
Sauerkraut, kimchi, kombucha,
naturally fermented pickles
KDA Food Establishment License required for production facility.
Symbiotic culture of bacteria
and yeast (SCOBY)
Used for production of kombu-
cha
KDA Food Establishment License required for production facility.
• Acidied shelf-stable canned
foods
• Low-acid shelf-stable canned
foods
• Pickles (includes pickled cucum-
bers, okra, and other vegetables
and pickled eggs), hot sauces,
lemon curd, canned tomatoes
†
• Canned vegetables, canned
pumpkin pie lling, canned
vegetable juice, shelf-stable cold-
brew coee, meats, cake/bread
baked in a jar
‡
KDA Food Establishment License or Food Processing License required
for production facility. Requires Process Authority review and recipe
approval; Better Process Control School (BPCS) required. KDA Meat and
Poultry inspection required if canned meat is sold wholesale. Contact
Kansas State University Value-Added Foods Lab for more information on
recipe approval and BPCS: www.ksre.ksu.edu/kva
Foods and beverages prepared
on or o site, sold ready for
immediate consumption — six
or more times per calendar year.
Burritos, egg rolls, pizza, grilled
hamburgers or other meats;
lemonade, refrigerated cold-
brew coee
If selling more than six times/year, vendor must have a KDA Food Estab-
lishment license. A Food Processing license is required for any wholesale
sales. KDA inspection is required for any wholesale sales.
Foods THAT REQUIRE proper licensing, cont.

6 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
Food Product Type Examples Regulatory requirements
Non-specialized processed
food that is made and sold six
or more days in a year. (Intended
for people to purchase and
consume at home.)
Frozen bierocks, frozen protein
popsicles, pork rinds, refrigerated
noodles, pesto, refrigerator pick-
les, refrigerated salsa, refrigerat-
ed elderberry syrup, refrigerated
cold brew coee, etc.
The calculation of 6 days or more includes the day the product is made
and each day they are sold. Food Establishment license is required. A
Food Processing license is required for any wholesale sales. KDA inspec-
tion is required for any meat or poultry wholesale sales.
Alcoholic beverages Beer, wine, possibly kombucha
drinks
Kansas Dept. of Revenue alcohol licensing requirements must be met.
(www.ksrevenue.org/abcstatutes.html)
Infused oils Infused cooking olive oils; garlic-
in-oil mixtures
KDA Food Establishment License or Food Processing License required
for production facility. If nished product is not shelf stable, Food Estab-
lishment license also required for point-of-sale.
Animal feed/treats Pet food/treats — regardless of
the type of ingredients in the pet
treats (meat or grain, etc.) or the
method of preparation (freeze
drying or other).
Kansas commercial feed license and small pet product application
required. Food safety license not required (may be made in a home
kitchen). Guaranteed analysis for protein, fat, and ber, and ingredient
statement required on label. (More information available from: http://
agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/dairy-inspection/feed-safety/feed-li-
censes) For more assistance with pet foods, contact the K-State Pet Food
Program at https://www.k-state.edu/pet-food/
Broths Bone broth If broth includes less than 2% meat or poultry (after cooking), KDA Food
Establishment license required for direct-to-consumer sales. KDA Food
Processing license required if selling wholesale. If canned and sold
shelf stable, follow acidied or low-acid canned food requirements (see
above).
Dairy products; milk Milk, cheese, yogurt, etc. from
cows, goats, other mammals
Pasteurized and processed at KDA licensed Dairy Manufacturing Plant;
KDA Food Establishment license required at point of sale. If a vendor can
provide information about a vacuum packaged cheese to show that it
does not require refrigeration for safety (typically low water activity and
low pH values), a Food Establishment license would NOT be required for
the point of sale. These regulations apply to products that start with a
raw milk product and is then pasteurized. If a producer purchases pas-
teurized milk to include in a product, the product would fall under the
appropriate category for the nal product. Note that freeze drying milk
and milk products requires proper licensing
Candy containing >1% alcohol
by volume
Bourbon balls
KDOR non-beverage manufacturer license would be required. More in-
formation available here: https://www.ksrevenue.gov/abcnonbevuser.html
Food Product Type Nature of test Notes
Pepper jams and jellies (canned,
shelf-stable, other than those
described above as exempt). In-
cludes jellies made with pepper
juice.
pH and/or water activity
‡
,
product formulation
If product is determined to have low water activity or is a formulated acid
food, product can be sold without a license. Otherwise, a KDA Food Estab-
lishment license required.
Flower jellies pH and/or water activity, prod-
uct formulation
If product is determined to be an acid food, formulated acid, or low water
activity food, no license is required. Otherwise, a KDA Food Establishment
license is required.
Low-sugar fruit jams and jellies
(canned, shelf-stable)
pH and/or water activity, prod-
uct formulation
If product is determined to be an acid food, formulated acid, or low water
activity food, no license is required. Otherwise, a KDA Food Establishment
license is required.
"Formulated acid food": salsa,
barbecue sauce and similar
foods (canned, shelf-stable). This
category also includes pur-
chased pickles repacked with
sugar and hot sauce.
pH and product formulation Depending on the pH of the nal product and the main product ingredi-
ents, the product may be exempt from licensing
†
or may be considered
an acidied canned food that requires a Food Establishment license (see
information on acidied foods in table above).
† Canned tomatoes must either have added acid (2 Tablespoons of bottled lemon juice, ½ teaspoon citric acid, OR 4 Tablespoons of 5% acidity vinegar per quart of
tomatoes. For pints, use half the amounts listed above.) Otherwise, a pH test (by the KS Value Added Foods Lab or other) must ensure it is below pH 4.6.
‡ Note that these products could be sold under refrigeration without the requirement for BPCS or a scheduled process (by a Process Authority), but they would still
require a Food Establishment license for direct-to-consumer sales.
