
International Journal of Doctoral Studies Volume 10, 2015
Cite as: Dusek, G. A., Yurova, Y. V., & Ruppel, C. P. (2015). Using social media and targeted snowball sampling to
survey a hard-to-reach population: A case study. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 10, 279-299. Retrieved
from http://ijds.org/Volume10/IJDSv10p279-299Dusek0717.pdf
Editor: Michael Jones
Submitted: June 2, 2014; Revised: November 21, 2014; Accepted: August 4, 2015
Using Social Media and Targeted Snowball
Sampling to Survey a Hard-to-reach Population:
A Case Study
Gary A. Dusek, Yuliya V. Yurova, and Cynthia P. Ruppel
Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA
Abstract
Response rates to the academic surveys used in quantitative research are decreasing and have
been for several decades among both individuals and organizations. Given this trend, providing
doctoral students an opportunity to complete their dissertations in a timely and cost effective
manner may necessitate identifying more innovative and relevant ways to collect data while
maintaining appropriate research standards and rigor. The case of a research study is presented
which describes the data collection process used to survey a hard-to-reach population. It details
the use of social media, in this case LinkedIn, to facilitate the distribution of the web-based sur-
vey. A roadmap to illustrate how this data collection process unfolded is presented, as well as
several “lessons learned” during this journey. An explanation of the considerations that impacted
the sampling design is provided. The goal of this case study is to provide researchers, including
doctoral students, with realistic expectations and an awareness of the benefits and risks associated
with the use of this method of data collection.
Keywords: sampling hard-to-reach populations, snowball sampling, sampling from social media,
response rate, LinkedIn
Introduction
Response rates to the academic surveys used in quantitative research are decreasing and have
been for several decades among both individuals and organizations (Baruch, 1999; Baruch &
Holtom, 2008; de Leeuw, 2005). Johnson & Owens (2003) attribute this decline to: privacy is-
sues, confidentiality issues, exploitation of personal information, and general cynicism. The re-
sults of a survey among non-respondents found the following reasons for not participating includ-
ed too busy 28%, not relevant 14%, address unavailable to return the questionnaire 12% [a mail
survey was used in this study], and company policy prohibits participation 22% (Baruch &
Holtom, 2008).
Given this trend, to provide doctoral
students an opportunity to complete
their dissertations in a timely and cost
effective manner, it may be necessary to
find ways to obtain funding for doctoral
students. Alternatively, they may be al-
lowed to use paid professional research
firms such as Qualtrics or Survey Mon-
key for data collection. However, this is
Material published as part of this publication, either on-line or
in print, is copyrighted by the Informing Science Institute.
Permission to make digital or paper copy of part or all of these
works for personal or classroom use is granted without fee
provided that the copies are not made or distributed for profit
or commercial advantage AND that copies 1) bear this notice
in full and 2) give the full citation on the first page. It is per-
missible to abstract these works so long as credit is given. To
copy in all other cases or to republish or to post on a server or
to redistribute to lists requires specific permission and payment
of a fee. Contact Publisher@InformingScience.org to request
redistribution permission.

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
280
an expensive option for students and how much they learn about data collection techniques is de-
batable. Perhaps, we need to find more innovative and relevant ways to collect data while main-
taining appropriate research standards and rigor. These may include the use of social media to
collect data as well as mining the existing data available on social media and other big data
sources.
Doctoral students often have limited funds and are faced with a limited timeframe due to comple-
tion deadlines to obtain their degree. De Leeuw (2005) suggests that these are frequently limita-
tions in research and suggests, “When designing a survey the goal is to optimize data collection
procedures and reduce total survey error within the available time and budget. In other words, it is
a question of finding the best affordable method” (p. 235).
These constraints played an important role in this case study given that data was collected by a
US citizen in the US and in Russia. Data collection from the targeted population in Russia was
hampered by several constraints such as language, travel costs, travel restrictions and others. Due
to the economic conditions in the industry in which he was employed, the researcher became un-
employed and under significant pressure to complete his degree as soon as possible and obtain an
academic position. Incurring travel costs for data collection in multiple countries was not a rea-
sonable option. Therefore, the student and his dissertation committee considered, and employed,
a method which was designed to balance reasonable time and cost constraints with an appropriate
level of rigor for a dissertation.
The resulting study is presented which describes the data collection process used to survey a
hard-to-reach population using social media. In this case LinkedIn was used to assess the study’s
feasibility, to target respondents, and to facilitate the distribution of the web-based survey. A
roadmap to illustrate how this process unfolded is presented, as well as several of the “lessons
learned” during this journey. The goal of this case study is to provide realistic expectations and
awareness of the data collection issues encountered that pose both benefits and risks with the use
of the method described in this case study. Explanations of the data collection techniques used,
and the adjustments required to these techniques for successful data collection, are presented to
allow the reader to anticipate and plan for the difficulties that may occur when conducting this
type of quantitative data collection. Continuous improvement, refinement, and adaptation of the
data collection method described may be required in different circumstances. Data collection is,
of course, predicated on the assumption that an appropriate dissertation topic has been chosen
(Luse, Mennecke, & Townsend, 2012).
To make this paper easier for the reader to follow, we have underlined the sections which de-
scribe the specifics of the case study undertaken. The theoretical underpinning of this case study
process and the concerns for the rigor of the process are discussed relative to the actions taken.
Background
Concern for Declining Response Rates
Since at least the 1990’s it has been noted that survey response rates have been steadily decreas-
ing. This has led to concerns about the quality (defined as reliability and validity) of the resulting
responses. This quality impacts the use of the data in drawing valid and reliable inferences and
conclusions (Baruch & Holtom, 2008; de Leeuw, 2005; Murphy, Hill, & Dean, 2013). The de-
cline in response rates is most troubling from the standpoint that the resulting sample may not be
representative of the population to be sampled, and thus any inferences drawn from the sample
data may not generalize to the desired population. Baruch and Holtom (2008), as well as those
they reviewed, suggest that representativeness is the main concern and suggest that it is possible
to have a low response rate and still collect a sample that is representative of the population from