Foods that must tested to determine if a license is required or not
Producers can send their products to the Kansas Value Added Foods Lab (www.ksre.ksu.edu/kva) or another accredited lab for testing. In addition
to the pricing listed on the website, pricing for individual tests is also available. Contact kva@ksu.edu or 785-532-1294 for more information. For
all products requiring testing, documentation of the product assessment must be kept by the operator and made available upon request.
K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices 7
Food Product Type Nature of test Notes
Homemade chocolate candies;
meringue cookies
Water Activity and product
formulation
If product is determined to require temperature control for safety in a
product assessment, KDA Food Establishment license is required. Other-
wise, no license is required.
Pecan pie Water activity of the lling If the lling is determined to require temperature control based on its
water activity, KDA Food Establishment license is required. Otherwise, no
license is required.
Powdered sugar/ milk icing Water activity of the icing Often used on cinnamon rolls and similar products. If product is deter-
mined to have low water activity, product can be sold without a license.
Otherwise, KDA Food Establishment license required. If the icing is
known to contain >65% sugar by weight, testing and licensing is not
needed.
Bread with cheese and/or vege-
tables (e.g. jalapenos) baked in/
on top
Water activity and product
formulation
If product is determined to have low water activity and thus not require
refrigeration for safety, product can be sold without a license. Otherwise,
KDA Food Establishment license required.
Homemade mustard pH and product formulation If the product is determined to have pH below 4.6 and that it can be safely
stored at room temperature, product can be sold direct-to-consumer
without a license. Otherwise, KDA Food Establishment license is required.
Herb-infused simple syrups, el-
derberry and other fruit syrups,
shagbark hickory syrup (sold
shelf-stable)
Water activity, product formu-
lation
If product is determined to be a low water activity food, no license is re-
quired. Otherwise, KDA Food Establishment license is required. If the ratio
of sugar-to-water in the syrup is at least 2:1, a license is not required and
no testing is required.
Tomato juice pH If the product is determined to have pH below 4.6, packaged product
can be sold direct-to -consumer without a license. Otherwise, KDA Food
Establishment license is required.
Pumpkin butter, squash butter Water activity, pH, product
formulation
If product is determined to be a low water activity food and/or below 4.6
pH, no license is required. Otherwise, KDA Food Establishment license is
required.
Candy containing <1% alcohol
by volume
Bourbon balls If the product water activity is <0.85, no license is required. If product
water activity is >0.85, KDA Food Establishment license is required.
How do I get the license(s) I need to meet the
requirements listed above?
More information on food safety licenses and the forms
needed to apply for the license is available from the Kansas
Department of Agriculture website: http://agriculture.ks.gov/
divisions-programs/food-safety-lodging/food-safety-egg-lodging-
app-forms or by contacting KDA Food Safety and Lodging
program ([email protected] or 785-564-6767). To obtain a KDA
Meat & Poultry Wholesale license for meat and/or poultry sales,
please contact KDA Meat & Poultry Inspection program (785-
564-6776). KDA will guide you through the process and answer
questions. After the appropriate application form is completed,
send the form with your payment to KDA. ey will contact you
to conduct an initial inspection.
What if I produce (and/or process) my food in Kansas
and want to sell in a neighboring state?
To sell products across state lines, you need to meet Federal
requirements, as well as the retail regulations for Kansas and the
state in which you are selling.
• To sell a processed (non-meat) product, you will need
to initially register (at no cost) your processing facility
online with the FDA, and then re-register it every 2 years
(October–December of the even numbered years (2018,
2020, etc.)), at: www.fda.gov/Food/GuidanceRegulation/
FoodFacilityRegistration/default.htm. FDA may then come
inspect your facility, and verify you are meeting their current
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs
1
– Code of Federal
Regulations (CFR) Title 21 Part 110: www.accessdata.fda.
gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?CFRPart=110)
and any other applicable regulations such as Acidied Foods
or Low Acid Canned Foods regulations. Such products may
also need to follow the requirements of the Federal Food
Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Preventive Controls
Rule, www.fda.gov/fsma (depending on the volume of
product sold).
• To sell a meat product across state lines, you must be
licensed with the USDA FSIS as a federally inspected
facility. A facility licensed with KDA Meat & Poultry
Inspection only cannot sell products across state lines.
• To sell fresh, whole produce, you may be impacted by
the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), regardless
if you are only selling in-state or across state lines. More
information available from: www.ksre.k-state.edu/foodsafety/
produce/index.html
1 A fact sheet on GMPs is available from: bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3201.pdf
‡ For more information about Product Water Activity and food safety, see Food Safety of Frostings and Fillings (MF3544),
https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3544.pdf
† Even if considered exempt, the producer should check the pH periodically to make sure the product pH (primarily the tomatoes) does not have large variations.
These pH records should also be kept by the producer.

8 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
In addition to food safety, what other regulatory
requirements do I need to follow to sell at a farmers
market?
• Sales tax: Every vendor must obtain a Retail Sales Tax
certicate; vendors should le their tax liability individually.
More information is available from the Kansas Department
of Revenue (https://www.ksrevenue.gov/bustaxtypessales.html)
or by calling 785-368-8222.
• Filing as a business entity: e Oce of the Secretary of
State (SOS) has the appropriate forms available online
2
or
by contacting 785-296-4564. Sole proprietorships do NOT
le with the SOS. General partnerships may le if desired,
but it is not required
3
.
• Registration of farmers market or roadside stand: Farmers
markets (as a whole, rather than individual vendors) and
roadside stands are encouraged to register in the Central
Registry of Kansas Farmers Markets
4
. Registration is
voluntary, but will provide advertising and limited liability
coverage for farmers markets and roadside stands.
• Licensing of particular products: More information on
the licensing requirements for growing, producing and
selling specic types of food products is available in KDA’s
Licensing Guides
5
. Topics of particular interest to farmers
market vendors include: food processor, food wholesaler
and distributor, home kitchen for retail food sales, meat or
poultry processing facility, mobile food unit, dairy processing
facility, and poultry farm and egg sales.
• Senior Farmers Market Nutrition Program (SFMNP):
Farmers, farmers markets, and roadside stands are eligible to
accept SFMNP coupons from customers. More information
on how to accept and redeem SFMNP coupons is available
from https://www.kdhe.ks.gov/1041/Kansas-Senior-Farmers-
Market-Nutrition-P.
• Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP):
Farmers markets are eligible to accept SNAP benets from
customers. Visit the USDA website
6
for more information
on accepting and redeeming SNAP benets from customers.
• Scale testing: Farmers market vendors using a scale to sell
products by weight must have a licensed service company
7
test their scales once annually. More information is available
from the KDA Weights and Measures website
8
or by calling
785-564-6700.
What are the labeling requirements for packaged food
products?
9
1. Common name of the product (e.g. apple pie).
2 Forms available from: www.kssos.org/forms/forms_results.aspx?division=BS
3 More information available from: hps://sos.ks.gov/business/business.html
4 Application and more information available from: www.agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-
source/ag-markeng/central-registraon-of-kansas-farmers%27-markets.pdf?sfvrsn=0
5 Licensing guides are available from:
hps://agriculture.ks.gov/kda-services/licensing-guides
6 USDA SNAP website: hps://snaped.fns.usda.gov/nutrion-educaon/nutrion-
educaon-materials/farmers-markets
7 List of licensed scale service companies available from:
hp://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/weight-measures/scales
8 KDA Weights and Measures website:
hp://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/weight-measures
9 More information on food labeling is available from a KSU Extension Food Safety
publication, Food Labeling for Kansas Food Producers and Processors: https://bookstore.
ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3385.pdf; or by contacting KDA Food Safety and Lodging (785-
564-6767 or KDA. [email protected]).
2. Name and physical address of the person that made or is
selling the product.
3. Product ingredients listed in descending order of
predominance. is is particularly important for customers
that have food allergies.
4. Quantity (net weight, volume, or count, depending on
product).
Meat products have additional labeling requirements, which
are included in the Selling Meat, Eggs and Dairy Products section.
If producers would like to label their product as “organic,”
they must meet the USDA organic certication requirements.
More information on obtaining such certication, including an
Organic Cost Share Program for Kansas farmers, is available
from: http://agriculture.ks.gov/kda-services/grants-and-cost-share-
programs/organic-cost-share-program. If products are labeled as
certied organic, proof of that certication must be on le with
the relevant state oce regulating the labeling of that product.
How are all these regulations enforced?
e Kansas Department of Agriculture Food Safety and
Lodging Program local inspectors and KDA meat and poultry
compliance ocers conduct random inspections of vendors at
farmers markets to check for food safety.
Farmers market managers, K-State Research and Extension
personnel, and other related individuals should only provide
information on regulations and could make suggestions on
how vendors can comply with regulations. However, they are
not regulators or enforcers of government regulations. Farmers
market managers should enforce any requirements specic to
their market.
General Food Safety Practices, Selling Fresh
Produce, Samples and Demos
All practices listed in the sections below which are REQUIRED by
state regulations are listed in bold and italics. All other practices listed
are strongly recommended for food safety.
Retail food sales (including at farmers markets) in Kansas
are regulated by the Kansas Department of Agriculture (KDA).
However, vendors should always check with the market where they
are selling, as their requirements may be more stringent than state
governmental regulations.
General steps to food safety for all farmers market
vendors
• Transport and store foods at proper temperatures to prevent
rapid bacterial growth
• Vendors selling perishable foods must have a suitable
thermometer with them at the market.
• Hot prepared foods must be held at 135°F or higher.
• Foods to be sold at room temperature (whole produce,
canned goods, baked goods) should be kept cooler than
80°F as much as possible.
• Cold perishable foods (such as potato salad or most dairy
products) must be 41°F or less.
• Frozen foods such as frozen meats and ice cream must be

K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices 9
Table 1. Method of Retail Sale for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Specic Commodity
Commodity Weight Count
Head or
Bunch
Dry Measure
(any
s
i
ze)
Dry
Measure
(1 dry qt
or
l
arger)
Artichokes X
X
Asparagus X X
Avocados X
Bananas X
X
Beans (green, yellow, etc.) X X
Brussels Sprouts (loose) X
Brussels Sprouts (on stalk) X
Cherries X X
X
Coconuts X
X
Corn on the Cob X X
Dates X
Eggplant X
X
Figs X
Grapes X
Melons (cut in pieces) X
Mushrooms (small) X X
X
Mushrooms (portobello, large) X
X
Okra X
Peas X X
Peppers (bell and other varieties) X
X
X
Pineapples X
X
Rhubarb X
X
Tomatoes (except cherry/grape) X
X
X
Table 2. Method of Retail Sale for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables General Commodity Groups
Commodity Weight Count
Head or
Bunch
Dry Measure
(any
s
i
ze) Dry
Measure
(1
dry qt
or
l
arger)
Berries and Cherry/Grape Tomatoes X X
Citrus Fruits (oranges, grapefruits,
lemons, etc.)
X
X
X
Edible Bulbs (onions [spring or green],
garlic, leeks, etc.) X X X X
Edible Tubers (Irish potatoes, sweet
potatoes, ginger, horseradish, etc.) X X
Flower Vegetables (broccoli,
cauliower, brussels sprouts, etc.) X X
Gourd Vegetables (cucumbers, squash,
melons, etc.) X X X
Leaf Vegetables (lettuce, cabbage,
celery, etc.)*
X X
Leaf Vegetables (parsley, herbs, loose
greens)*
X X
X
Pitted Fruits (peaches, plums, prunes,
etc.)
X
X
X
Pome Fruits (apples, pears, mangoes,
etc.)
X
X
X
Root Vegetables (turnips, carrots,
radishes, etc.)
X X
*Gallon bags are NOT considered a dry measure, so leafy greens cannot be sold by the gallon. They would need to be sold by a 4 quart dry measure container (or other dry measure, or by
the head/bunch, or by weight.) The product must be measured by an acceptable measurement and then could be transferred to a re-closeable plasc bag for transportaon home.