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
281
which it was drawn. While the preferred method for dealing with a low response rate is to avoid
having one in the first place, due to time and cost constraints as well as the possibility of a hard-
to-reach population, this is not always feasible for doctoral students. Based on declining response
rates, it appears that most populations currently used for survey research can be increasingly clas-
sified as “hard-to-reach” populations when employing traditional sampling techniques.
However, this study also faced additional factors that suggest it is a hard-to-reach population such
as its target population is multinational. While Russia was not included in her study, Harzing
(1997) reported international mail surveys have a typical response rate of between 6% and 16%
after multiple mailings, suggesting that international populations can be classified as hard-to-
reach populations for many researchers. The greater the geographical and cultural distance be-
tween the researcher sending the survey and the recipient of the survey, the lower the response
rate achieved (Harzing, 1997). Russia has large distances both geographically and culturally (The
Hofstede Center, n.d.) from the US doctoral student. However, the response rates achieved using
this sampling design resulted in response rates of 31% in the United States and 29% in Russia.
While researchers would always prefer a response rate greater than the one they achieved, achiev-
ing these rates in a situation where many experts felt that responses would be almost unattainable
suggests that this method of data collection deserves further study. A timeline that outlines the
following discussion of subject recruitment and the data collection procedure can be found in Ap-
pendix A. Given these challenges in collecting data for quantitative research, we examined the
extant literature concerning hard-to-reach populations as a guide to improve survey response
rates.
Snowball Sampling
One method that is becoming increasingly popular to recruit subjects is snowball sampling.
Snowball sampling is undertaken when a qualified participant shares an invitation with other sub-
jects similar to them who fulfill the qualifications defined for the targeted population (Berg,
2006). Historically, snowball sampling has been used in qualitative research where a qualified
subject is contacted by the researcher and a social relationship developed (“Snowball Sampling –
II,” 2006). Once the qualitative researcher has obtained responses of interest to the study from
the subject, a referral to another qualified subject is sought (Coleman, 1958-1959). This tech-
nique is particularly useful in hard-to-reach populations (i.e., HIV patients) where a network of
the qualified study subjects is assumed to exist and the researcher is hoping to be linked into this
network through social interaction with the initial subject in the network (Atkinson & Flint, 2001;
Faugier & Sargeant, 1997). These networks among hard-to-reach populations are not generally
open to researchers who do not have social entrées into the hidden population. Surveys received
from unknown researchers on sensitive topics will not be welcomed if no relationship, particular-
ly a trusting one, exists. However, when sending quantitative surveys which can be forwarded to
anyone, unlike the researcher interviewing subjects in qualitative research, the researcher has less
ability to scrutinize the qualifications of the referred subject. Thus, additional rigor concerns may
arise.
Targeted Sample for Survey Research
One documented approach to maintaining rigor when surveying hard-to-reach populations is
the use of targeted sampling (Watters & Biernacki, 1989). “It [targeted sampling] draws from
both survey and qualitative research methods…. through an interactive process of adjusting re-
search targets, recruitment methods, and research questions and instruments, inquiry can be fo-
cused on the most appropriate subjects for study” (Watters & Biernacki, 1989, p. 427). Snowball
sampling or chain of referral is one such targeted recruitment method. “The creative application
of deliberate recruitment activity is one of the more obvious distinctions between targeted sam-