10 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
stored and sold frozen (below 0°F is the best practice).
• Coolers and ice packs or ice surrounding the product
can be used to transport and hold cold foods. Check the
temperature occasionally (about once/hour) with a stem
food thermometer
10
.
• Reduce possible cross-contamination that can transfer
bacteria from one food to another.
• Ensure that raw meat or poultry does not contact ready-
to-eat food or fresh produce.
• If re-using bags for selling products, they must be clean
and not previously used for meat.
• Wash, rinse, and sanitize food contact surfaces,
equipment, and utensils between uses (unless using
disposable equipment and utensils).
• Practice good personal hygiene (clean clothes, clean hands)
to prevent transferring bacteria to your food.
• Shaking hands, touching money, animals, soiled
produce, or utensils can transfer bacteria to your hands.
• Wash hands as needed and do not touch prepared foods
and baked goods with your bare hands (use gloves or
tongs or other method).
• Hand sanitizer is not a substitute for handwashing;
however, it can be used after washing your hands.
• Ensure that any ingredients you use to prepare food for market
are from safe sources.
• For example, use inspected meat, pasteurized milk from
a licensed producer, and ingredients from reputable
suppliers. Ensure that produce or other products have
not been contaminated with ood waters, etc.
• Food vendors are not allowed to have dogs (or other
animals), except for service animals in or near their booths
(where food is displayed).
• e common areas of the farmers market outside of the
vendor’s booth are governed by the market and local
rules related to pets being present (there are no state
rules in this regard).
• Dispose of any food that might have been contaminated
by a dog or other pet.
• More specic information on good food safety practices and
requirements for various types of food are included in the
relevant section of this document.
Chef demonstrations
• Foods prepared at chef demonstrations can be oered as
small samples at no cost. ere is no limit to the number of
times/year that such samples can be oered.
• If the resulting food does NOT meet the sample denition
(oered at a cost or larger portions), that individual can do
six or less such demonstrations per calendar year without a
license.
10 Stem food thermometers and refrigerator thermometers can be purchased for
less than $10 at most grocery stores and hardware stores. Be sure the stem food
thermometer can be calibrated and check its calibration occasionally to ensure
accuracy.
• Even if not licensed, the chef must still follow the
“Sanitation and hygiene requirements for exempt
food establishments” listed in Kansas Administrative
Regulation 4-28-33. is is similar to the provisions for
licensing for a Food Establishment (including a Mobile
Unit) (see section on Selling Prepared Foods and Baked
Goods).
• It is recommended that a chef do the majority of
preparation work at a licensed facility.
• If a person sells the results of a chef demonstration more than
six times per year, a Food Establishment License is required.
• Contact KDA’s Food Safety and Lodging program for more
information ([email protected] or 785-564-6767).
Selling fresh produce
• Unprocessed whole fruits and vegetables, nuts and other
whole agricultural products do not require inspection
for sale, unless they would be covered by the FDA Food
Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Produce Safety Rule
11
.
Inspections under the Produce Safety Rule are pre-
announced.
• Produce growers selling at markets are encouraged to know,
understand and apply the principles of the FSMA Produce
Safety Rule, even if they are exempt from FSMA coverage.
• Vendors must follow the KDA Weights and Measures Division
regulations
12
for the method of selling produce (by weight,
count, head or bunch, or by dry measure) e list of allowed
methods of retail sale by commodity is available in Tables 1
and 2.
• Vendors using a scale to sell products by weight must have
a licensed service company
13
certify their scales
14
annually.
Before buying a new scale, ensure that the scale can
be certied. Information on buying scales is available
from: https://cdn.ncwm.com/userles/les/Resources/
Consumer%20Information/Buying%20Scales%20Online.
pdf. Scales can also be purchased through any of the
scale service companies licensed in Kansas
• Produce must be stored and displayed so it is protected from
contamination.
• Store o the ground and protect from rain, dust or other
environmental contaminants.
• Sprouted seeds are NOT allowed for sale at a farmers market
without proper food safety licensing from KDA.
• Mushrooms picked in the wild must be individually inspected
for safety by a KDA-registered mushroom identier.
• To become a registered mushroom identier, a
statement of qualication in mushroom identication
must be submitted to KDA’s Food Safety and Lodging
11 More information on FSMA is available from www.ksre.k-state.edu/foodsafety/produce
12 More information is available from hp://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/weight-
measures
13 List of companies available from: hp://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/weight-
measures/scales
14 Reporting form for KDA Weights and Measures available from: hp://agriculture.
ks.gov/docs/w-m/scale-di701.pdf?sfvrsn=2
Information on buying scales is available from: https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-
source/w-m/scale-di701.pdf?sfvrsn=cde3b376

K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices 11
program via email, [email protected]; fax, 785-564-
6779; or in person. One way for the applicant to be
considered a registered mushroom identier is to
complete a certication workshop or course , but
attendance at a workshop is not required to be added to
the registry. Once the identier is registered by KDA,
the identier must individually identify each mushroom
sold. Mushrooms may not be harvested for sale without
prior approval from the landowner, either public or
private.
• Contact KDA for more information or for a list of
experts ([email protected], 785-564-6767, or fax: 785-
564-6779).
• If not processed beyond cleaning and not heat-
treated, cultivated mushrooms may be sold without
a license. Mushrooms must be grown in protected
environments and kept free from contaminants.
Following the Mushroom Good Agricultural Practices
is recommended: https://www.ams.usda.gov/services/
auditing/gap-ghp/mushroom-gap. Mushrooms should not
be packaged to be sealed from normal atmosphere (such
as vacuum packing or heat-shrink plastic). Any plastic
lm used to package fresh mushrooms must be visibly
perforated to allow air circulation to the mushrooms.
Studies have shown that this can be accomplished with
a minimum of two 3.0 mm (approximately 1/8 inch)
holes situated over the top of the tray. Alternatively,
lines of perforations which provide an air exchange
equivalent to the 3.0 mm holes are acceptable.
Additional information is available from: www.
americanmushroom.org/food-safety/food-safety-training-
kit/
• Oer clean produce. If appropriate, wash produce with
potable water before selling. Remove visible dirt from
potatoes, onions, and other products where washing would
reduce quality or increase spoilage.
• Water used to “freshen” produce at market must be potable
(suitable for drinking).
• Transport produce to market in clean boxes or containers.
Selling live plants at a farmers market
• If someone selling live plants (including “living greens,” such
as microgreens still growing in their grow trays) collects
MORE than $10,000 annually in gross receipts from the
live plant sales, they are required to have a live plant dealer
license.
• Live plants include any living plant, cultivated or wild, or
any part thereof, that can be propagated, EXCEPT for the
following:
1. eld and forage crops;
2. seeds of any kind;
3. cut owers and cut greenery not used for propagation; and
4. fruits and vegetables used for food or feed. If someone
selling live plants is exempt from the requirements of a live
plant dealer license, the vendor still needs to request the
exemption by lling out an application from https://www.
agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-source/default-document-library/
live-plant-dealer-application.pdf
• More information and an application are available from the
KDA Plant Protection and Weed Control Program: http://
agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/plant-protect-weed-
control/live-plant-dealer or by calling 785-564-6700.
Selling unique agricultural products (live birds,
manure, worms, compost, etc.)
ere are currently no ocial state requirements for selling
agricultural products such as live chickens, manure, worms,
compost, etc. at farmers markets. Vendors should check with the
market where they are selling, as well as to see if there are any
local policies restricting the sale of these products. Contact KDA
with any additional questions: [email protected] or 785-564-
6700 or https://agriculture.ks.gov/contact-us.
Oering product samples
Providing samples at a farmers market is allowed if certain
conditions are met. e fact sheet Sampling Safely at Kansas
Farmers Markets, Farm Stands, and Related Events contains
detailed information on sampling and is available at
bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3311.pdf
Note: ere is NO limit to the number of times per year that
samples can be oered. Any food product legal to sell can be
sampled. Wine can also be sampled, but the vendor must obtain
a special event permit from the Kansas Division of Alcoholic
Beverage Control (www.ksrevenue.org/abc.html).
Calibrating a thermometer
ermometers must be used to measure the temperature of food
that is sold or provided as samples if that food requires temperature
control for safety. at thermometer must be properly calibrated
before each day’s use to ensure accuracy, following the procedure
below:
1. Fill a cup with ice.
2. Add enough water so that there is at least 2 inches of liquid
in the bottom of the cup.
3. Leave the thermometer in the cup for at least 2 minutes to
equilibrate.
4. Read the thermometer. If it does not read 32°F, adjust
Head
Hex adjusting nut
Stem
Ice water
(32ºF, 0ºC)
2” (5 cm)
minimum

12 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
the thermometer reading according to the thermometer
instructions — often by turning (with a pliers) the hex
adjusting nut immediately below the thermometer head.
Digital thermometers may not be adjustable and should be
replaced if inaccurate.
5. If adjustments were made, recheck the temperature reading
in ice water.
Keep in mind the following tips:
• Be sure that your thermometer is designed for the
temperature range in which it will be used. ermometers
designed only for hot foods are discouraged because the ice
water temperature check is not possible.
• Hot foods: 135°F to at least 165°F
• Cold foods: at least 0°F to 41°F
• Temperatures should be taken once per hour to ensure the
foods are the proper temperature.
Selling Prepared Foods and Baked Goods
**Practices below that are REQUIRED by state regulations
are listed in bold and italics. All other practices listed are strongly
recommended for food safety.
Selling Prepared Foods (ready-for-immediate-
consumption foods that require temperature control
for safety)
Please refer to KSRE/KDA publication Food Handling
Guidelines for Exempt Food Vendors (https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.
edu/pubs/MF3472.pdf) for more information on the licensing
requirements for selling prepared foods for immediate
consumption.
How do I get a Food Establishment License?
Vendors must complete and submit a license application
15
along with the appropriate fees, which includes an application
and an annual license fee that varies depending on the type and
size of operation. e facility must also pass a KDA licensing
inspection. Most farmers market vendors will also need to
complete the Mobile Unit Log
16
, providing information to KDA
on the city or cities where you will be operating. e equipment
required depends on the menu items served. In general, the
following is required to be in your farmers market stand when
selling foods ready for immediate consumption
17
:
• Hand washing facilities.
• Ability to control temperature of perishable foods.
• Potable water (drinking water) supply.
• Sewage storage tank and ability to transport for proper
disposal in a sanitary sewer (not a storm sewer).
What are the regulations for selling prepared (or
15 Available from: http://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/food-safety-lodging/food-
safety-licenses or by contacting the KDA Food Safety and Lodging program at
[email protected] or 785-564-6767.
16 http://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-source/rc-food-safety/mobile_unit_log.
pdf?sfvrsn=2
17 More detailed requirements are listed in the Kansas Food Code (2012):
hps://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-source/fsl--handouts/2012_kda_food_
code_12_14_12.pdf
shelf stable) foods through a Community Supported
Agriculture (CSA)?
e regulations for each type of product would be similar to
those for selling at a farmers market as it is generally considered
a direct-to-consumer sale. e regulations would also vary
depending on the type of business relationship. Contact the
KDA Food Safety and Lodging program for more information.
Selling baked goods (breads, cakes, cookies, pies, etc.)
• Products should be proportioned and pre-packaged in clean,
new wrappings, jars, or bags.
• Packages should be sealed and not be opened to sell
part of the contents.
• If a vendor displays products in bulk and then pulls out
individual orders for customers onsite, the vendor must
have handwashing facilities in their booth.
Selling jams, jellies, and shelf-stable canned foods
See KSRE publication “Selling Safe Canned Foods in
Kansas” https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3555.pdf for more
information on selling canned foods.