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
282
ples and the asystematic recruitment of research subjects in convenience samples on the one hand
and the more rigid cluster and stratified samples on the other. Unlike convenience samples, re-
search subjects are selected for specific attributes that preliminary research has defined as targets
for study” (Watters & Biernacki, 1989, p. 425). Targeted sampling allows the researcher to main-
tain greater control over both who initially receives the invitation to participate in the survey, as
well as attempts to maintain some control over the resulting sample through adjusting all the
available tools (research targets, recruitment methods, research questions, and instruments) to
make the sample more closely mirror the population under study. “Nearly all studies of hidden
populations are carried out in circumstances that do not permit true random sampling. Under
these conditions, and if properly conducted and tied to what is known or can be learned about
population parameters, targeted sampling provides a more powerful sampling mechanism than
convenience sampling and a more feasible approach than random sampling” (Watters & Bier-
nacki, 1989, p. 427). To determine if the targeting method was successful involves obtaining
values for variables from external data sources and comparing these known values of the targeted
population to those obtained from the sample. Significant differences in the values may suggest
an adjustment in the targeting is needed. Baruch (1999) also reports this comparison procedure as
a common method to indicate the sample’s representativeness of the population.
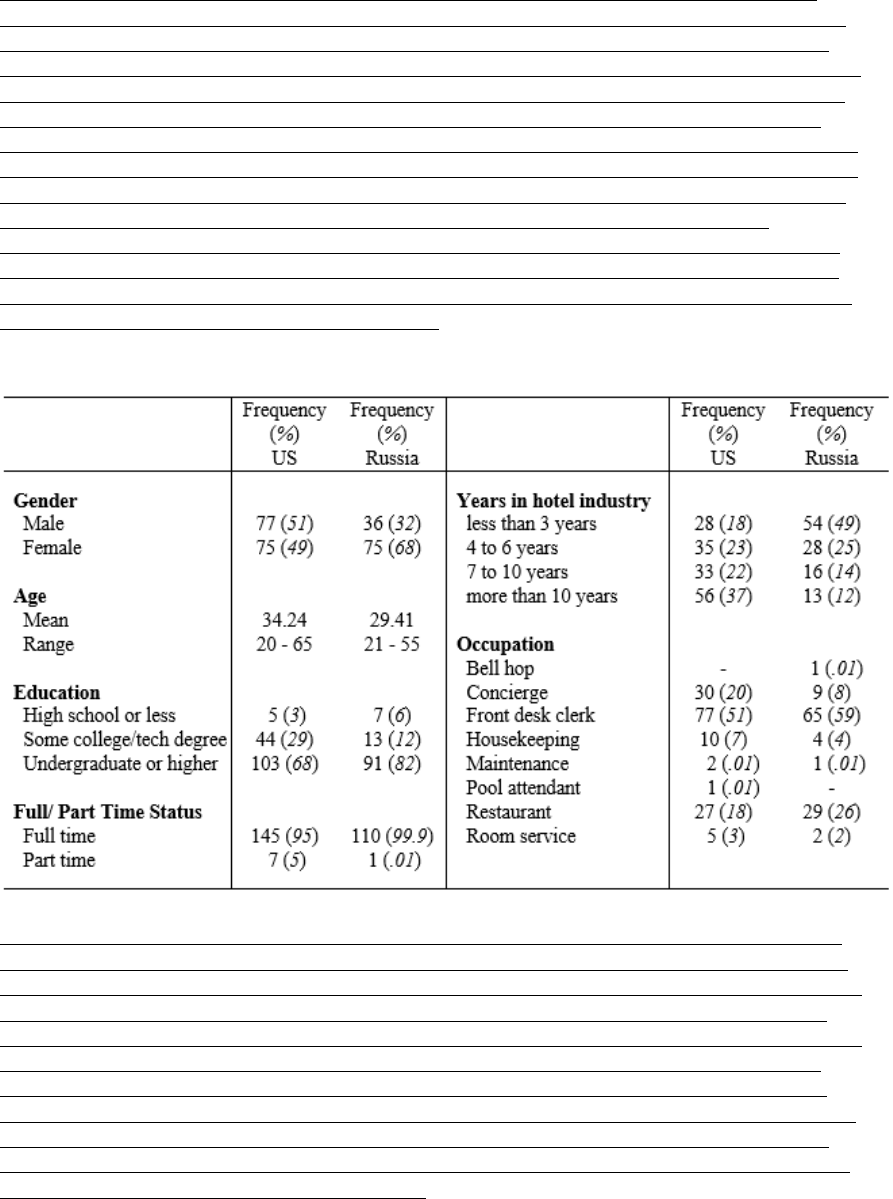
In this case study, demographic information was collected and used to compare the sample de-
mographic statistics to those reported in the extant literature and industry reports of statistics,
where available. This comparison indicated that the sample was representative of the population
on several of these variables. For example, demographic variables such as age, gender, job ten-
ure, and education level distributions were consistent with previous related studies and industry
statistics. We felt that these were the variables that the literature suggests are relevant to the re-
search model under study and thus are also potential control variables.
Targeted Sampling Using Social Media
Murphy et al. (2013) state that survey research is by definition “a social interaction between a
researcher and a (potential) respondent – a ‘conversation with a purpose’” (p. 1). Additionally,
they suggest that since the methods employed by individuals today to carry on such conversations
have changed, so should the tools used for survey research. The conversation should take place
using the tools the targeted population is currently using to carry on the conversation. Murphy et
al. (2013) define social media as it relates to survey research as “the collection of websites and
web-based systems that allow for mass interaction, conversation and sharing among members of
the network.” (p. 3). Unlike Facebook and other more general social media, LinkedIn is a plat-
form that connects professionals in various fields and, therefore, provides greater ability to target
data collection to an appropriate social network.
PC Magazine identified LinkedIn as “the most important cross-industry professional network
around” and made it an Editors’ Choice site (Duffy, 2013). Importantly, there is a free version
available to anyone with an email address that provides mobile access for those without comput-
ers. They suggest, “It’s such an important place that we recommend everyone over the age of 20
have a LinkedIn account” (Duffy, 2013), thus increasing the ability to appropriately target study
subjects.
LinkedIn’s membership grew steadily reaching 300 million LinkedIn members with more than
half of the membership residing outside the US. The company announced a strategic shift to
achieve their vision of “creating economic opportunity for every one of the 3.3 billion people in
the global workforce (“LinkedIn reaches 300 million,” 2014). The company is expanding
LinkedIn Groups and mobile access, suggesting potential access to a greater number of respond-
ents and a reduction of the digital divide bias. Importantly for this study, on June 21, 2011
LinkedIn made its site available in the Russian language at http://ru.linkedin.com (Posner, 2011).

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
283
Although LinkedIn communities are not exhaustive populations of industry representatives, they
might be considered suitable for initial targeting of subjects, an important step in snowball sam-
pling technique (Goodman 2011; Handcock & Gile, 2011). Goodman (2011) argued that even in
the case of populations which are not hard-to-reach, it is possible to collect a representative sam-
ple provided that the initial contact and requests for participation was made with appropriate indi-
viduals from the population of interest.
Case Study Process Description and Justification
Study Description
The dissertation topic that is the subject of this case study investigates turnover intentions and its
antecedents such as the service orientation of hotel employees in the United States and Russia.
Front-line employees are identified in previous hotel industry studies as possessing a high turno-
ver rate (Hinkin, Holtom, & Liu, 2012). Thus, to target the appropriate population to answer the
research question (Luse et al., 2012) the proper target population was defined as front-line em-
ployees of Western-based hotel operators. It was assumed that the management of Western-
branded hotels would be more open to participation in a bi-national academic research project and
be willing to provide assistance with data collection. Also, the use of Western Branded hotels al-
lowed the organizational factors to be similar in the US and Russia. Eight Western hotel brands
operating in Russia (Best Western International, Carlson Hotels Worldwide, Choice Hotels Inter-
national, Hilton Worldwide, Hyatt Hotel Corporation, Marriott International, Starwood Hotels &
Resorts, Wyndham Hotel Group) were identified as having hotels in both study locations.
Initial Recruitment Strategy
The initial strategy to achieve the targeted sample began with contacting properties which were
located near the student’s home, to discuss project feasibility and recruitment of targeted re-
spondents. Manager’s responses indicated that they required approval from their superiors to par-
ticipate and further suggested contacting the human resource (HR) departments in the corporate
offices. Responses from these HR representatives indicated they could not participate for various
reasons including an excessive number of similar solicitations already received, the desire to
avoid accusations of favoritism to some researchers, advice from the legal department against
becoming involved in a survey project, and conflict with existing internal employee surveys.
Many of these branded locations were franchisees and required individual inquires. The phone or
email messages sent to franchisee operators were not returned. Similarly, a LinkedIn group dis-
cussion board posting made to US hotel operators and managers did not result in any interest to
participate among the group members. Thus, the recruitment strategy needed to be adjusted to
reach the targeted population.
A US hotel manager had mentioned cooperating on a limited number of academic projects with
the International Council of Hotel, Restaurant and Institutional Education (ICHRIE), a leading
organization in the hospitality industry supporting hospitality education and hospitality research
projects. Potentially, ICHRIE’s assistance in the survey distribution appeared to provide several
advantages. Hospitality educators might be more inclined to help and may have students or grad-
uates that would be potential subjects for the survey. Also, hotel operators that are members of
ICHRIE may be more likely to have an interest in, and take part in, a hospitality research project.
Thus, the data recruitment strategy was targeted to include contacting individual franchisees
through support from the professional organization ICHRIE. To build social capital with ICHRIE
the researcher agreed to fill a vacant board member position. The ICHRIE Director of Research
distributed a message from the researcher to the membership with a link to the research survey.
However, the response rate from the targeted ICHRIE membership was low (<0.1%) and no usa-

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
284
ble surveys were completed. Clearly, a recruitment strategy adjustment to reach the target popu-
lation was necessary.
The same recruitment strategy used for contacting hotels in the US was attempted in Russia to
determine whether it would succeed in a different context. Contact information for Western
branded hotels operating in European Russia was obtained from the hotels’ websites. A recruit-
ment e-mail and FAX from the researcher, and the native Russian dissertation committee mem-
ber, was sent in both English and Russian to each hotel. The involvement of the native Russian
committee member was considered an important adaptation to ensure cultural sensitivity was ob-
served.
Comments concerning data collection in Russia were received while attending an international
business conference where the researcher’s proposal was met with skepticism concerning the fea-
sibility of collecting data in Russia. Concerns that Russians may be averse to participating in a
US research project or with an unknown researcher were raised again suggesting this was a hard-
to-reach population. This potentially could result in limited ability to collect data in Russia. Fur-
ther, they suggested respondents might hesitate to complete the survey or be untruthful in their
responses if it was presented to them by hotel management. They may feel that management
could attain their responses. This perception may thwart the snowball/chain of referral recruit-
ment strategy.
As was done in the US, General Managers of seventeen Russian hotels were contacted and only
two expressed interest in the project and requested additional information. Ultimately both Gen-
eral Managers were unable to participate in the survey; however, one offered to provide expert
advice concerning the Russian hotel industry. The disappointing response from direct contact
with the hotels is consistent with Baruch & Holtom (2008) who found that using organizational
responses results in a lower response rate. Thus, the lack of cooperation from the Russian and US
hotel managers together with the feedback that management should not be involved in the survey
distribution, particularly in Russia, the recruitment strategy was once again adapted to overcome
these barriers. It was retargeted to the individual level rather than an organizational level to re-
cruit participants. Although managers were ultimately used to distribute the survey link, the
manager was not using their organizational authority, rather he/she was simply acting as a direct
conduit to the researcher by forwarding the researcher’s link to an external research website ex-
plaining the study. The survey link on the researcher’s website stated that the survey responses
were completely anonymous and de-identified. Building personal relationships with each poten-
tial respondent to ensure participation and accurate and honest responses was paramount. Thus,
the use of social media to build the required relationships was explored.
Plan B – Social Media to Target Individuals
The Russian advisor suggested that social media usage was becoming very popular with many
Russian people from a broad age range for personal and professional reasons. It also provides a
way to build relationships with potential respondents in Russia. He explained that his hotel’s par-
ent company had created a LinkedIn group for use by managers and employees with about 16,000
members worldwide. A search on LinkedIn for this group, as well as groups for other targeted
hotel chains, identified eight Western branded hotel related groups with members in either the
United States and/or Russia. For the researcher to contact members of these groups, membership
to the group was required. Group membership was requested by the researcher and all eight
groups accepted his request within five days. Once granted, a group message introducing the re-
searcher and thanking them for granting membership was posted on the group’s discussion board
with the goal to first establish a conversation/relationship with members. In every group, some
members responded suggesting that a relationship was forming between as least some members
of the network and the researcher.

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
285
Building a credible network and nurturing trusting relationships from a distance with both hotel
managers who would be asked to simply forward the survey link to their front-line employees and
self-identified front-line employees who would complete the survey directly on the research web-
site was important but time consuming. This time factor was weighted against the costs of both
attempting to collect data personally and the cost of not obtaining sufficient dissertation data.
Trust building is important in data collection (de Leeuw, 2005) and particularly in the Russian
context.
Despite the fact that the student researcher could not control to whom the network connections
sent the referrals, the researchers built into the survey design questions to confirm the respondents
were members of the targeted population. For example, a question concerning who employed the
respondents was included as a target check. The researchers examined responses to this question
to ensure the hotel listed matched the targeted groups. Other attributes of the target population
such as job description were also verified to ensure that respondents were front line hotel em-
ployees.
Network Building, Development, and Targeting Adjustment
The researcher created a LinkedIn profile with the goal that individuals viewing the profile felt
they learned something personal about the researcher. The profile included the fact that the re-
searcher was a doctoral student conducting academic research to earn his doctoral degree, and his
educational and professional background. The profile included a picture of the researcher on a
trip to Russia taken several years ago to show his interest in Russia and to facilitate relationship
building. It generated favorable comments from Russian network participants. The profile clear-
ly indicated that the researcher was using LinkedIn for research purposes and this research profile
was exclusively used to recruit network members in both subject countries.
In addition to the individual contacts solicited in the LinkedIn groups, individual members of the
targeted population were identified on LinkedIn by searching using the keyword “hotel” and
specifying country as “Russian Federation”. Over 4,200 search results were obtained, including
large numbers of targeted employees. One hundred requests were sent to managers to join the
researcher’s LinkedIn network with 45 acceptances. To limit accepted requests to persons in the
target population, the LinkedIn default invitation was replaced with an invitation to join the doc-
toral student’s “research network”.
Based on the positive response to this approach, the researcher continued to send personalized
requests via LinkedIn to both Russian hotel employees and managers to join his research net-
work. Once they responded a personalized note was sent thanking them for joining. These docu-
ments can be found in Appendix B. To further build and maintain relationships, personalized
emails were sent to network contacts on special occasions.
Early results from Russian subjects indicated that the individual requests were far more success-
ful than prior group mailings. It was decided that US hotel managers and employees would be
recruited using a process corresponding to the one used for the Russian network. This maintained
a consistency of sample recruitment and data collection across both subject countries.
Data Collection and Invitation Adaptations
Invitations to participate in the survey were developed for managers and employees (see Appen-
dix C). The management invitations included the study purpose, the anonymous and voluntary
nature of the survey, both the English and Russian language survey links and a request that they
forward the e-mail to their subordinates or other contacts that were members of the targeted popu-
lation of front line hotel employees. Employee invitations contained the same information, how-
ever, the employee was asked to complete the survey prior to forwarding it.