Selling refrigerated/frozen processed foods
Examples include garlic-in-oil mixtures, and other products
containing ingredients that require temperature control for
safety.
• Requirements for selling include:
• Producer must have the appropriate KDA Food License
(likely a Food Establishment License).
• e facility must be suitable for the process to
obtain a license.
• e license is for the producer in a specic
facility. You cannot operate under someone
else’s license unless they are willing to take on
the liability.
• Product must be labeled according to the food labeling
requirements listed in the baked goods section.
• Proper temperature (<41°F for refrigerated, <0°F for
frozen) must be maintained at the market.
• Processed food containing 2% or more cooked meat or
cooked poultry by weight or more than 3% raw meat by
weight that is sold wholesale (not direct-to-consumer)
refrigerated or frozen must be processed at a USDA or
KDA meat inspected facility.
• Most non-specialized processed food, such as frozen
bierocks, can use the 6-day exemption of not requiring a
license. e product can be made on day one and each day
they are sold adds up to a total of 6 days without requiring
a license. However, the producer must follow Kansas
Administrative Regulations (KAR) 4-28-33 “Sanitation
and hygiene requirements for exempt food establishments.”
More details also in KAR 4-28-34 (Exemption from
licensure; denitions).
• If a licensed restaurant is selling products such as salsa at a
farmers market, the restaurant would not need an additional
license if the salsa formulation has been conrmed as

K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices 13
an acid food and it is packaged at the restaurant. If not,
then the restaurant would need an additional mobile food
establishment license for the point of sale, if done more
than 6 times in a year at any location other than the licensed
location (the restaurant).
Selling Meat, Eggs, and Dairy Products
Selling meat and poultry products
**Practices below that are REQUIRED by KDA regulations
are listed in bold and italics. All other practices listed are strongly
recommended for food safety.
Meat and poultry products (raw or processed)
18
must meet the
following requirements:
• Meat labeled as “Custom – Not for Sale” cannot be used for
retail sales.
• All meat and poultry products must be slaughtered and
processed in either a USDA or KDA fully inspected facility
and labeled properly for resale.
• Poultry growers raising fewer than 1,000 birds/year can
slaughter and sell these birds direct-to-consumer at their
own facility without registration or inspection. e same is
true for rabbits, but the exemption limit is 250 head/year.
• Growers selling 1,001 to 20,000 birds/year must
register their exemption from inspection with the
KDA Meat & Poultry Inspection Program by
obtaining a KDA Poultry Wholesaler license with
a poultry exemption. Registration form and more
details available at https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-
source/meat-and-poultry/poultry-exemption-5-1-19.
pdf?sfvrsn=43488bc1_4
• Poultry growers raising more than 20,000 birds/year
must only sell product that has been slaughtered and
processed at an inspected facility.
• When selling meat either wholesale or direct-to-consumer,
product must be slaughtered and processed under USDA
or KDA inspection at a KDA or USDA fully inspected
facility.
• Meat packaging labels must be approved by the KDA Meat
and Poultry program or USDA and all labels must be applied
by the inspected facility. Only a farm label, with business
name and contact information only, may be applied by the
business.
• Label claims such as grain or grass fed and raised without
antibiotics must be registered (at no cost) with KDA
19
,
including provision of appropriate documentation for
approval.
• Meat products must be held, stored, and transported in a clean
and sanitary environment, to keep products wholesome. is
includes having a proper rodent and insect control program.
If a vendor sells only products bearing the mark of inspection in
the original packaging, they must have a KDA Meat & Poultry
18 Products containing 2% or more cooked meat or cooked poultry or more than 3% raw
meat by weight are considered meat and poultry products.
19 Contact the KDA Meat and Poultry program at 785-564-6776 for more information on
registering label claims and label requirements. Information on the meanings of meat
label claims is available from: bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3209.pdf
Wholesaler License for the point of sale.
• Any person engaged in the distribution of inspected and passed
meat, meat products, poultry, or poultry products within the
state of Kansas must obtain a KDA Meat & Poultry Wholesaler
license through the KDA Meat & Poultry Inspection Program.
is includes selling both direct-to-consumer and to wholesale
accounts (i.e. restaurants, retail stores).
• License must be renewed annually, at a cost of $25/ year
20
.
• Raw product must be transported and sold solidly frozen
(0°F or below) or fresh (36°F or below) in freezers or coolers
equipped with properly calibrated thermometers.
Other regulations and recommended best practices for
selling meat and poultry
• Coolers and ice packs or ice can be used to safely transport
and hold meats. Vendors must have a thermometer. Check
the temperature occasionally (about once/hour) with a stem
food thermometer
21
.
• In storage and display, ensure that the juices of one species
(for example, beef, chicken, pork, etc.) do not drip onto and
contaminate another species, or any other type of product, with
bacteria.
• Bag meat separately from any other products
(particularly fresh produce, ready-to-eat foods, baked
goods) to prevent cross-contamination.
• Label the product with “Safe Handling Instructions”
22
and
understand these safe practices so that you can explain them
to customers to increase the likelihood that the customer
will handle the product safely.
Selling eggs
If you have 50 or fewer hens and all sales are direct to
consumers, you are exempt from all requirements for selling eggs
unless you choose to grade your eggs or sell them for resale. You
can choose to sell ungraded or graded eggs.
• Selling graded eggs
23
requires obtaining a Kansas Egg License
and paying inspection fees.
20 License application available from: hps://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/meat-
and-poultry-inspecon/registraon
21 Stem food thermometers and refrigerator thermometers can be purchased for around
$10 at most grocery stores, variety stores, and hardware stores. Quick-read digital
thermometers usually cost only a little more. Be sure the food thermometer can be
calibrated and check its calibration occasionally.
22 These instructions are available from: https://www.fsis.usda.gov/sites/default/les/
media_le/2021-08/Safe_Handling2.pdf
23 More information on egg sales requirements, including for selling graded eggs is
available: hp://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/food-safety-lodging/food-safety-
egg-lodging-app-forms
USDA

14 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
Regardless of ock size, the items listed below (which are
requirements for vendors with 51 or more hens) are strongly
recommended best practices to reduce the risk of illness.