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
286
Data collection in the Russian LinkedIn network had the subject line “<NAME>, will you please
give me your opinion?” This approach was suggested by a Russian contact who explained that
Russians welcomed the opportunity to be heard. From Table 1 it can be seen that only eight sur-
veys were started and five completed out of 61 invitations sent yielding 5% response rate.
The poor response rate was again discussed with Russian contacts and it was suggested that the
request should stress a call for their professional opinion, rather than for their personal opinion.
From February 12
th
to the 14
th
, twenty-nine additional invitations to participate were sent to Rus-
sian network contacts with a slightly altered subject line asking for their “expert” opinion (see
Appendix D). As a result, response rates improved considerably (48% response rate). At this
time data collection in the US also began with a nine percent response rate.
It was noted that participants seemed most likely to respond on the day the invitation was sent.
Culturally sensitive reminder e-mails, which avoided any perception of aggressiveness or hard
deadlines, were sent to Russian invitees. The researcher was informed that Russians do not appre-
ciate pushiness and deadlines, preferring to be asked respectfully for their participation. The re-
minder subject line was modified to: “A gentle reminder and a plea for help”. The reminder
acknowledged the subject’s busy schedule, noted the e-mail previously sent, reassured the subject
of anonymity and requested if they were managers they forward the link to hotel employees. If
they were employees, they were asked to complete the survey and to forward it to fellow hotel
employees.
Simultaneously, US membership in the LinkedIn research network rapidly expanded and as a re-
sult 222 invitations to participate were sent to US members with 36 surveys completed (16% re-
sponse rate). Although there was some improvement in the Russian response rate, further im-
provement was needed. Thus, the subject line was modified to reflect an appeal for sympathy (as
the doctoral student’s deadline for meeting graduation requirements was rapidly approaching).
The subject line “<NAME> please help me graduate this April” was used (see Appendix E).
Eighty-three invitations were sent to Russian members with only 6 surveys began and 4 complet-
ed (5% response rate).
Russian contacts advised that Russians highly respect the pursuit of education, thus, the subject
line was subsequently changed to “<NAME>, will you please help with an education project?”
Russian response rates improved dramatically. From February 25
th
to the end of the data collec-
tion period on March 15
th
, 2014, 210 Russian invitations were sent and 88 surveys were returned
completed (42% response rate). US response rates during this period remained strong: Two hun-
dred four invitations were sent and 110 usable surveys were returned (54% response rate).
Figure 1 presents the dynamics of the collection process and indicates the number of survey re-
quests sent to network members and the responses received (surveys completed). Table 1 sum-
marizes the response rates obtained with each adaptation.

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
287
Figure 1. Invitations sent and responses received
Table 1. Distribution of response rated
Representativeness of the Targeted Population
We examined the representativeness of the sample to the targeted population as well as examined
responses to demographic questions designed to assure target population membership. A total of
111 properly targeted responses from Russian network and 152 properly targeted responses from
US network were collected prior to graduation deadlines. As presented in Table 2 below, both
United
States
Russia
Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
288
samples consisted mainly of full-time, front-line employees of Western-branded hotel opera-
tors. A comparison of sample demographic characteristics with those reported previously in the
literature was conducted to assess the representativeness of the targeted sample of the targeted
population. As seen in Table 2, the Russian sample has considerably greater proportion of women
(χ
2
= 8.696, df = 1, p = .0032). Similar results were reported by Swerdlow & Cummings (2000)
who conducted a paper-based survey of Russian and US hotel employees and found 73% and
55% of females in their Russian and US samples respectively. Additionally the author’s personal
interviews and visits to hotel properties further support for this finding. There were a significant-
ly larger number of respondents with undergraduate and graduate degrees in the Russian sample
compared with the US sample (χ
2
= 6.702, df = 1, p = .0096), a result also supported by
Swerdlow and Cummings’ similar findings. The proportion of employees with a university de-
gree was high in the US sample as well (68%) and this fact is consistent with Lin, Wong, & Ho
(2013) who surveyed 587 frontline employees of leisure industries in the US and reported 68.5%
respondents with professional or college degrees.
Table 2. Demographic characteristics of US (n = 152) and Russia (n = 111) samples
The average age of respondents was 34.2 and 29.4 years in the US and Russian samples respec-
tively suggesting a dominance of young employees with short tenure. About half of the Russian
respondents (49%) have worked in the hospitality industry 3 years or less compared to 18% in the
US sample. Similar composition of the hotel workforce was reported by Swerdlow and Cum-
mings (2000), Lin et al. (2013), and Sverdlin (1998). In particular, about 27% of the US respond-
ents in Lin et al.’s (2013) study had worked in the industry less than 2 years and 48.9% of re-
spondents were under the age of 30. Sverdlin (1998) studied work compensation systems and
motivation in a Russian hotel. Out of the 202 employees surveyed, about 30% had worked three
years or less in the industry, 51% were under the age of 34; and 52% had college or university
degree. The method of targeted recruitment appears to have resulted in a sample that we believe
appropriately represents the targeted population.

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
289
Findings
Lessons Learned
The researcher’s profile on social media should reflect that he/she is an academic researcher.
Many people indicated they participated since the researcher’s profile made it clear that he was
not someone from their company collecting data. This was an equal concern in both countries.
If you are using LinkedIn to collect data from populations, verify that there is an adequate num-
ber of potential respondents available in the targeted population. For example, several smaller
cities in Russia had no hotel industry presence on LinkedIn. Assess study feasibility by investi-
gating subject availability using LinkedIn’s advanced search capability using the fields “industry
& location”. This will provide insight into the potential of using this process to gather data. It
will also guide you in identifying and refining the existence of a population for your study.
When you are sending network invitations develop a personalized message rather than sending
the default LinkedIn invitation. Once connected personalize your response with their first name
to establish a closer, less formal relationship. No one in our sample overtly stated an objection to
being addressed on a first name basis.
Discussion board traffic is dense. LinkedIn members generally scan the subject lines and delete
messages without reading them. If you send individual responses to network members, they re-
ceive a personalized email rather than an email announcing a “New LINKEDIN DISCUSSION
POST”. In our experience, posting the link to your survey on a group discussion board will not
result in many responses and may identify respondents outside your targeted population.
To reduce survey dropout rates, the surveys were developed with a completion bar to indicate the
portion of the survey completed. Survey drop rates indicated that as participants perceived pro-
gress towards completion, they were more likely to continue and complete the survey. However,
upon reaching the last page of the survey where the demographic questions were located, dropout
rates increased as shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Drop-out points
Perhaps respondents were sensitive to personal demographic questions. Carefully word de-
mographics questions to minimize potential sensitivity issues and thus increase the rate of survey
completion. Remember, these demographic variables are instrumental in ensuring your respond-
ents are part of your targeted population and your resulting sample is representative.
Interestingly, the doctoral student continued to receive messages from network members inquir-
ing as to whether he has been successful in completing his dissertation. Apparently, these mem-
Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
290
bers were motivated by helping the student succeed and have taken an interest in his success and
the possibly they had contributed to it.
Since the researcher cannot control external factors, try to avoid short data collection timelines.
Expect long timelines and hope you do not need them. During the data collection period, external,
uncontrollable factors included issues regarding Internal Review Board approval of translated
surveys, the Sochi Olympic Games in Russia, and the Crimean Peninsula Crisis in Ukraine. The
official translations and back translations (Brislin, 1970; Watkins, 2010) are time consuming. In
addition to translating, translations must be scrutinized by someone who understands the target
population and culture so the translated measures will correctly identify the intended constructs in
the targeted population. Sometime the questions need to be altered to make them culturally ap-
propriate to ensure the equivalency of the construct measurement.
While time was allocated for translation, the Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval exceeded
timeline expectations causing the data collection to occur during the Olympics. The IRB reviews
all proposals to conduct research to be sure it is “adhering to basic ethical principles underlying
the acceptable conduct of research involving human subjects” (Institutional Review Board of
Nova Southeastern University, 2015). To meet graduation deadlines data collection was neces-
sary during the Olympics, which created an abnormally busy time for front-line hotel workers
around Sochi, including some of whom had come from hotels in Moscow to provide service dur-
ing this rush period. This may have contributed to lower response rates from hotel workers than
anticipated.
Additionally, the Crimean Peninsula Crisis in Ukraine began immediately after the Olympics had
concluded, producing another unforeseeable event that involved the forced resignation by Kiev
protestors of the Pro-Russian Prime Minister of Ukraine. These events raised tensions among
Russian hotel workers and resulted in a three-day period during which no Russian responses were
received. These events, all of which the researcher could not control or foresee, had unanticipated
impacts on data collection in Russia.
The questions designed to validate the respondent’s membership in the targeted population are
very important and can provide unexpected but interesting results. While the number of respond-
ents from Russia used for the dissertation was 111 (see Table 3) the student received an additional
41 completed surveys from Russia. The survey’s targeting question concerning citizenship al-
lowed us to determine that these respondents were actually immigrants working in Russian hotels,
which represents another hard-to-reach population. The Russian advisor reported that if we had
directly asked immigrants to participate, they would not have done so. This provided the student
with another interesting data set. The importance of well thought out targeting questions cannot
be underestimated when using this technique. Don’t expect all completed surveys will be from
your targeted population and thus, be useable for the original purpose.
LinkedIn Caveat for Research Network Development
LinkedIn’s original purpose was to connect people that are already acquainted or are referred by a
friend. If three LinkedIn members complain that they have received invitations from the same
person they do not know, the person sending the invitations may be placed on probation. The
result of being reported is that you are limited to inviting only those for whom you have an email
address. Persons connecting to subjects through LinkedIn should be aware of this possibility,
personalize their network invitations and be clear about their purpose to minimize the possibility
people will be offended and report the activity.