Although it is not required for vendors with fewer than 50 hens,
it is strongly recommended to keep eggs at temperatures below
45°F for safety. (Find more information in the Egg Fact Sheet at
https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-source/rc-food-safety/egg-fact-
sheet-selling-eggs-without-a-license.pdf.)
If you have 51 to 249 hens, the following requirements must
be met to sell eggs at a farmers market:
• Eggs must be kept at or below 45°F when transporting,
storing and displaying.
• is requires that eggs are in a cooler or similar
temperature-controlled container.
• If you want to display an open egg carton on your table,
you should hard boil then air cool those eggs and mark
the display with a sign stating “For display only. Not for
sale.”
• If re-using egg cartons, make sure they are clean and free of
any foreign materials, to prevent the transfer of bacteria to
the eggs.
• Mark out all incorrect information, such as the previous
producer’s name and address, grade and previous pack
and expiration dates.
• Eggs must be washed and cleaned before sale.
• All egg cartons must be labeled with the following:
• Name and address of the producer
• Quantity of eggs
• Identity if other than chicken eggs (for example, duck,
goose, etc.)
• Note that eggs sold graded have additional labeling
requirements and require a Kansas egg license and
inspection fees.
• If all sales are direct to consumers, you can choose to sell
graded or ungraded eggs (selling graded eggs requires a
Kansas egg license and inspection fees). If you are selling
ungraded eggs, you must label the carton as being ungraded.
If you have more than 249 hens, you are required to obtain a
Kansas Egg License, sell only graded eggs, and pay inspection fees.
Note: Eggs other than chicken eggs can be sold and must
meet the same requirements as listed above for each ock size
but can only be sold ungraded.
• Baluts (fertilized eggs incubated for a period of time shorter
than required for hatching) can be sold but must follow
certain requirements. (More information on selling baluts is
available in the KDA Egg Fact Sheet.
24
)
Selling dairy products
e following requirements must be met:
• All dairy products sold at a farmers market must be produced
in a KDA-inspected dairy processing plant.
• KDA Dairy Inspectors are available to help in planning
24 https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-source/rc-food-safety/egg-fact-sheet-last-handler-
distributor.pdf?sfvrsn=2847bbc1_4
stages of facility.
• Dairy processing plants are inspected about six times
per year, with frequent testing of pasteurization
equipment and sample testing.
• Labeling and label claims for dairy products must be approved
by KDA Dairy Inspection program
25
.
• Vendors that are selling directly to the consumer must have a
KDA Food Establishment license for the point of sale (at the
farmers market).
• Milk, cheese, and other non-frozen dairy products must be
maintained at <45°F at all times for safety and should be
<40°F for product quality.
• Frozen dairy products, such as ice cream must be solidly frozen
and < 0°F at all times.
• Coolers, refrigerated vehicles or freezers may be used.
• All of the above must be equipped with properly
calibrated thermometers.
• All uid milk sold at a farmers market in Kansas must be
pasteurized.
• Raw milk can only be sold on the farm.
• More information available from: http://agriculture.
ks.gov/divisions-programs/dairy-inspection/dairy-industry
References and other resources:
• Kansas Food Code 2012: https://agriculture.ks.gov/docs/default-
source/statutes-foodsafety-lodging/kda_food_code_7_1_2012.
pdf?sfvrsn=70daac1_6
• Kansas Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Lodging
Program website: agriculture.ks.gov/fsl
• Kansas Department of Agriculture Meat & Poultry Inspection
Program website: https://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/meat-
and-poultry-inspection
• Kansas Meat and Poultry Inspection Act: https://agriculture.ks.gov/
docs/default-source/meat-and-poultry/kansas-meat-and-poultry-
inspection-act.pdf?sfvrsn=5bcbe79b_0
• Kansas Farmers Market Resources and resources for consumers,
producers, and organizers of farmers markets: https://www.
fromthelandofkansas.com/page/farmers-market-resources
• Starting a Seasonal Open-Air Market in Kansas. K-State Research
and Extension and the Kansas Rural Center. 2008. https://bookstore.
ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/S140.pdf
• Buying Guide for Kansas-Grown Fresh Fruits and Vegetables. K-State
Research and Extension. January 2021.
http://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/mf2647.pdf
• Vegetable Garden Planting Guide. K-State Research and Extension.
October 2017. https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/mf315.pdf
• Kansas Garden Guide. K-State Research and Extension. 2010.
https:bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/S51.pdf
• Kansas State University Extension Food Safety website, including
numerous publications and resources related to farmers market
vendors and produce safety: www.ksre.ksu.edu/foodsafety
25 Contact information for the KDA Dairy Inspection program: hps://agriculture.ks.gov/
divisions-programs/dairy-inspecon/dairy-consumers

K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices 15
Key Contacts
Questions on? Who to contact Website Email Phone
Food Safety licensing and
inspection
KDA Food Safety and
Lodging program
https://agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-
programs/food-safety-lodging
KDA.FSL@ks.gov 785-564-6767
Value added product
process authority recipe
approval, product devel-
opment, Better Process
Control School, HACCP,
etc.
Kansas State University
Value-Added/ Product
Development Lab
www.ksre.ksu.edu/kva kva@ksu.edu 785-532-1294
Sales tax information and
alcohol regulations
Kansas Department of
Revenue
www.ksrevenue.org/ tac@kdor.ks.gov 785-368-8222
Filing as a business entity Kansas Secretary of
State
www.kssos.org/main.html 785-296-4564
General information on
Kansas farmers markets,
registering a farmers
market
From the Land of Kan-
sas program
https://www.fromthelandofkansas.
com/page/farmers-market-resources
farmersmarkets@
kda.ks.gov
785-564-6755
Accepting Senior Farmers
Market Nutrition Program
(SFMNP) coupons
Kansas Department of
Health and Environ-
ment
https://www.kdhe.ks.gov/1041/
Kansas-Senior-Farmers-Market-Nutri-
tion-P
785-291-3742
Accepting SNAP (Benets
Cards) from customers
USDA Supplemental
Nutrition Assistance
Program (SNAP)
https://www.fns.usda.gov/snap/
apply-to-accept
Scale testing, method of
selling produce
KDA Weights and
Measures
agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/
weight-measures
785-564-6700
Selling live plants KDA Plant Protection
and Weed Control
Program
agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/
plant-protect-weed-control/live-plant-
dealer
785-564-6700
Meat and poultry inspec-
tion and registering of
label claims
KDA Meat and Poultry
program
agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-
programs/meat-and-poultry-
inspection/general-information
785-564-6776
Questions on dairy
processing, licensing, and
product labeling
KDA Dairy Inspection
program
agriculture.ks.gov/divisions-programs/
dairy-inspection/dairy-consumers
Je[email protected] 785-564-6700
Business consulting for
small businesses
Kansas Small Business
Development Center
www.kansassbdc.net/ [email protected] English, 800-
949-7661; or
Spanish, 800-
707-0580
Information and per-
sonal assistance to start
or maintain a Kansas
business
Kansas Business One
Stop
https://ksbiz.kansas.gov ks-helpcenter@
egov.com
800-4-KANSAS
or 785-296-
5059
Small business develop-
ment assistance
Kansas Department of
Commerce
https://www.kansascommerce.gov/ 785-296-3481
Information on funding
opportunities for rural
food businesses
USDA Rural Develop-
ment
www.rd.usda.gov/ks 785-271-2700
Resources and infor-
mation on Sustainable
Agriculture
Kansas Center for
Sustainable Agriculture
and Alternative Crops
kansassustainableag.org/ kebert@k-state.
edu
913-856-2335,
ext. 102
General farmers market
food safety best practices
questions; produce safety
Kansas State University
Extension Food Safety
Program
www.ksre.ksu.edu/foodsafety lnwadike@ksu.
edu
913-307 -7391
Information on produc-
tion of fruits, vegetables,
and live plants
Kansas State University
Extension Horticulture
Program; Specialty
Crop Growers Associ-
ation
https://hnr.k-state.edu/extension/;
https://www.kscga.org/
785-532-6173

16 K-State Research and Extension — Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices
Contents
Foods Sold Direct to Consumers in Kansas:
Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices .......................1
Overview: Allowed Foods, Label Requirements ..........................1
Foods that are ALLOWED to be sold directly to consumers in
Kansas WITHOUT licensing, according to state regulations
... 2
Foods THAT REQUIRE proper licensing (temperature control
for safety or specialized process foods and beverages)
.............. 4
Foods that must tested to determine
if a license is required or not
..........................................................6
How do I get the license(s) I need to meet the requirements listed
above?
............................................................................................7
What if I produce (and/or process) my food in Kansas and want to
sell in a neighboring state?
...........................................................7
In addition to food safety, what other regulatory requirements do I
need to follow to sell at a farmers market?
....................................8
What are the labeling requirements for packaged food products?
.8
How are all these regulations enforced?
.......................................8
General Food Safety Practices, Selling Fresh Produce,
Samples and Demos .................................................................8
General steps to food safety for all farmers market vendors ..........8
Table 1. Method of Retail Sale for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
Specic Commodity
.....................................................................9
Table 2. Method of Retail Sale for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
General Commodity Groups
........................................................9
Chef demonstrations
...................................................................10
Selling fresh produce
.................................................................10
Selling live plants at a farmers market
.........................................11
Selling unique agricultural products (live birds, manure, worms,
compost, etc.)
..............................................................................11
Oering product samples
..........................................................11
Calibrating a thermometer
..........................................................11
Selling Prepared Foods and Baked Goods .........................12
Selling Prepared Foods (ready for immediate consumption foods
that require temperature control for safety)
.................................12
How do I get a Food Establishment License?
............................12
What are the regulations for selling prepared (or shelf stable) foods
through a Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)?
.............12
Selling baked goods (breads, cakes, cookies, pies, etc.)
..............12
Selling jams, jellies, and shelf-stable canned foods
......................12
Selling refrigerated/frozen processed foods
................................12
Selling Meat, Eggs, and Dairy Products ..............................13
Selling meat and poultry products...............................................13
Other regulations and recommended best practices for selling meat
and poultry
.................................................................................13
Selling eggs
.................................................................................13
Selling dairy products
..................................................................14
References and other resources: ........................................14
Key Contacts .............................................................................15
Kansas State University Agricultural Experiment Station and Cooperative Extension Service
K-State Research and Extension is an equal opportunity provider and employer. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work, Acts of May 8 and June 30,
1914, in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Director of K-State Research and Extension, Kansas State University, County Extension Councils,
Extension Districts.
MF3138 rev. January 2024
Date shown is that of publication or last revision. Brand names appearing in this publication are for product identication purposes only. No
endorsement is intended, nor is criticism implied of similar products not mentioned.
Publications from Kansas State University are available at: www.bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu
Contents of this publication may be freely reproduced for educational purposes. All other rights reserved. In each case, credit
Londa Nwadike, Ph.D., Foods Sold Directly to Consumers in Kansas: Regulations and Food Safety Best Practices, Kansas State University,
January 2024.
Prepared by
Dr. Londa Nwadike, Kansas State University/University of Missouri
Extension Food Safety Specialist
22201 W. Innovation Dr
Olathe, KS 66061
913-307-7391
Fact sheet reviewed by:
• Karen Blakeslee, Kansas State University Value Added Foods Lab
• Adam Inman, Kansas Department of Agriculture Food Safety and
Lodging Program
• Jeremy Schooler, Kansas Department of Agriculture Meat &
Poultry Inspection Program
105 East 5th St., Suite 200
Kansas City, MO 64106