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
291
Conclusions
To increase doctoral completion rates the required dissertation must be completed in a timely,
efficient and cost effective manner while still maintaining appropriate rigor (Byers et al., 2014).
Students should be able to choose a topic that interests them so they remain motivated to finish,
even if the topic choice requires gathering data from hard-to-reach populations. This was the sit-
uation in this case study. The student in this case study had a strong interest in studying a Rus-
sian business. He has studied the Russian language for several years and made many Russian
friends in his area of residence in Texas, USA. Cost and time constraints, which are major issues
for most doctoral students, represent major factors which impact dissertation completion.
The research literature suggests that methods of gathering data have been changing over time as
the way we communicate has changed and response rates have declined. Today data collection
can potentially be global with the use of these new communication capabilities and thus improve
generalizability. However, new communication capabilities such as the use of social media poses
rigor issues since there are currently no widely established standards for the use of these methods.
This introduces some level of risk, particularly for publishing in high-level journals, which are
required by some schools. Thus, careful planning of the study and attention to study design are
very important to minimizing this risk.
The declining response rates currently being observed using traditional methods of surveying the
population also introduce risk by challenging the validity and reliability of the study. Traditional
survey methods also require careful design and documentation to demonstrate the representative-
ness of the targeted population. This often requires additional costs and time. Among the ad-
vantages of the newer methods of communication are that they may be able to improve response
rates by reaching the targeted population more effectively, providing respondents with greater
privacy for sensitive questions, providing easier access to the survey, lowering data collection
costs and reaching traditionally hard-to-reach populations. However there may be disadvantages
to the newer methods such as difficulty in obtaining and documenting the target population, diffi-
culty in following-up with non-respondents due to confidentiality, and providing less control over
who responds when a snowball technique is used.
This case study documents the process used to survey a hard-to-reach population, at a reasonable
cost and in a reasonable length of time for this particular doctoral student. In this case the cost
associated with data collection was reduced since no targeted contact lists were purchased; no
specific monetary contact costs were incurred and the only cost was to post the survey on Survey
Monkey for a period of time. However, it was very consumptive of non-monetary direct costs
related to the researcher’s personal time. At least five hours each day were devoted to building
and maintaining the network. Developing the network by issuing invitations to join via LinkedIn
and building relationships prior to inviting the subjects to participate in the study required a sig-
nificant time and effort commitment. Since the researcher was unemployed, it was an appropriate
personal tradeoff for the doctoral student’s situation at the time. Thus, it is important to note that
this method is not without costs and commitments, which must be identified and weighed relative
to the student’s personal and professional situation.
Since this data collection process represents a tradeoff, planning and diligence are necessary. The
earlier in the doctoral program the networking process begins, the better the position of the stu-
dent at dissertation time. It can be argued that conducting research by examining discussion
boards, particularly professional ones, to identify possible research needs/topics and networking
should be a part of the doctoral student’s academic knowledge and professional development. In
this case, LinkedIn was the appropriate social media tool for this international business student.
Given the diversity of people on the LinkedIn network, there are individuals and groups in many
fields of research.

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
292
This case study presents a targeted snowball approach through social media to target hard-to-
reach populations at a reasonable cost and in a reasonable time frame. While this methodology
may not be appropriate in all situations or for all students, it provides an example of the approach
taken by this student when faced with numerous obstacles. The traditional approaches of survey-
ing a company or a professional organization or contacting a random sample did not reach the
targeted population in sufficient numbers. This case study shares a method to minimize out-of-
pocket cost and time constraints and allow the student to complete his dissertation while main-
taining appropriate rigor.
References
Atkinson, R., & Flint, J. (2001). Accessing hidden and hard-to-reach populations: Snowball research strate-
gies. Social Research Update, 33.
Baruch, Y. (1999). Response rate in academic studies: A comparison analysis. Human Relations, 52(4),
421-438.
Baruch, Y., & Holtom, B. C. (2008). Survey response rate levels and trends in organizational research.
Human Relations, 61(8), 1139-1170.
Berg, S. (2006). Snowball sampling 1- Sequential estimation of the mean in finite population to Steiner’s
most frequent value. Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, 12. Doi: 10.1002/0471667196.ess2478.pub2
Brislin, R.W. (1970). Back-translation for cross-cultural research. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology,
1(3), 185-216.
Byers, V. T., Smith, R. N., Hwang, E., Angrove, K. E., Chandler, J. I., Christian, K. M., & Onwuegbuzie,
A. J. (2014). Survival strategies: Doctoral students’ perceptions of challenges and coping methods. In-
ternational Journal of Doctoral Studies, 9, 109-136. Retrieved from
https://ijds.org/Volume9/IJDSv9p109-136Byers0384.pdf
Coleman, J. S. (1958-1959). Relational analysis: The study of social organization with survey methods.
Human Organization, 17, 28-36.
de Leeuw, E. D. (2005). To mix or not to mix data collection modes in surveys. Journal of Official Statis-
tics, 21(2), 233-255.
Duffy, J. (2013). LinkedIn. Retrieved from http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2120736,00.asp
Faugier, J. & Sargeant, M. (1997). Sampling hard-to-reach populations. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 26,
790-797.
Goodman, L. (2011). Comment: On respondent-driven sampling and snowball sampling in hard-to-reach
populations and snowball sampling not in hard-to-reach populations. Sociological Methodology, 41(1),
347-353. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9531.2011.01242.x
Handcock, M. S., & Gile, K. J. (2011). Comment: On the concept of snowball sampling. Sociological
Methodology, 41(1), 367-371. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9531.2011.01243.x
Harzing, A. W. (1997). Response rates in international mail surveys: results of a 22-country study. Interna-
tional Business Review, 6(6), 641-665. Retrieved from
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969593197000401
Hinkin, T., Holtom, B., & Liu, D. (2012). The contagion effect: Understanding the impact of changes in
individual and work-unit satisfaction on hospitality industry turnover. Cornell Hospitality Report,
12(9).
The Hofstede Centre (Russia). (n.d.). What about Russia? Retrieved 2014 from http://geert-
hofstede.com/russia.html
Institutional Review Board of Nova Southeastern University. (2015). Welcome. Retrieved from:
http://www.nova.edu/irb/

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
293
Johnson, T., & Owens, L. (2003). Survey response rate reporting in the professional literature. In 58th An-
nual Meeting of the American Association for Public Opinion Research, Nashville. Retrieved from
http://www.amstat.org/sections/srms/Proceedings/y2003/Files/JSM2003-000638.pdf
Lin, J., Wong, J., & Ho, C. (2013). Promoting frontline employees’ quality of life: Leisure benefit systems
and work-to-leisure conflicts. Tourism Management, 36(1), 178-187. doi:
org/10.1016/j.tourman.2012.12.009
LinkedIn reaches 300 million members worldwide (April, 2014). Retrieved from
http://press.linkedin.com/News-Releases/333/LinkedIn-reaches-300-million-members-worldwide
Luse, A., Mennecke, B., & Townsend, A. (2012). Selecting a research topic: A framework for doctoral
students. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 7, 143-152. Retrieved from
http://ijds.org/Volume7/IJDSv7p143-153Luse330.pdf
Murphy, J., Hill, C. A., & Dean, E. (2013). Social media, sociality, and survey research in social media,
sociality and survey research. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Posner, N. (2011, June 21). Look who’s talking Russian, Romanian and Turkish now! Retrieved from
http://blog.linkedin.com/2011/06/21/russian-romanian-turkish/
Snowball Sampling – II, Sequential estimation of the mean in finite populations to Steiner’s most frequent
value. (2006). Encyclopedia of Statistical Science, 12. Doi: 10.1002/0471667196.ess2479.pub2
Sverdlin, O. (1998). Affect of incentives on motivation of hotel workers: A case study of the Grand Hotel
Europe, St. Petersburg, Russia. (Master’s Thesis, University of Wisconsin- Stout). Retrieved
http://www2.uwstout.edu/content/lib/thesis/1998/1998sverdlino.pdf
Swerdlow, S., & Cummings, W. T. (2000). Toward a better understanding of U.S. and Russian lodging
employees: A discriminant analysis approach. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research. 24(3),
336-349.
Watkins, L. (2010). The cross-cultural appropriateness of survey-based value(s) research, International
Marketing Review, 27(6), 694-716.
Watters, J., & Biernacki, P. (1989). Targeted sampling: Options for the study of hidden populations. Social
Problems, 36(4), 416-430.
Appendix A
Timeline for Data Collection
Date
United States
Russia
12/15/2011
Began search for American branded hotels in Rus-
sia.
3/12/2012
Began recruiting Russian hotels to request partici-
pation in the survey.
5/7/2012
Began recruiting executives at national
headquarters of US hotel brands that were
operating in Russia for participation in
survey.
6/1/2012
Created English research website to make
project details available to persons consid-
ering taking part in the survey.
8/1/2012
Added Russian versions of English pages to re-
search website.
10/14/2012
Began recruiting US franchisees of US
hotel brands operating in Russia to partic-
ipate in the survey.

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
294
Date
United States
Russia
7/16/2013
Began searching for hotel themed
LinkedIn groups and requesting member-
ship.
Began searching for Russian hotel or hospitality
themed LinkedIn groups and requesting member-
ship.
8/1/2013
Began posting recruitment message to
discussion boards of US LinkedIn hotel
groups, which I was a member.
8/8/2013
Began posting recruitment messages to discussion
boards of Russian LinkedIn groups, which I was a
member.
10/24/2013 through
10/27/2013
International business conference.
11/6/2013
No responses from Russian LinkedIn group dis-
cussion board postings. Began personally recruit-
ing Russian hotel managers and employees to join
the research network.
11/14/2013
Only one response from US LinkedIn
hotel group discussion board postings.
ICHRIE agrees to distribute survey to US
membership upon IRB* approval of pro-
ject.
12/10/2013
To build relationships, all Russian contacts are
sent personalized Christmas/New Year’s messag-
es.
12/22/2013
IRB* approval granted to send survey to
US hotel managers and employees. Sur-
vey distributed to US ICHRIE member-
ship.
2/3/2014
IRB* approval granted to send survey to Russian
hotel managers and employees. Began sending
surveys to Russian LinkedIn contacts. Subject line
asks for contacts opinions.
2/6/2014
No ICHRIE responses. Began recruiting
US hotel managers and employees to join
the research network.
2/10/2014
Subject line changed to a request for expert opin-
ion.
2/17/2014
Began sending survey to US LinkedIn
contacts. Subject line asks for expert opin-
ion.
2/21/2014
Subject line change. Asking for help with a deadline included.
2/25/2014
Subject line change. After advice from a Russian contact, deadline removed and subject line
changed in US and Russia. Now asking for help with an education project.
3/13/2014
Last invitations are sent to the US and Russia.
3/24/2014
Survey closed.
*IRB refers to the Institutional Review Board, which reviews studies of human subjects for their
protection.

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
295
Appendix B
Invitation to join the researcher’s network

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
296
Appendix C
Invitation to participate in survey

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
297
Appendix D
First revision of invitation to participate in survey

Media and Targeted Snowball Sampling
298
Appendix E
Second revision of invitation to take survey

Dusek, Yurova, & Ruppel
299
Biographies
Gary A. Dusek earned his Doctor of Business Administration degree
from Nova Southeastern University with a concentration in Interna-
tional Business in 2014. His Masters of Business Administration in
Management and undergraduate degree in Finance were earned from
Texas State University. Dr. Dusek’s research interests include the
study of Eastern European transitioning economies, employee turno-
ver, service orientation theory and data collection through social me-
dia. Dr. Dusek currently serves on the editorial review board of the
Journal of Organizational Culture, Communication and Conflict and as
the Director of Membership and Development for the International
Council of Hotel, Restaurant and Intuitional Education’s West Federa-
tion.
Yuliya V. Yurova (Yuliya.[email protected]) is Assistant Professor
of Research Methods and Decision Sciences at the H. Wayne Huizenga
School of Business and Entrepreneurship, Nova Southeastern Universi-
ty. Her research interests cover a range of topics in quantitative re-
search methods including time series analysis, structural equation
modeling, and multivariate analysis in economics, finance, and market-
ing.
Cynthia P. Ruppel is a Professor of Information Technology at the H.
Wayne Huizenga School of Business and Entrepreneurship at Nova
Southeastern University. Her research interests include many facets of
virtual teams and telework including leadership, healthcare and the
adoption and diffusion of innovations as well as creativity enhance-
ment. Her research has appeared in many journals and research read-
ings books.
